![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
parts of a wave: crest, wave length, trough, wave height, Fetch
|
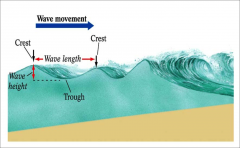
fetch- distance across which the wind and water interact
|
|
|
Oscillatory and Translatory Motion
|
Oscillatory
Translatory-re-suspends sediment |
|
|
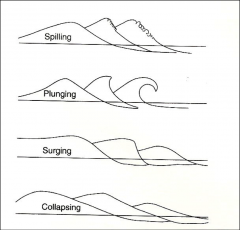
different waves-spilling
plunging, surging, collapsing |
|
|
|
Waves in deep water
|
travel faster, approach coast at an angle
|
|
|
waves in shallow water
|
travel slower, crest nearly parallel to coast
|
|
|
swash
|
a turbulent layer of water that washes up on the beach after an incoming wave has broken. The swash action can move beach materials up and down the beach, which results in the cross-shore sediment exchange
|
|
|
backwash
|
the motion of receding waves.
|
|
|
Shorelines
|
are places where bodies of water meet dry land
|
|
|
Coasts
|
are landward of ocean shorelines
|
|
|
Beach
|
a narrow strip of land, washed by waves or tides .
|
|
|
how are Ordinary Waves produced?
|
Waves are produced when wind drag causes the surface water of oceans/lakes to rise and fall
- Waves get refracted on approaching shoreline |
|
|
Foreshore
|
is the area between low tide and high tide
|
|
|
Backshore
|
is the area between high tide and sea cliff or inland vegetation line
|
|
|
Beach face
|
is the steepest part of Foreshore
|
|
|
Berm
|
is a horizontal bench of storm sediment
|
|
|
picture beach
|
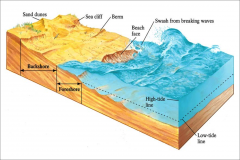
Beach a narrow strip of land washed by waves or tides
Foreshore is the area between low tide and high tide Backshore is the area between high tide and sea cliff or inland vegetation line Beach face is the steepest part of Foreshore Berm is a horizontal bench of storm sediment |
|
|
how is a Longshore current produced?
|
is produced as water flows parallel to coastline
|
|
|
how are Rip Currents produced?
|
are produced when water piles up in surf zones and flows seaward, generally perpendicular to the coast.
|
|
|
tides
|
Daily rise/fall of surfaces of oceans/lakes due to gravitational pull of the Moon/Sun on the Earth– also due to force created as Earth spins on its axis
|
|
|
Flood tides
|
- elevate sea surface that cause shoreline to move inland
|
|
|
Ebb Tides
|
- low sea surface that cause shoreline to move seaward
|
|
|
Tidal Bulges
|
combination of gravity and inertia create two bulges of water. One forms where the Earth and moon are closest, and the other forms where they are furthest apart. Over the rest of the globe gravity and inertia are in relative balance. Because water is fluid, the two bulges stay aligned with the moon as the Earth rotates
|
|
|
Wave erosion occurs when
|
deep water waves hit the shore with full force
Air and water are forced into cracks at high pressure |
|
|
Headlands-
|
cliffs that jut seaward
|
|
|
Sea Caves are produced when
|
waves are refracted against the side of headland
|
|
|
Sea Arch forms when
|
two Sea Caves erode completely through the headland
|
|
|
Sea Stack is formed when
|
Sea Arches collapse
|
|
|
tombolo
|
formed from wave refraction. the waves sweep sediment together from both sides. Eventually, when enough sediment has built up, the beach shoreline, known as a spit, will connect with an island and form a tombolo.
|
|
|
coastal protection:
Riprap/Seawall- Groins – Jettys – |
Riprap/Seawall- protects shore lines. riprap is a bunch of rocks, seawall is just a wall. both catch the waves to stop erosion
Groins – Stabilize beaches. they jut out into the ocean and catch the sand Jettys – Keep inlets clear. extends channel so deposition occurs further out |
|
|
Volcanic Black Sand Beach
|
need active volcano, mafic magma. they erode quickly thats why it needs to be active.
|
|
|
transport and depositional features:
Spit- Hook Baymouth Bar |
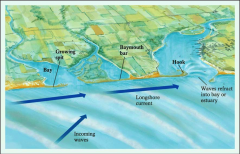
Spit is a finger-like ridge of sand deposited where Longshore drift encounters deeper water
Hook is a curved spit Baymouth Bar is a spit that covers the access to a bay – the area behind it fills with sediment |
|
|
Filling of Tidal Inlets: 3 steps
|
1) streams bring sediment to coast
2)coastal bay beaches filled w/ sediments as outlet becomes blocked by bar 3) tidal inlet completely fills in |

