![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Population Dynamics (1/6)
World Population Growth |
● World population has grown by 6 billion in the past 108 years mainly due to a fall in death rate ● More recently there has been a fall in birth rate. This means that the rate of growth is predicted to slow down |
|
|
World growth cont. |

|
|
|
Population Dynamics (2/6)
Population & Development |
● Population pyramids show the number/percentage of different age groups for each gender in the population ● Changes shape as the country develops ● Classic pyramid shape (wide base, narrow top)= Developing country i.e Indonesia ● Narrow top, wide middle, slightly narrower base = Developed country i.e UK ● Can be used to forecast population change ● Shows short term factors impact on population i.e war leading to a high death rate espescially in young adult males |
|
|
Population Dynamics (2/6)
Malthus & Boserup |
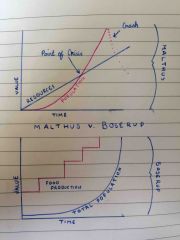
• Malthus-said that the population would grow in doubles and the food production would only grow in doubles creating a gap. This would lead to war and tension in society • Boserup- Predicted that as soon as possible started to run out, humans would invent a way to increase food production |
|
|
Population Dynamics (3/6)
Population Issues |
•Ageing- High proportion of people over age 65. Issues: - Money for state pensions - Social provisions (suitable homes, nurses) - Medical provision (care homes, specialised doctors) • Youthful- High proportion of people aged 16/18 years or younger. Issues: - Social provisions (nurseries, schools,etc.) - Medical provisions (maternity units, paediatricians) |
|
|
Population Dynamics (4/6)
Managing Populations |
• Sustainable Population- can be maintained without harming the environment or quality of life of the people. •Overpopulation- More people than can be supported by its resources •Underpopulation- More resources than people |
|
|
Population Dynamics (4/6)
Managing Populations |
• Sustainable Population- can be maintained without harming the environment or quality of life of the people. •Overpopulation- More people than can be supported by its resources •Underpopulation- More resources than people |
|
|
Population Dynamics (5/6) Pro- and Anti-Natal Policies |
• Anti-Natal~ China -One child policy - Incentives given (cash bonuses, better childcare, longer maternity leave) - Why? Huge BR in 20th Century - Successful? Yes. BR & pop'n have fallen - consequences; More boys than girls, possible future labour shortage, no more huge famines. • Pro-Natal~ Singapore - why? Policy reducing pop'n so successful in the '60s it led to pop'n decline - What? Have 3+ kids. {Singapore three or more} - How? Incentives include tax rebates, cheap nurseries, spacious apartments. Counselling offered to discourage abortion - Success? Yes. BR and total pop'n has increased |
|
|
Population Dynamics (4/6)
Managing Populations |
• Sustainable Population- can be maintained without harming the environment or quality of life of the people. •Overpopulation- More people than can be supported by its resources •Underpopulation- More resources than people |
|
|
Population Dynamics (5/6) Pro- and Anti-Natal Policies |
• Anti-Natal~ China -One child policy - Incentives given (cash bonuses, better childcare, longer maternity leave) - Why? Huge BR in 20th Century - Successful? Yes. BR & pop'n have fallen - consequences; More boys than girls, possible future labour shortage, no more huge famines. • Pro-Natal~ Singapore - why? Policy reducing pop'n so successful in the '60s it led to pop'n decline - What? Have 3+ kids. {Singapore three or more} - How? Incentives include tax rebates, cheap nurseries, spacious apartments. Counselling offered to discourage abortion - Success? Yes. BR and total pop'n has increased |
|
|
Population Dynamics (6/6) Migration Policies |
• Open Door- Allows anyone to live in country. The EU has an open-door policy • Quotas- Restricts the number of people allowed into the country per year • Skills tests- Potential migrants have to pass a 'skills test'. Only those who are highly skilled are allowed. May also involve a points system. E.g. Australia |
|
|
Consuming Resources (1/6) Categories of Resources |
• Non-Renewable- Fixed amount available. Can't be remade/renewed over a short period of time e.g coal • Renewable- Resources that don't need to be managed to renew themselves e.g sunlight • Sustainable- Resources that can be managed so they renew themselves e.g. Wood |
|
|
Consuming resources (1/6) Types of Resources |
• Energy- heating, cooking, transport, electricity, etc. Non renewable and renewable • Mineral- Building, jewellery making, manufacturing. Non-renewable • Physical- Energy. Renewable. •Biological- Food production, energy, manufacture. Sustainable. |
|
|
Consuming Resources (2/6) Resource Supply & Use 1 |

•The global consumption of resources is unequal |
|
|
Consuming Resources (3/6) Managing Consunption |
•Education- Changing behaviour - Public awareness, ads - Walking, cycling, turn off lights etc. • Conservation- Maintaining health of natural world - Grants and quotas, laws, taxes etc. - Reducing car tax for less polluting cars • Recycling- Recycling collection etc. |
|
|
Consuming Resources Potential of Renewables |
• Alternative and renewable sources are ways to achieve sustainsability • problems: renewables not as efficient - Cannot meet same demand - Less availability to resources - The tech is expensive • Oil alternative- Hydrogen cell; lots of hydrogen available (water), good source of power |
|
|
Globalisation- Employment sectors Primary Sector |
• Jobs such as agriculture, building, mining, etc. • Hands on |
|
|
Globalisation: Work sectors Secondary |
•Jobs such as factory jobs I.e. Textiles |
|
|
Globalisation: Work Sector Tertiary |
• new ways of working e.g. From home • good wages • services |
|
|
Globalisation: Work Sector Quarternary/ orher |
• informational • technology e.g. Computer technician or programmer |
|
|
Globalisation: Impact of Globalisation |
World-Wide •increase in working women • improved working conditions • increased skills • more goods available to everyone
Developed World • Wages improved • almost everyone benefits from 'global' goods and services • Mostly good working conditions • More flexibi |

