![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Terrestrial Planets and Composition
|
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
(solid) Fe, Ne, Si, O |
|
|
Jovian Planets
|
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto
(gas) H, He, Ch4, Nh3 |
|
|
How was earth's age and composition determined?
|
Meteorites found in Antarctica.
|
|
|
Describe Earth's formation
|
4.6 Billion years ago earth = hot an molten and therefore homogeneous
1) Denser material settles 'down' to the center and the lighter material begins to rise. ---> while cooling down, earth experiences de-gassing, which is how the atmosphere is formed Collisions w/ small planet = debris circle around earth which condenses and forms the moon. |
|
|
What gasses were in the newly formed atmosphere and how did they lead to the formation of the oceans?
|
Ch4, Nh3, H2O (g), H2S
H2O(g) --> H2O (l) = Oceans |
|
|
Composition of the Earth
|
Fe, O2, Si, Mg (in order of highest concentration)
|
|
|
Depth of crust and composition
|
0-100km; Silicates, Si, O2, Al, K, Mg, Ca, Na, Fe
|
|
|
Composition of Core
|
Fe and Ni
|
|
|
Mantle: List the composition and explain how we know this
|
Fe, Mg, Si, O2
Volcano's give us a direct insight to the composition of the mantle. |
|
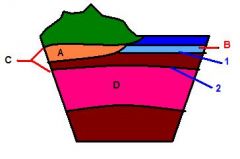
List and name the indicated areas
|
A = Continental Crust
B = Oceanic Crust C = Lithosphere(0-100km) D = Asthenosphere 1 = Physical & Chemical Barrier 2 = Physical Barrier |
|
|
Describe the Lithosphere
|
-Equivalent to the plates
-Solid, brittle -Crust + Upper most Mantle - About 100km thick |
|
|
Describe the Asthenosphere
|
- "lubrication" for plate motion
-partially molten, behaves in plastic sense (bendy) -About 250km thick |
|
|
Compare Oceanic and Continental Crust
|
Ocean is made almost entirely of Basalt and is very dense (3g/cc)
Continental crust is composed mostly of granite and is there for lighter (2.7g/cc) |
|
|
What drives the magnetic Field?
|
Fluid motions in outer core
|
|
|
How was continental drift proved?
|
-Shape of the continents
-Fossils of plants an animal found on continents that were very far apart -Glacial sediments indicated Africa, Australia, India, and South America were all co-located around Antarctica. -Mountain Chains: Appellation + Atlas = same ages -sea floor spreading |
|
|
Explain the two theories explaining the apparent wandering pole and state which one is more likely and why.
|
Theory 1: Wandering Pole;
---- Continents stay the same and the Pole itself wanders Theory 2: Fixed Pole; ---- Pole stays fixed and the continents wander. Theory 2 is much more probably because we have proof that the continents are moving. |
|
|
When the magnetic field was measured, what was found about the crust?
|
Mirror images of the reversals on either side of the midocean ridge.
|
|
|
What is the oldest crust, where is it, and why is there not older crust?
|
180 mya in the Western Pacific; subduction zones recycle the ocean crust.
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of plate boundaries and examples of occurrences that occur in relation to them.
|
Divergent Boundaries:
Ocean Ridge ( <--- ---->) Convergent Boundaries: -subductive: ---><--- ocean goes under continental which = Volcanic Mountain Chain -C---><----C = Mountain Chain -Transform Boundaries: /|\ \|/; California |
|
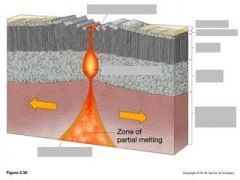
|
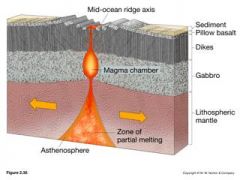
|
|
|
What are chimneys and pillow lava?
|
Found where there is ocean floor spreading; they are erupting hot, metal rich fluid
Chimneys provide habitat for chemo-synthetic organisms Pillow lava comes from slow bubbles of slow erupting lava. |
|
|
What is the range of rates for Plate Spreading and where are the respective rates seen?
|
1cm-18cm a year
Atlantic spreads at a rate of 1cm a year while the Pacific spreads at a rate of 18cm a year. |
|
|
What is the result of the rate of plate spreading the Pacific? Atlantic?
|
The Pacific sea floor is very smooth, where the Atlantic floor is very choppy.
|
|
|
What accounts for the wavy ridgeline?
|
Transform faulting
|
|
|
Declare whether the statement is true or false, if it is false, correct it.
