![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Quartz hardness
|
very hard (H=7)
|
|
|
Quartz cleavage
|
lacks cleavage
|
|
|
Quartz fracture
|
semi-conchoidal fracture;
|
|
|
Quartz Crystal Shape
|
no room for perfect crystal faces (last mineral to crystallize in igneous rock) -> amorphous shape
|
|
|
Quartz Color
|
colorless when pure with small impurities that give it a translucent white (milky quartz), rose (rose quartz), yellow, or gray color
|
|
|
Potassium Feldspar hardness
|
hard (H=6)
|
|
|
Potassium Feldspar Cleavage
|
well-developed cleavage in two directions that are perpendicular to each other
|
|
|
Potassium Feldspar Crystal Shape
|
crystals are often rectangular (lath shape) and posses at least some good crystal faces
|
|
|
Potassium Feldspar Color
|
can vary; pearly like compared to Plagioclase Feldspar usually white (can be confused for plaadioclase Feldspar or milky quartz [quartz more translucent & lacks a lath shape]) or salmon pink
|
|
|
Plagioclase Feldspar hardness
|
hard (H=6)
|
|
|
Plagioclase Feldspar cleavage
|
good cleavage; two perpendicular directions
|
|
|
Plagioclase Feldspar Crystal Shape
|
crystals often lath-shape and possess at least some good crystal faces
|
|
|
Plagioclase Feldspar color
|
varies white to light gray; earthy when compared to Potassium Feldspar
|
|
|
Plagioclase Feldspar Confusion
|
Na and Ca properties can change; be confused for potassium Feldspar especially lighter ones and some occur together in igneous rock; confused for quartz but this one has lath shape and less translucent
|
|
|
calcite hardness
|
quite soft (H=3)
|
|
|
calcite cleavage
|
excellent; none perpendicular to one another
|
|
|
calcite crystals
|
vitreous luster but smaller crystals that are more typical in limestone are earthy
|
|
|
calcite color
|
usually white to light gray.
|
|
|
calcite confusion
|
color alone can be confused for quartz, either Feldspar, or gypsum. its softness and that it fizzes vigorously in hydrochloric acid easily distinguishes it.
|
|
|
gypsum hardness
|
extremely soft (H=2)
|
|
|
gypsum cleavage
|
3 good cleavages; none perpendicular to one another
|
|
|
gypsum crystals
|
big, fresh crystals have vitreous luster but smaller crystals are earthy. small crystals = white; large ones = clear
|
|
|
gypsum color
|
small crystals = white; large = clear
|
|
|
gypsum confusion
|
can be confused for quartz, either Feldspar, or calcite. it's extremely soft and doesn't fizz
|
|
|
kaolinite hardness
|
extremely soft (H = 2); dull, earthy luster; chalky substance comes off
|
|
|
kaolinite crystals
|
microscopically small, like clay
|
|
|
kaolinite cleavage
|
only one; hard to spot
|
|
|
kaolinite confusion
|
with gypsum or calcite on color alone; doesn't fizz, it's earthy more than vitreous (glass)
|
|
|
halite (NaCl) hardness
|
very soft (H=2.5)
|
|
|
halite cleavage
|
3 good ones; mutually perpendicular
|
|
|
halite crystals
|
clear
|
|
|
halite confusion
|
doesn't fizz and salty
|
|
|
chert hardness
|
very hard (H=7)
|
|
|
chert cleavage
|
lacks it
|
|
|
chert fracture
|
good Conchoidal fracture; sharp edge when flaked
|
|
|
chert color
|
commonly red (known as jasper), yellow, or gray
|
|
|
chert crystals
|
microscopically small crystals of quartz (shares many of quartz's properties)
|
|
|
muscovite hardness
|
very soft (H=2-2.5)
|
|
|
muscovite cleavage
|
one single perfect one; like sheets of paper; part of mica family
|
|
|
muscovite color
|
clear; when stacked looks silver
|
|
|
biotite hardness
|
soft (H=2.5-3)
|
|
|
biotite cleavage
|
single perfect one; like muscovite; another mica
|
|
|
biotite color and confusion
|
dark brown to black color
|
|
|
chlorite hardness
|
soft (H=2-2.5)
|
|
|
chlorite cleavage
|
also mica; crystals too small to make it easy to identify cleavage
|
|
|
chlorite crystal color
|
green
|
|
|
hornblend hardness
|
hard (H=5.5)
|
|
|
hornblend cleavage
|
amphibole family; two good cleavages at angles 60 and 120 to each other.
