![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
area of triangle
|
base * height ÷2
|
|
|
area of trapezoid
|
(base1 + base2) * height ÷2
|
|
|
area of parallegoram
|
base * height
|
|
|
area of a rhombus
|
diagonal1* diagonal2 ÷ 2
|
|
|
surface area
|
the sum of all the faces
|
|
|
volume
|
length *width *height
|
|
|
angles of a tiangle
|
sum of the three angles = 180°
|
|
|
isosceles triangles
|
triangle with 2 equal sides
|
|
|
sides of a triangle
|
the sum of any 2 sides of a triangle must be greater than the third side
|
|
|
Pythagorean Theorem
(right triangles) |
a^2+b^2=c^2
|
|
|
Pythagorean Triples
|
3-4-5
multiples 6-8-10, 9-12-15 12-16-20 5-12-13 multiples 10-24-26 8-15-17 |
|
|
iscolese right triangle
|
45-45-90
2 sides are equal is half of a square 1:1:x√2 AB=BC AC is x √2 5=5 5√2 |
|
|
Equilateral triangle
|
all sides are equal
each angle measures 60° can be split into two 30-60-90 🔺's A= 1/2s [s√3÷2] = s^2√3÷4 |
|
|
diagonals of Square & Cube
|
d=s√2 where s is a side of a square
d=s√3 where s is an edge of a cube |
|
|
Similar Triangles
|
if two similar triangles have corresponding side lengths in ratios a:b, then their areas will be a^2:b^2
volumes will be a^3:b^2 |
|
|
deluxe Pythagorean theorem
(rectangular solid) |
d=diagonal
d^2=length^2+width^2+height^2 |
|
|
Radius, diameter, circumference, area
|
If you know any of these you can find the rest
C= the distance around a 🔴 c=π•d d=diameter the distance across 🔴 r= radius half the distance across 🔴 A=area = π•r^2 1 full revolution or turn = 1 circumference |
|
|
cylinders and surface area
|
surface area = 2 circles +rectangle=
2(πr^2)+2πrh only info you need to find area of cylinder is the radius of the cylinder and the height |
|
|
cylinders and volume
|
V=πr^2h
|
|
|
exterior angles of a triangle
|
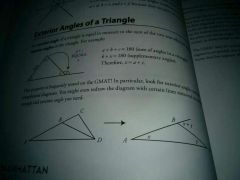
|
|
|
slope of a line
|
rise/run
rise=difference btwn 2 Y-coordinates ÷ run=difference btwn 2 X-coordinates |
|
|
x intercept
|
point on the line at which y=0
(x,0) I.e. (-4,0) -4 is the x intercept |
|
|
y intercept
|
point on the line at which x=0
(0,y) i.e.(0,6) y-intercept =6 |
|
|
slope-intercept equation
|
y=Mx+b
m=slope of the line b=y-intercept of the line |
|
|
linear equations
|
Ax+By=C
where A,B,C are numbers I.e. 6x+3y=18 is linear never involve terms such as , x^2, √x, or xy. when you want to feel graph linear equations rewrite in the slope intercept form (y=MX+b) 6x+3y=18 3y=18-6x y=6-2x y=-2x+6 y intercept is (0,6), slope is -2 |

