![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Parallel Lines |
Lines in the same plane that do not intersect. |
|
|
Parallel Planes |
Planes that do not intersect. |
|
|
Perpendicular Lines |
Lines that intersect at 90 degree angles. |
|
|
Skew Lines |
Lines that are not coplanar. |
|
|
Perpendicular Bisector |
A line perpendicular to a segment at the segments' midpoint. |
|
|
Angle Bisector |
A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles. |
|
|
Vertical Angles |
The non-adjacent angles formed by two intersecting lines. |
|
|
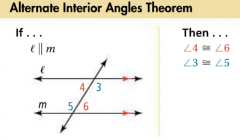
Alternate Interior Angles |
For two lines intersected by a transversal, a pair of angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and between the other two lines. |
|
|
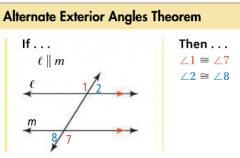
Alternate Exterior Angles |
For two lines intersected by a transversal, a pair of angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and outside the other two lines. |
|
|
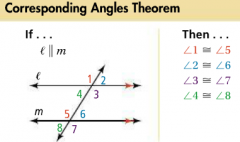
Corresponding Angles |
For two lines intersected by a transversal, a pair of angles that are on the same side of the transversal and on the same sides of the other two lines. |
|
|
Supplementary Angles |
Two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 degrees. |
|
|
Transversal |
A line that intersects two coplanar lines at two different points. |
|
|
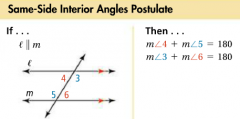
Same-Side Interior Angles |
For two lines intersected by a transversal, a pair of angles that are on the same side of the transversal and between two lines. |
|
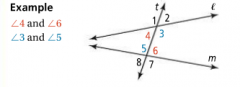
|

|
|
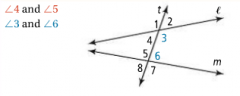
|

|
|
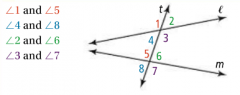
|

|
|
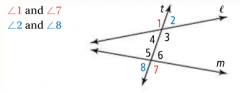
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
Parallel Postulate |
Through any point not on a line, there is one and only one line parallel to the given line. |
|
|
Triangle Angle Sum Theorem |
The sum of the angles of any triangle is 180. |
|
|
Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem |
The measure of each exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the measures of its two remote interior angles. |
|
|
Slope Intercept Form |
y = mx + b |
|
|
Point Slope Form |
y - y1 = m(x - x1) |

