![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an einzellagen?
|
Vineyard
|
|
|
What is a walled vineyard called?
|
Ortsteil
|
|
|
What is a monopole in German?
|
Alleinbesitz
|
|
|
What was the influence of Napoleon in German wine?
|
Seizure of vineyards from the church and the Napoleonic Code of Succession
|
|
|
How many different vineyard sites were in West Germany in the 1960's?
|
Over 30,000
Major reason for vineyard reorganization and registration in German Wine Law of 1971 |
|
|
What were the major effects of the German Wine Law of 1971?
|
Organizing 30,000+ vineyards into 2,600 registered vineyards with a min 5 hectares
Only exception is Doctor vineyard in Bernkastel (three proprietors shrunk boundaries to 8 acres in 1984) |
|
|
What is the significance of Schloss Johannisberg?
|
Monastery in Rhiengau that "discovered" Spatlese in 1775
|
|
|
What is Edelfaule?
|
Noble rot
|
|
|
When was Auslese introduced?
|
1787 by Schloss Johannisberg
|
|
|
Was the English market important for German wine?
|
Yes. In 19th century best wines from the Rhine were called Hock in English markets and sold often over the prices of first growth Bordeaux
|
|
|
Why are German vineyards located so high up on slopes?
|
Demand for farmland in 1700's pushed vineyards up slopes
|
|
|
What is Muller-Thurgau?
|
Grape crossing created in Giesenheim in 1882
In late 1960's displaced Silvaner to become Germany's most planted grape Thought to be a cross between Riesling x Silvaner, but recent testing says Riesling x Madeline Royale |
|
|
What happened post-WWII in German wine?
|
Phylloxera, mildew, WWI, Great Depression and WWII shrunk domestic wine
Focused on higher yields from crosses planted on flat land for mechanical harvesting |
|
|
What is Liebfraumilch?
|
Wine with 18th century origin
In 1980s 60% of German wine exports had this on label Sweet, cheap, character-less wine usually from Muller Thurgau No varietal labeling and often blended from across the country |
|
|
What is the Verband Deutscher Pradikatsweinguter?
|
Committee of top 200 producers, as voted on by their peers
|
|
|
What are the top white grapes in Germany?
|
Riesling
Muller Thurgau X Silvaner Grauburgunder (Pinot Gris) Weisburgunder (Pinot Blanc) Kerner X Bacchus X |
|
|
What are the top red grapes in Germany?
|
Spatburgunder
Dornfelder X Blauer Portugeiser Trollinger Schwarzriesling (Pinot Munier) |
|
|
What are the four major German wine categories?
|
Deutscher Wein
Landwein Qualitatswein bestimmter Anbaugebite Qualitatswein mit Pradikat |
|
|
What are the levels of QmP wine?
|
Determined by levels of sugar at harvest on the Oechsle scale
Kabinett Spatlese (late harvest) Auslese (selection) Beerenauslese (BA - berries selection) Eiswein Trockenbeerenauslese (TBA - dry berries selection) |
|
|
What are some of the peculiarities of QmP wine?
|
Each anbaugebiete has its own minimum requirements for authorized grapes
Winemakers can declassify their wines from a higher QmP level to a lower one |
|
|
What are the minimum alcohol levels for QmP wines?
|
7% (5.5% for BA, TBA and Eiswein)
|
|
|
What is Amtliche Prufungsnummer (AP Number)?
|
Set of five sets of numbers indicating that the wine has been approved by a tasting panel.
1st set is region 2nd set is commune 3rd set is bottler's code 4th set is unique code for the bottling 5th set is year in which the application was filed |
|
|
What is Grosses Gewachs?
|
Used to indicate top level dry wines from selected sites (except Mosel and Rheingau)
|
|
|
What is trocken? Halbdtrocken?
|
Dry and off dry
|
|
|
What are the Anbaugebite of Germany?
|
Mosel
Ahr Mittelrhein Rheingau Rheinhessen Nahe Pfalz Hessische-Bergstrasse Baden Wurttemberg Franken Sachsen Saale-Unstrut |
|
|
When was the VDP founded?
|
1910 as the Verband Deutscher Naturweinversteigerer
Originally to promote unchaptalized wines |
|
|
What is Charta?
|
Organization founded in 1984 to promote classic, dry style of Rheingau Riesling
Distinguished by an icon of three Roman arches Assimilated into Rheingau branch of the VDP in 1999 |
|
|
What is the first tier of VDP wine? What are its requirements? When my they be released?
