![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How much energy did primitive vs modern societies use? |
100W Per person 10,000W Per person |
|
|
What is the relation of energy "cutoff" point where people have a very high quality of life and where our energy production is? |
600 x 10^12 needed 470 x 10^18 have |
|
|
Order of top energy sources. |
Petroleum = 40% Coal = 23.2% Natural Gas = 22.5% |
|
|
What can you say about the energy system graph? |
37 Quads "useful energy" 58 Quard "Wasted energy" |
|
|
What is energy? |
The capacity to do work |
|
|
What is work? |
The application of a force over a distance |
|
|
What is a force? |
Something that pushes / pulls |
|
|
Units of energy : |
Force: Mass x acceleration Work: force times a distance, units are kg* m ^2 / s^2 = N* m = Joules |
|
|
What is a calorie? |
Energy required to raise 1 gram of water one degree Celsius ( 1 cal = 4.184 Joules) |
|
|
What is a BTU? |
Raises 1 pound of water one degree F (1 BTU = 1,055J) |
|
|
What is power? |
Energy / time, energy exchanged per time unit, how fast you get work done |
|
|
Power measurement? |
Joules / sec = Watts 1 watt = 1 J / second |
|
|
How much energy does a 100W light bult use? |
100W is rate of energy use 100W bult uses 100 J / s or 360,000 J / hr |
|
|
Power vs Energy |
Power is rate of usage Energy is amount used |
|
|
Kilowatt-hour measures? |
Energy 1000 W for one hour, 1 hr = 3600 sec so 1 kWh = 3,600,000 J |
|
|
KE formula |
KE = 1/2 m v ^2 |
|
|
What is temperature? |
Measure of kinetic energy of molecules |
|
|
Celcius to K ? |
C = K - 273.16 |
|
|
Photon energy _________ with increasing frequency (or decreasing wavelenght) |
increases |
|
|
About how much is blackbody radiation of Sun? |
3.9 x 10^26 Whatts |
|
|
Where does sun get all its energy?
|
Themonuclear fusion |
|
|
How much more potent is nuclear fusion than most chemical reactions? |
~20m times |
|
|
What's reflect / absorb rates of sun's energy hitting Earth? |
35% reflected 65% absorbed |
|
|
First law of thermodynamics |
Energy can not be created or destroyed, only transformed. Energy is always conserved. |
|
|
How can fluorescent light bult produce same light as an incandescent, but use less power? |
Fluorescent bult doesn't generate as much heat, more energy is released as visable light |
|
|
Santa Ana winds represent what process? |
Adiabatic process. Air is compressed as it moves from mountains to lower elevations, pressure is higher lower so volume decreases, work done on system increases temperature |
|
|
How does the sun "create" energy ? |
It exchange mass for energy |
|
|
If most energy processes release heat, why isn't the Earth heating up rapidly? |
Earth radiated much of its heat |
|
|
What makes work "useful"? |
Whether it can be done on another system, whether the associated energy is able to do further work |
|
|
What is it called when heat is coerced into useful energy? |
Heat engine |
|
|
Draw a picture of how work is extracted from heat. |
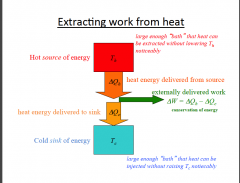
|
|
|
What is efficiency? |
Work done / heat supplied Energy out / energy in |
|
|
What is the limit to efficiency?
|
Carnot efficiency |
|
|
Carnot efficiency formula: |
(T hot - T cold) / T hot Measured in K Only applies to heat engines. |
|
|
How efficient are power plants today? |
33% |
|
|
What is it called to make use of "waste" heat? |
cogeneration |
|
|
Is it possible to "beat" the Carnot efficiency? |
Yes, with cogeneration. However, it is impossible to reach 100%. |
|
|
2nd law of themodynamics: |
All energy trasnformations lead to increase entropy, a measure of disorder in universe |
|
|
Net system efficiency? |
Multiplication of efficiency of each transformation |
|
|
Non-renewable |
Nature resource that cannot be re-made or re-grown on a timescale comparable to its consumption or use |
|
|
Renewable |
Resource that is replenished over a short period of time, quickly enough to replace what is consumed |
|
|
Reserves |
Economically extractable today |
|
|
Resources |
Total amount that exists, some of which may become economically extractable in the future |
|
|
What the problem with our estmations of how long our non-renewables will last? |
All based on current consumption, even though consumption is growing exponentially |
|
|
What is the basic form of fossil fuels? |
Hydrocarbon |
|
|
How are hydrocarbons formed? |
Phtosynthesis forms carbohydrates Hydropcarbons form when Oxygen burns off |
|
|
Can hydrocarbons form without sunlight? |
Yes |
|
|
What makes up natural gas? |
Methane 70-90% |
|
|
Talk about petroleum. |
-Huge complexity in content -Many aromatic rings -Range greatly in size -Crude Oil Refining - Works to take certain components of petroleum and separate them out - Gasoline = one part of crude oil (petroleum), also the lighter part (smaller molecules) - Separated by refining - Each barrel of crude oil goes into a wide variety of products - Octane Ratings - How molecules are branched determines their octane ratingIt is a rating of how straight (heptane) vs how branched (isooctane) the fuel source is |
|
|
Pro/Cons of big three: |
Coal AD: Cheap, lots of it DIS: Direty, dangerous to mine Gas AD: Little processing, cleaner to burn, efficient to burn DIS: Difficult to transport, dangerous to extract Petroleum AD: Easily transported, clean due to refining process DIS: More CO2 emissions than gas, environmental concerns (spills) |