|
|
|
hornblend color
|
black or dark brown
|
|
|
pyroxene hardness
|
hard (H=5.5-6)
|
|
|
pyroxene cleavage
|
two good cleavages that are perpendicular to one another
|
|
|
pyroxene color
|
black or dark green
|
|
|
olivine hardness
|
hard (H=7)
|
|
|
olivine cleavage
|
lacks it
|
|
|
olivine fracture
|
Conchoidal
|
|
|
olivine color
|
shade of green; light to dark; brown or brownish - yellow ; leave behind iron stained marks where it's crystals existed b4
|
|
|
Hematite hardness
|
ranges (H=1-6)
|
|
|
Hematite cleavage
|
none
|
|
|
Hematite color
|
in tiny crystals = red or orange most of time with earthy luster (literally rust); large crystals = steel gray with metallic luster
|
|
|
Bowen reaction series
|
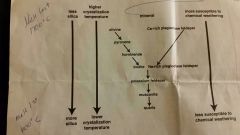
|
|
|
color
|
dark silicate = rich in iron and magnesium; light = high in silica and low on iron and magnesium
|
|
|
hardness (Mohs Scale of Hardness)
|
fingernail = 2.5; penny = 3; nail = 4.5; glass = 5.5
|
|
|
crystals
|
larger crystals = slowly cooled and stayed under ground longer
|
|
|
fracture
|
rough edges since cut not along plane of atoms; Conchoidal = curved ripple cuts
|
|
|
luster
|
way mineral reflects light; metallic = reflects like metal; vitreous = glass; pearly; earthy = dull like soil; -> can look at chemical weathering withstanding by comparing difference between fresh and weathered sample
|
|
|
degree
|
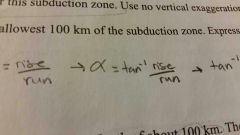
|
|
|
topographic profile
|
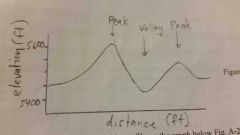
|
|
|
which way do Vs point on river
|
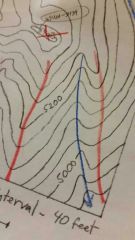
upstream
|
|
|
where do tips of Vs on ridges point to?
|
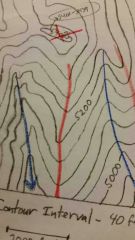
towards lower elevation
|
|
|
igneous
|
interlocking crystals that are angular; visible or microscopic; extrusive or intrusive
|
|
|
igneous extrusive
|
some or all crystals = microscopic; rhyolite, andesite, basalt, komatiite; heterogeneous
|
|
|
rhyolite
|
igneous extrusive; light colored due to high silicate
|
|
|
andesite
|
igneous extrusive; intermediate color due to intermediate silica content
|
|
|
basalt
|
igneous extrusive; dark color (black or gray) due to low silica content
|
|
|
komatiite
|
igneous extrusive; dark like basalt but heavy; low silica
|
|
|
igneous intrusive
|
all of mineral crystals are big enough to be visible; granite, diorite, gabbro, periodite; homogenous
|
|
|
granite
|
igneous intrusive; light color; high silica
|
|
|
diorite
|
igneous intrusive; intermediate color; intermediate silica
|
|
|
gabbro
|
igneous intrusive; dark color (black or green); low silica
|
|
|
periodite
|
igneous intrusive; dark like gabbro but heavy; very low silica
|
|
|
sedimentary
|
rounded sediment particles cemented together. layers of sediments; clastic or biochemical
|
|
|
sedimentary clastic
|
sediment particles derived from erosion of preexisting rocks. dominantly silicate; conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, mudstone, claystone
|
|
|
conglomerate
|
sedimentary clastic; > 2mm; larger than sand
|
|
|
sandstone
|