|
Created in 2002
Erste Lage - dry are Grosses Gewachs (Rheingau are Erstes Gewachs), sweet are labeled by Pradikat Hand harvested with max yield of 50 hl/ha Min must equiavlent of Spatlese Grosses Gewachs whites may not be released until Sept 1 after harvest, reds get 1 more year of aging Erste Lage Pradikats may be released May 1 after harvest Einzellage must be on label and vineyard approved by VDP (stricter than German wine law's demarcation) |
|
|
What is the second tier of VDP Classification?
|
Klassifizierte Lagenweine (classified sites)
Ortsweine (from specific regions or villages, but not grosslagen or bereiche) max 65 hl/ha Distinct from Grand Gru sites in Erste Lange |
|
|
What is the third tier of VDP Classification? What are the criteria?
|
Gutswein
Basic house style of traditional grapes from a region max 75 hl/ha |
|
|
What are "Classic" German wines?
|
Labeling term selected by the German Wine Institute at Mainz for drier styles of wine
Introduced in 2000 vintage Harmoniously dry with max 15 g/L RS Single varietal and no vineyard mentioned on label Min alcohol 12% (11.5% in Mosel) |
|
|
What are "Selection" German wines? When were they introduced? What are the specs?
|
Labeling term selected by the German Wine Institute at Mainz for drier styles of wine
Introduced in 2000 vintage Superior dry with max 9 g/L RS (12 g/L for Riesling) Single varietal and vineyard Min alcohol 12% (11.5% in Mosel) Yields restricted to 60 hl/ha Must weight equivalent to Auslese Hand harvested May not be released until Sept 1 after harvest |
|
|
What are the typical characteristics of Mosel Kabinett Riesling?
|
Star bright with green apple, slate and candle wax
Rarely more than 8% alcohol Racy, high acidity |
|
|
What is the significance of a Goldkapsel on a German wine?
|
Indicates a Mosel Riesling, typically a reserve, with additional sweetness due to a higher must weight
|
|
|
What is a Lange Goldkapsel?
|
Longer golden capsule which indicates a richer bottling
|
|
|
What are the geographic levels of classification in German wine?
|
Anbaugebiet - Region (13)
Bereich - District (39) Grosslage- Collective site (170) Eincellage - Single vineyard (2600) |
|
|
What does Erzeugerabfullung mean?
|
Estate wine from one grower or a cooperative of growers
|
|
|
What does Gutsabfullung mean?
|
Estate wine in which the estate grows, produces and bottles its own wine
|
|
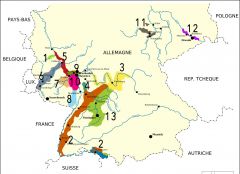
What is region 1?
|
Ahr
|
|
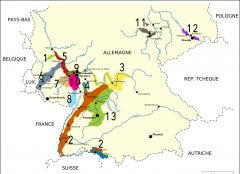
What is region 3?
|
Franken
|
|
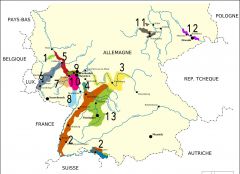
What is region 4?
|
Hessische Bergstrasse
|
|
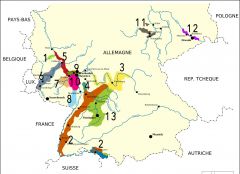
What is region 6?
|
Mosel
|
|
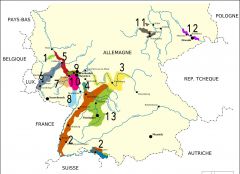
What is region 7?
|
Nahe
|
|
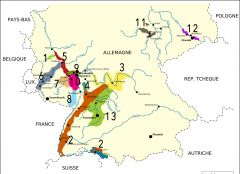
What is region 8?
|
Pfalz
|
|
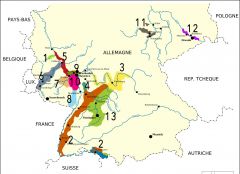
What is region 9?
|
Rheingau
|
|
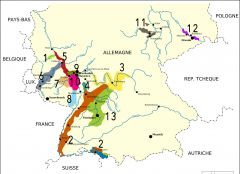
What is region 11?
|
Saale-Unstrut
|
|
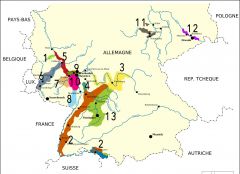
What is region 2?
