![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Potholes |
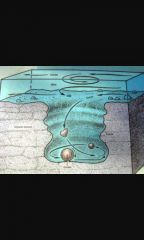
Pebbles carried in a high turbulent flow become trapped in small hollows in the stream bed. Vertical eddie's in the flow cause the pebbles to grind holes into the rock by abrasion. Conditions are most often found in the middle course of a river. |
|
|
Waterfalls, rapids and gorges |

Waterfalls and Rapids are found where there is an increase in the rivers gradient. Search gradient changes are normally due to the river channel encountering bands of erosion resistant rock. A waterfall retreats upstream forming a gorge. The river falls into a deep plunge pool, in this pool the soft, surrounding rock is eroded more rapidly than the overlying erosion-resistant rock, deepening and widening the pool. This causes the pool to undercut overlying rock until it collapses under the force of gravity. |
|
|
Meanders |
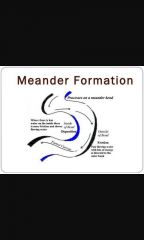
Alternating bars of sediment form on the bed of straight river channels in low flow conditions. As water flows around these alternating bars, centripetal force directs the water towards one of the banks resulting in high velocity flow, erosion and undercutting. This creates a concave outer bank. On the inside of the bend the velocity is slower and deposition occurs. This results in an increase in rivers sinuosity.
• Asymmetrical cross section |
|
|
Braided channels |

Braided rivers are rivers which are split into several smaller channels that diverge and converge repeatedly as they flow around small islands. Braided channels form when a river has fluctuating discharges and a sufficient supply of sediment to result in the periodic occurrence of high sediment loads. |
|
|
Oxbow Lakes |
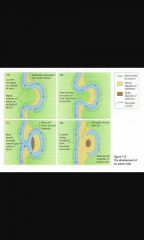
|
|
|
Levees |
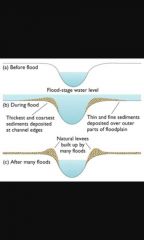
Rivers flood during times of high discharge. Has the river overtops its banks, the velocity of the flow drops resulting in deposition. As the coarsest material will be deposited first, this process results in the development of levees along the sides of the channel. |
|
|
Floodplains |
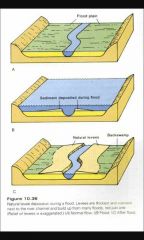
They are formed when a river overflows it's banks during a flood event. The resulting loss in velocity and increase in wetted perimeter combined to cause deposition of flat layers of alluvium (silt and clays). |
|
|
Deltas |
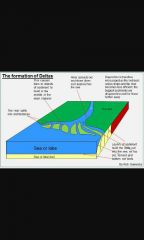
When a river enters the lake of the sea the velocity of the river decreases causing deposition. Arcuate delta - curving convex shoreline with a dendritic drainage pattern Cuspate delta - pointed like a cup or tooth with sediment deposited equally on either side of the channel
Birds foot delta - singers of deposition stretch out into the sea along channels |