Convergent earthquakes have deeper, larger foci and therefore are more damaging. |
False;
Convergent earthquakes do have large and deep foci, but deeper doesn't necessarily indicate more damage. |
|
|
Divergent Earthquakes
|
Small Shallow Foci
Magnitude of 1-2 |
|
|
Convergent Earthquakes
|
Deeper and larger foci
magnitude of 5-9 |
|
|
Benioff Zone
|
The edge of a subducting plate that is outlined in quake foci
|
|
|
Andesite and Rhyolite are types of volcanic rock but they are light in both color and weight, why?
|
They rocks that are formed from volcanic arcs which spew subducted continental rocks and are there of the lighter and less dense substance that its respective crust is composed of.
|
|
|
minerals are defined as
|
naturally occurring inorganic solids that have a definite composition and a regular internal structure
Silicates are the dominant form, Quartz, feldspar, mica, hornblende, etc... |
|
|
A minerals structure...
|
tells you how it behaves
|
|
|
Three types of Rocks:
|
Igneous: Magma (Primary rocks)
ex: basalt Sedimentary: Deposited (By wind water or ice) Metamorphic: Igneous or Sedimentary rock that has been pressurized, heated, and transformed, usually during mountain making |
|
|
Paleozoic
|
Pennsylvania moved to Mississippi to see Devon, who is Silurian, because they needed and ORthodontist for CAMera Brian
Pennsylvanian, Mississippian, Devonian, Silurian, Ordovician, Cambrian |
|
|
Cenozoic
|
Neo and Paleo Genes are better!
Genes had to come first before anything else could be made. Neogene and Paleogene |
|
|
Mezozoic
|
Started 65mya
Creative (Cretaceous) Juries (Jurassic) Try (Triassic) 250 millon (250 mya) People (Permian) |
|
|
Eons
|
Pharos take Prozac to heal their Arches
Phanerozoic Eon, Protozoic Eon, Archean Eon |
|
|
Biostratigraphy
|
fossil record = relative ages; evolution and extinction; ranges of fossils
|
|
|
Magneto stratigraphy
|
Sedimentary and Igneous rock acquire earth's magnetic field and formation;
rocks can be correlated with ocean's floor |
|
|
Absolute dating and radio active decay. In a graph, the Daughter (halves/doubles) and the parent (halves/doubles)
|
doubles; halves
|
|
|
Volcanic Ash Bed
|
1) Ash = hot and liquid in the air, when it cools, it crystallizes
2) Ash contains many minerals 3) The mineral and ash bed is a closed system, so when the minerals decay, the ratios can be looked at to determine the age |
|
|
Granite
|
1) Crystallizes, forms minerals upon cooling
2) Mineral becomes a closed system, radioactive decay occurs inside |
|
|
Things you can date with C14
|
Calcite (Shells); Bones, wood, pottery, cloth, manuscripts, tissue, etc....
|
|
|
Weathering; definition, explain HI example and importance
|
HI island has faults along it, at some point, a portion of the island will break off and fall into the ocean, this will cause a huge Tsunami.
Weathering: The way geological materials break down in situ (on site) Weathering leads to soil formation |
|
|
Physical Weathering is seen in _____
List 3 examples of physical weathering |
Cold climates
Examples: 1) Freeze/Thaw - ICE 2) Heating/Cooling 3) Tree roots |
|
|
Explain dissolution
|
CHEMICAL
Calcite + H2Co3 --> Ca + CO2 + H20 Calcite breaks down into Limestone regolith |
|
|
Explain Oxidation
|
Rusting = CHEMICAL
Fe+2 + 3O2 --> 2Fe2O3 Fe +2 = green Fe +3 = red |
|
|
Explain Hydrolysis
|
Chemical
Feldspar weathers into a clay mineral when H+/OH- is added |
|
|
Physical weathering is found in _________; and Chemical weathering is most often found in _________. What is the result of this?
|
Cold climates; hot and humid climates.
The soil composition is completely different. |
|
|
What are suture lines?
|
Where convergent plate boundaries and mountains form; possible future rifting.
|