|
Baden
|
|
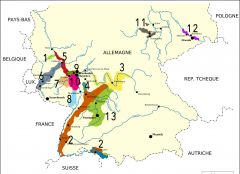
What is region 5?
|
Mittelrhein
|
|
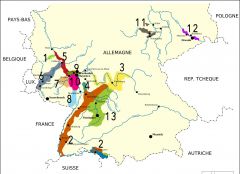
What is region 10?
|
Rheinhessen
|
|
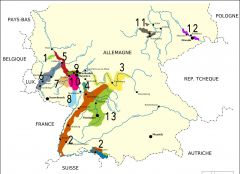
What is region 12?
|
Sachsen
|
|
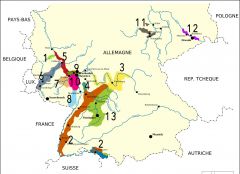
What is region 13?
|
Wurttemberg
|
|
|
What are the bereiche of the Mosel from upstream to downstream?
|
Moseltor
Obermosel Saar Ruwertal (Ruwer) Bernkastel (Mittelmosel) Burg Cochem (Terrassenmosel) |
|
|
Where are the best vineyards in the Mosel located?
|
In Bernkastel (Mittelmosel), from the villages Trier to Zell
|
|
|
What are the villages of the Bernkastel (Mittelmosel)?
|
Trittenheim
Piesport Brauneberg Bernkastel-Kues Graach-an-der-Mosel Wehlen Zeltingen-Rachtig Urzig Erden |
|
|
What are the soils of the Mosel?
|
Dark blue Devonian slate (red slate near Erden)
Radiates heat on the vines when average temp is only 49F |
|
|
What is the greatest vineyard of Piesport?
|
Piesporter Goldtropfchen (not to be confused with Piespoerter Michelsberg, an inferior vineyard)
|
|
|
What is the climate of the Saar?
|
Cooler than Bernkastel (Mittelmosel) due to higher altitude and less uniform soils (less of a warming effect)
Higher acid wines |
|
|
What are the gemeinde of the Saar?
|
Wiltingen
Saarburg |
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Ruwertal?
|
Cooler than Bernkastel (Mittelmosel) with gentler slopes
|
|
|
What are the gemeinde of the Ruwertal?
|
Eitelsbach
Metesdorf |
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Burg Cochem?
|
Winningen
|
|
|
What is the significance of the Rheingau in German wine history?
|
Where modern viticulture first appeared
Earliest beneficiary of church influence First vineyards to be demarcated Height of German wine fame in 19th century Origin of recent drive to produce noble dry Riesling (Charta) |
|
|
What is the percentage of Riesling in Rheingau?
|
80%, higher than any other anbaugebiet
|
|
|
What are the bereiche of Rheingau?
|
Johannisberg
|
|
|
What are the gemeinde of the Rheingau from upstream to downstream?
|
Hoccheim am Main
Eltville Kiedrich Erbach Hallgarten Hattenheim Winkel Johannisberg Rudesheim Assmanshausen |
|
|
What is the climate of the Rheingau in comparison to Rhein?
|
Warmer than areas on the Rhein to the south
Steep slope provides good exposure |
|
|
What are the soils of the Rheingau?
|
Upper slopes - slate
Lower slopes - mixture of clay, loess, alluvial sand and slate |
|
|
What is the style of Riesling from the Rheingau?
|
More powerful, rounder style of Riesling than the Mosel
Fuller in body, more concentration, more balanced acidity 1/2 of production is dry Traditionally uses the Rheingauer Flote (brown bottle) |
|
|
Where is the production of red located in the Rheingau?
|
Assmanshausen
|
|
|
Where is the Rheinhessen located?
|
Directly south of the Rheingau, bordered by the Rhine river to the north and east, the Nahe to the west and the Pfalz to the south
|
|
|
How much land is under cultivation in the Rheinhessen?
|
26,000 ha
More land than any other angaugebiet |
|
|
What is the most planted grape in the Rheinhessen?
|
As of 2008, Muller Thurgau
|
|
|
Where is Liebfraumilch typically from?
|
Rheinhessen
|
|
|
What are the bereiche of the Rheinhessen?
|
Nierstein
Wonnegau Bingen |
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Nierstein from upstream to downstream?
|
Oppenheim
Nierstein Nackenheim |
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Wonnegau from upstream to downstream?
|
Florsheim-Dalsheim
Westhofen |
|
|
What is Pfalz? What is the terrior?
