![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Geography |
The study of Place and Space. |
|
|
Geographers look at... |
Where things are, and why they are there. |
|
|
Physical Geography |
The study of the Natural landscape of the earth. |
|
|
Cultural Geography |
The study of the Human Landscape of the earth. |
|
|
Cartographers |
Makers of maps. |
|
|
Atlas |
Book of maps |
|
|
Parts of a map |
Title, Compass rose, legend/Key, and scale. |
|
|
Title |
Explains the subject of the map. |
|
|
Compass Rose |
Shows the "Cardinal Directions", meaning North, South, East, and West. |
|
|
Legend/Key |
Shows and explains the symbols used on the map. |
|
|
Scale |
Shows the true size of the objects used on the maps. |
|
|
Physical maps show... |
Natural Features on the earth |
|
|
Political Maps show... |
Human made features on the earth |
|
|
Thematic maps show... |
Information, such as population, resource, weather, and topographic. |
|
|
Choropleths |
Use difference in shading or colors to show variables. |
|
|
Cartogram |
Represent map feature surfaces in such ways, as to make them proportional to a given statistical variable. |
|
|
Geographers study the world by looking at... |
M.R. H.E.L.P
Movement, Region, Human interactive environment, Location, and Place. |
|
|
Absolute Location |
Exact place on earth where a Geographic feature is found. |
|
|
Relative Location |
A place in comparison to other places around it. |
|
|
Place |
Describes the physical features and cultural characteristics of a location. |
|
|
Reigon |
Describes an area of the earth's surface with similar characteristics, usually more than one. |
|
|
What defines a Region? |
Human and Physical characteristics. |
|
|
Movement |
How and why people, plants, animals, and ideas move through time and space. |
|
|
Human environment interaction |
People learn to use what that environment offers them and to change that environment to meet their needs. |
|
|
Equator |
Divides the earth between Northern and Southern Hemisphere. |
|
|
Prime-Meridian |
Divides the Eastern hemisphere from the Western Hemisphere |
|
|
Hemisphere |
One half of the earth.
(North, South, East, West) |
|
|
Latitude |
Runs parallel to the equator |
|
|
Longitude |
Runs parallel to the Prime Meridian |
|
|
4 layers of the earth's structure |
Inner-core, outer-core, mantle, crust |
|
|
Earth's Core |
Solid metalic inner core, liquid metalic outer core, and both made of iron and nickl. |
|
|
Mantle |
Surrounds the core, soft layer of molten (melted) rock called magma. |
|
|
Crust |
Thin layer of rock at the earth's surface. |
|
|
Atmosphere |
Layers of gas surrounding the earth. |
|
|
Lithosphere |
Solid rock portin of the Earth's surface. |
|
|
Hydrosphere |
All the water elements of the Earth; Oceans, seas, rivers, and lakes. |
|
|
Biosphere |
Where plants and animals live. This includes the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere. |
|
|
Plate Tectonics |
Movement of large plates (crust) above magma in the mantle. |
|
|
Lowest point on Earth: |
Dead Sea in South Asia |
|
|
Chemical Weathering |
When minerals are changed completely when they mix with water and air. Like metal changing into rust. |
|
|
Mechanical Weathering |
when rocks and other minerals are broken into smaller pieces. |
|
|
Loess |
Wind erosion from blown sand, clay, and silt. |
|
|
Water erosion: |
Precipitation, mudslides, and avalanches. |
|
|
Glaciation |
Changes in landform made from a slowly moving sheet of ice. (Glacier) |
|
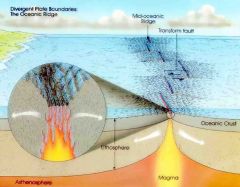
Front (Term) |
Divergent |
|
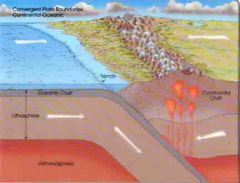
Front (Term) |
Convergent Subtraction |
|
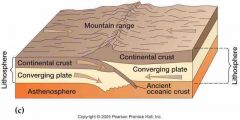
Front (Term) |
Convergent Collision |
|
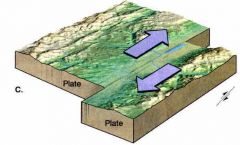
Front (Term) |
Transformation |
|
|
Highest point on earth: |
Mt. Everest |
|
|
Supercontinent |
Panegaea |
|
|
Seismograph |
Measures Earth Quakes |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Divergent |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Convergent Subtraction |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Convergent Collision |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Transformation |

