![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does cAMP affect so many different signaling pathways?
|
cAMP is formed by the activation of adenylate cyclase and the change of ?? +[cAMP] => activation of PKA which is an enzyme that can activat or ???? other enzymes (of different pathways) by phosphorylation.
|
|
|
Why is it necessary that second messengers are short living?
|
Because the signal not only is transduced, it is amplified and it is important to stop its effect at the right time.
|
|
|
Describe in general terms the IP3 (inositol 1,4,5 triphosphate) cascade.
|
PIP2 ->(phosphorylase C)-> IP3 + diacylglycerol
IP3 will activate the Ca++ channel, raising the Ca++ concentration in the cytosol. Different cellular processes happen. Muscle contraction. IP3 is dephosphorylated -> inositol cease the signal |
|
|
Signaling pathways use proteins with specific adaptor modules. Describe one of those. Why is the use of modules such a powerful mechanism?
|
??IRS (insulin substrate proteins) bind lipid kinase and take it to the membrane where it can act on substrate a membrane lipid.
|
|
|
Suppose you have discovered a new yeast strain that contains a new enzyme in the glycolytic pathway and catalyzes the following reaction:
Glyceraldehys 3-P + NAD+ +H2 ---> 3-phosphoglycerate + NADH + H+ This shortens the pathway but would it benefit the cell? Explain. |
The cell will not benefit because
PGA --> P 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (using Pi +NAD+--> NADH + H+) --> 3-phosphoglycerate (using ADP -> ATP) So the cell will lose the opportunity to yield ATP during glycolysis |
|
|
In 1906 Harden & Young performed experiments using yeast extracts and glucose.
They found that fermentation stopped when the assay mixture had exhausted the supply of phosphate. Explain. |
PGA -->1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (via Pi+NAD+). Exhausted the supply of phosphate would stop glycolysis at this step
|
|
|
In 1906 Harden & Young performed experiments using yeast extracts and glucose.
Ethanol and CO2 accumulated, why was pyruvate converted to these molecules? |
To regenerate NA+, to keep the redox ?? ???? balance
Pyruvate --> ethanol +CO2 via (NADH + H+ --> NAD+) |
|
|
In 1906 Harden & Young performed experiments using yeast extracts and glucose.
They noticed that when fermentation ceased a hexose-bisphosphate had accumulated, which bisphosphate is this and why did it accumulate? |
Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate, because all other reactions are reversible.
Fructose 6-P + ATP --> Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + ADP + H+ |
|
|
In 1906 Harden & Young performed experiments using yeast extracts and glucose.
When they added arsenate to the mixture instead of phosphate they noticed that the hexose-bisphosphate did not accumulate and that the fermentation to ethanol and CO2 went to completion. Explain. |
Arsenate bound to the PGA and ?IG? glycolysis will continue to pyruvate --> ethanoly + CO2 (via NADH + NAD+), but the cell will not yield ATP during glycolysis.
|
|
|
Proteins, Polysacchardies and lipids all yield the same two carbon metabolite.
What is this metabolite? |
Acetyl - SCoA
|
|
|
Proteins, Polysacchardies and lipids all yield the same two carbon metabolite.
What is the major carbon containing compoun produced from this metabolite? |
CO2
|
|
|
2-Phosphoglycerate --> _____ + H2O
|
2-Phosphoglycerate --> PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) + H2O
Glycolysis Step #9 Enolase performs dehydration |
|
|
Glucose + ATP --> _________ + _________
What enzyme is used in this reaction? |
Glucose + ATP --> Glucose 6-phosphate + ADP + H+
Step #1 in glycolysis Hexokinase does a phosphoryl transfer |
|
|
Oxaloacetate + acetyl-CoA ⇒ ________
|
Citrate
(citric acid cycle) |
|
|
Oxaloacetate + acetyl-CoA ⇒ Citrate
uses what enzyme? |
Citrate synthase
(citric acid cycle) |
|
|
SuccinylSCoA + ___ ⇒ Succinyl-P ⇒ Succinate
|
Pi
(citric acid cycle) |
|
|
SuccinylSCoA + Pi ⇒ Succinyl-P ⇒ Succinate
This reaction is called? |
Substrate level phosphorylation
The reaction proceeds through a phosphorylated enzyme intermediate |
|
|
Malate + ____ ⇒ (Malate dehydrogenase) ⇒ ___ + NADH + H+
|
NAD+ ⇒ OAA
(citric acid cycle) |
|
|
What is the precursor for citrate?
|
Acetyl-CoA + OAA
|
|
|
What is the precursor for succinate?
|
Succinyl-SCoA
|
|
|
What is the structure of oxaloacetate?
|
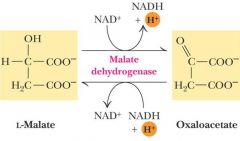
.
|