sedimentary clastic; sand sized; 1/16 to 2 mm
|
|
|
siltstone
|
sedimentary clastic; silt sized; 1/256 to 1/16 mm
|
|
|
mudstone
|
sedimentary clastic; mix of silt and clay
|
|
|
claystone
|
sedimentary clastic; clay size; <1/256 mm
|
|
|
sedimentary biochemical
|
sediment particles newly formed chemically or biologically; mostly non-silicate
|
|
|
limestone
|
sedimentary biochemical; made of calcite; fizzes
|
|
|
chert
|
sedimentary biochemical; microscopic quartz crystals; hard and smooth; when flaked, breaks with Conchoidal fracture
|
|
|
evaporite
|
sedimentary biochemical; salt; crystal due to water evaporation
|
|
|
coal
|
sedimentary biochemical; organic compound deposited in swamps; black or brown
|
|
|
metamorphic
|
interlocking crystals that grow during solid state transformation of another rock due to hear and or pressure. minerals frequently aligned parallel to each other; foliated or non-foliated
|
|
|
metamorphic foliated
|
crystals aligned parallel to each other; like layers of crystals (layers of color); slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, migmatite
|
|
|
slate
|
metamorphic foliated; clean breakage with smooth planes; breaks along parallel alignment of clay minerals
|
|
|
phyllite
|
metamorphic foliated; parallel of tiny mica crystals hard to distinguish individually; sparkly sheen
|
|
|
schist
|
metamorphic foliated; mica crystals easily seen; larger than phyllite
|
|
|
gneiss
|
metamorphic foliated; parallel light and dark bands
|
|
|
migmatite
|
metamorphic foliated; black bands with pods of granite
|
|
|
metamorphic non-foliated
|
mineral crystals not parallel; dominant of single colored minerals; homogenous color; marble, quartzite, greenstone, hornfels, metaconglomerate
|
|
|
marble
|
metamorphic non-foliated; calcite crystals; fizzes; hard and sparkly; crystals interlock
|
|
|
quartzite
|
metamorphic non-foliated; quartz crystals; hard and sparkly; crystals large and interlock;may have bedding
|
|
|
greenstone
|
metamorphic non-foliated; metamorphosed basalt; green hue due to chlorite mica growth
|
|
|
hornfels
|
metamorphic non-foliated; fine grain texture; individual crystals not visible; any color; usually dark gray or green; tough and hard; brake into cubes not sheets
|
|
|
metaconglomerate
|
metamorphic non-foliated; non-foliated or foliated (pebbles stretched in same direction)
|
|
|
contour lines
|
Connect spots of same elevation
|
|
|
cultural map features
|
built by humans
|
|
|
contour interval
|
vertical spacing between contour lines
|
|
|
mineral
|
naturally occurring, inorganic, crystalline solid that has fixed chemical composition
|
|
|
superposition
|
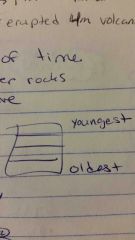
|
|
|
lateral continuity
|
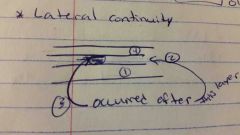
|
|
|
cross cutting
|

|
|
|
original horizontality
|

|
|
|
divergent
|
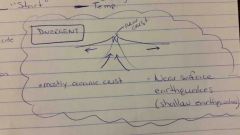
|
|
|
convergent
|
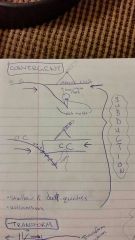
|
|
|
collision
|

|
|
|
transform
|
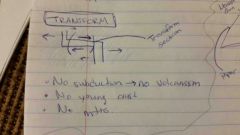
|
|
|
hot spots
|
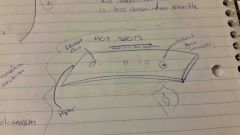
|