|
Natural continuation of Alsace in Germany
Rain shadow effect by the Haardt Mountains Similar climate to Alsace Complex soil makeup of sandstone, limestone, basalt, granite and alluvial gravel |
|
|
What are the bereiche of the Pfalz?
|
Sudliche Weinstrasse
Mittelhaardt-Deutsche Weinstrasse |
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Mittelhaardt-Deutsche Weinstrasse in the Pfalz from upstream to downstream?
|
Ruppertsberg
Deidesheim Forst Wachenheim Bad Durckheim Ungstein Kallstadt |
|
|
Where are the best vineyards in the Pfalz?
|
Forst
|
|
|
What are the bereiche of Nahe?
|
Nahetal
|
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Nahetal from upstream to downstream?
|
Schlossbockelheim
Oberhausen Niederhausen Norheim Bad Munster Bad Kreuznach |
|
|
What is the style of wine in the Nahe?
|
Riesling based, generally sweet and between Mosel and Rheingau in style
|
|
|
What are the features of the Ahr?
|
Northernmost wine region dedicated to red (88%)
10th in overall size for anbaugebiete Terraced vineyards sheltered from winds by Eifel mountains Rocky, volcanic slate |
|
|
What are the bereiche of Ahr?
|
Walporzheim-Ahrtal
|
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Walporzheim-Ahrtal?
|
Klosterberg
|
|
|
What are the reds of the Ahr like?
|
Pinot Noir
Light in color Bright acidity Red fruit Lean structure |
|
|
What are the bereiche of Franken?
|
Maindreiech
Mainviereck Steigerwald |
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Maindreieck?
|
Wurzburg
Escherndorf |
|
|
What are the gemeinde of Steigerwald?
|
Iphofen
|
|
|
What are the features of the Franken? What are the main varietals? What is their style of wine? How is it bottled?
|
Centered along Main river flowing westward from Bamberg to Frankfurt
Produces a lot of beer Silvaner and Muller Thurgau thrive Almost all Franken wine is dry Some Spatburgunder and Fruhburgunder (early ripening strain of Pinot Noir) Traditionally bottled in bocksbeutel (squat, flask-shaped bottle) |
|
|
What are the bereiche of the Mittelrhein?
|
Siebengebirge
Lorelei |
|
|
What are the features of the Mittelrhein?
|
Narrow anbaugebiet following the Rhine northward pass Assmanshausen and Lorch in the Rheingau
Steep slate riverslopes with Riesling 80% of wine is trocken or halbtrocken |
|
|
What are the bereiche of the Hessische-Bergstrasse?
|
Starkenburg
Umstadt |
|
|
What are the features of the Hessische-Bergstrasse?
|
One of the smallest angaugebiete
Only region without a VDP Erste Lage site |
|
|
What are the bereiche of Baden?
|
Badische-Bergstrasse Kraichgau
Bodensee Breisgau Kaiserstuhl Markgraferland Ortenau Tauberfranken Tuniberg |
|
|
What are the features of Baden?
|
One of Germany's larger anbaugebiete
Covers large area along French border Has a separate zone along the Swiss border to the south on the border of Lake Boden Dominated by mass production and cooperatives Produces weissherbst |
|
|
What are the bereiche of Wurttemberg?
|
Wurttembergisch Unterland
Wruttembergisch Bodensee Kocher-Jagst-Tauber Oberer Neckar Remstal-Stuttgart Bayerischer Bodensee |
|
|
What are the features of Wuttemberg?
|
One of Germany's larger anbaugebiete
Covers large area south of Franken Has a separate zone along the Swiss border to the south on the border of Lake Boden Dominated by mass production and cooperatives Produces Schillerwein |
|
|
What is schillerwein?
|
Rose popular in Wurttemberg
Made by cofermentation of white and red grapes |
|
|
What is weissherbst?
|
Sagnee rose
|
|
|
What are the bereiche of Sachsen?
|
Elstertal
Dresden Meissen |
|
|
What are the bereiche of Saale-Unstrut?
|
Schlossneuenbburg
Thuringen |
|
|
What are the features of Sachsen?
|
Added after reunification
Located in the Elbe River valley Germany's smallest wine growing region Muller Thurgau is most planted grape Glosriesling, aromatic cross developed in Alsace, is a local speciality |
|
|
What are the features of the Saale-Unstrut?
|
Confluence of the Saale and Unstrut rivers
Germany's most northern wine region Muller Thurgau and Weisburgunder are common |

