![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Plate Tectonics |
The theory that states that Earth's outer shell consists of plates that move due to convection currents. |
|
|
Define the Folding of Plates |
When two plates converge and the sedimentary rocks around the edge of the plates crumple and fold. |
|
|
Define Faults in the Tectonics Plates |
A fracture in the Crust of the Earth due to plate movement. |
|
|
Define Humus |
The dark, upper layer of soil made up of partially decayed plant material. |
|
|
Define Parent Material |
Rock from which soil is derived. |
|
|
Define Maritime Climate. |
Climate Type that is strongly influenced by the closeness of an Ocean or another large body of water. The annual temperature range tends to be small and Precipitation is high. |
|
|
Define Continental Climate. |
Climate Type that develops away from the influence of the ocean. The annual temperature range tends to be large and Precipitation is low. |
|
|
Define Extreme Range. |
When the temperature will reach extreme highs in Summer and extreme lows in Winter. |
|
|
Define Moderate Range. |
When the Temperature will remain moderate to a point through tout the year (never too cold and never too hot). |
|
|
What is the LARGEST Vegetation Type in Canada. |
Coniferous Trees; e.g., white and black spruce , balsam fir, pine (evergreens) which lose few needles. Hardy Deciduous Trees (Poplar and white birch) in southern portion. |
|
|
Define Tree Line. |
The Boundary between the Tundra and the Boreal Forest Zone. North of this line it is too cold for trees to grow. |
|
|
Define Permafrost. |
Permanently frozen ground that does not completely thaw in the Summer. |
|
|
What are the three ways in which Tectonic plates interact? |
They Converge, Diverge, and Transform. |
|
|
Define Convergent. |
When plates collide with each other. |
|
|
Define Divergent. |
When plates move apart from each other. |
|
|
Define the Transform Movement. |
Plates moving past each other. |
|
|
What are the four main components of soil? |
Minerals (Rocks), Organic Material, Moisture, and Air. |
|
|
Define Minerals (Rocks) as a component of soil. |
Minerals come from rock and become part of the soil when rock is worn down into smaller particles. This provides the soil with nutrients. |
|
|
Define Organic Material as a component of Soil. |
When plants and animals die, bacteria helps them decompose. Humus is formed and provides nutrients and gives soil it's dark colour. |
|
|
Define Moisture as a component in soil. |
Water dissolves nutrients in the soil and is taken up the plant through its roots. Moisture is necessary for plant survival. |
|
|
Define Air as a component in soil. |
Plants need air around their roots to breathe. Insects, such as worms that travel through soil provide air spaces as well as Humus. |
|
|
Define Deciduous Trees. |
Broad-leaved trees that shed their leaves annually in the fall. |
|
|
Define Coniferous Trees. |
Trees with cones and often needle-like leaves; evergreen. |
|
|
How do Glaciers form? |
Since Summer never comes to melt the snow, snow will accumulate and compress over many years, gaining a new layer every snowfall. Eventually, this compression of snow will lead to the forming of solid Ice. |
|
|
When is the Winter Solstice and what is it? |
The winter Solstice occurs every December 21st and it is the shortest day of the year. Note, the day it falls on can vary sometimes. |
|
|
When is the Summer Solstice and what is it? |
The Summer Solstice occurs every 21st of June, and it is the longest day of the year (sunlight). Note, the day it falls on can sometimes vary from the 21st. |
|
|
What is a Dry Air Mass? |
A large body of air that is exempt from most moisture and is hot throughout. |
|
|
What is a moist Air Mass? |
A large body of air that tends to have large amounts of moisture within it, and due to this will sometimes be a bit colder. As it passes over land it will affect that areas climate. |
|
|
How are Winds created? |
Winds are created by air moving from high pressure areas towards low pressure areas. |
|
|
What are Ocean Currents? |
The temperature of an Ocean will affect the air that passes over it. For example the North Pacific Current heats the cool, moist air that passes over it. Some examples of it would be the chilly Labrador Current, the Gulf Stream, and the North Pacific Current. |
|
|
What are Prevailing Winds? |
Prevailing Winds are well-established patterns of wind movement. The Prevailing Winds in Canada are called the Westerlies. |
|
|
What is elevation? |
If you climb to a top of a mountain, it will be colder there. This is because as the air rises it expands due to lower air pressure; and as air expands it cools. |
|
|
What is Relief? |
Relief is where the area around the slope of the mountain is very dry since the air condensed so much going up and down the mountain. |
|
|
What is Natural Vegetation? |
Vegetation grown without the added interference of Human beings. |
|
|
What is Glacial Retreat, and Glacial Advance? |
When the glacier grows through Precipitation quicker than it can melt (advance) . Or when a glacier melts quicker than it accumulates ice (retreat). Glaciers are currently retreating. |
|
|
Why are Glaciers important? |
Glaciers are important because they basically formed our land, creating valleys, water basins, and valleys when they advanced towards the equator. |
|
|
What % of the earth is covered in glaciers? |
About 10% or 15 Million Square kilometres. |
|
|
What are the three types of landforms in Canada? |
There is the shield, the Highlands, and the Lowlands. |
|
|
What landforms region is Canada's Breadbasket? |
The Interior Plains or Prairies. |
|
|
What are the three Highland Mountain Regions and where are they located? |
First is the Appalachian Mountains which are in the east around Southern Quebec and the Maritimes. Second are the Innuitian Mountains which are in the far north. And finally the Western Cordillera is in the west. |
|
|
Which landforms region covers more than half of Canada? |
The answer is the Canadian Shield. |
|
|
What landform region is Canada's oldest Highland Region? |
The Appalachian Mountains formed the longest time ago. |
|
|
What landform region has the greatest population? |
The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands Region by far. |
|
|
What landform region do you live in? |
The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands Region. |
|
|
How do you find average annual temperature? |
You simply find the mean of all the average temperatures of each month. |
|
|
How do you find the temperature Range? |
By finding the difference between the lowest and highest temperature. |
|
|
How do you find total annual Precipitation? |
You simply add all the amounts together. |
|
|
What is the Season of maximum Precipitation. |
Simply add all the Precipitation up for each month and find the season that quite simply had the most Precipitation. |
|
|
How to determine if it is Continental or Maritime Climate. |
Simply look out for extremities vs. Moderate temperatures; and low Precipitation vs high Precipitation. |
|

|
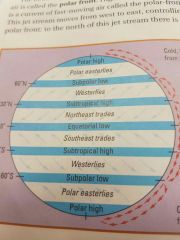
|
|
|
Do a diagram of Leaching. |
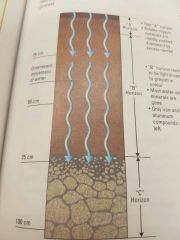
Water moving down into and within the soil. |
|
|
Do a diagram of Calcification. |
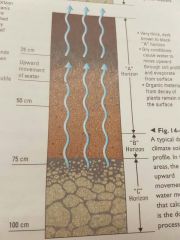
The upward movement of water. |

