![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Swidden Cultivation |
a type of agriculture characterized by land rotation in which temporary clearings are used for several years and then abandoned to be replaced by new clearings |
|
|
Slash-and-Burn |
"burned clearing"; farmers set land on fire after the dead vegetation dries out |
|
|
Paddy Rice Farming |
-cultivation of rice from a paddy (small flooded field), practiced in humid areas of Far East -system of irrigation is key, large amount of fertilizer |
|
|
Monoculture |
the raising of only one crop on a huge tract of land in agribusiness |
|
|
Plantation Agriculture |
-system of monoculture for producing export crops requiring relatively large amounts of land and capital; originally dependent on slave labor -tend to specialize in one cash crop |
|
|
Livestock Fattening |
-commercial type of agriculture that produces fattened cattle and hogs for meat -Corn Belt of US Midwest, Brazil, and South Africa |
|
|
Hunting-and-Gathering |
-nonagricultural groups -fewer than 1% of humans practice hunting-and-gathering today |
|
|
Earliest Hearth of Animal Domestication |
early farmers in the Fertile Crescent (Middle Eastern Countries) |
|
|
The Green Revolution |
recent introduction of high-yield hybrid crops and chemical fertilizers and pesticides into traditional Asian agricultural systems |
|
|
Von Thunen Model |
a core-periphery model to address the problem of the distribution and intensity of agriculture based on transportation costs to market |
|
|
Industrial Regions |
-least developed regions -developing regions -developed regions |
|
|
Industry Types |
-primary industry (ex. oil, mining, fishing) -secondary industry (ex. packaging, canning) -service industry ~consumer service (ex. Amazon, Starbucks) |
|
|
Industrial Revolution |
began pre-1700s, cottage and guild industries, local manual labor |
|
|
Megacity |
particularly large urban center |
|
|
Primate City |
a city of large size and dominant power within a country (ex. Buenos Aires) |
|
|
Central-Place Theory |
a set of models designed to explain the spatial distribution of urban service centers |
|
|
Threshold |
the size of population required to make goods and services economically feasible |
|
|
Range |
the average maximum distance that people will travel to purchase a good or service |
|
|
Earliest Hearth of Urbanization |
regions in which the world's first cities evolved (ex. Mesopotamia) |
|
|
Cosmomagical Cities |
types of cities that are laid out in accordance with religious principles |
|
|
Factors Contributing to the Rise of Cities |
1. Technical Factors -hydraulic civilization (ex. Egypt, Mesopotamia) 2. Religious Factors 3. Political Factors -institution of kingship 4. Multiples Factors -king may have functioned as priest, healer, astronomer, and/or scribe -fusing secular and spiritual power |
|
|
Factors Influencing Site Selection of Cities
|
1. defensive sites 2. trade-route sites 3. confluence sites - allow cities to be situated at the point where two navigable streams flow together |
|
|
Renewable Resources |
a resource which can be used repeatedly because it is replaced naturally (es. oxygen, fresh water, solar energy, timber) |
|
|
Concentric-Zone Model |
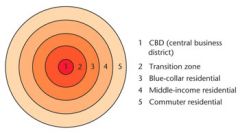
|
|
|
Sector Model |
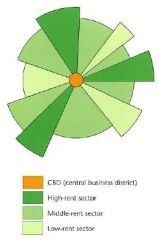
|
|
|
Causes of Return Migration to Central Cities |
1. economic advantages -accessibility -location near transportation facilities -communication -agglomeration - a snowballing geographical process by which secondary and service industrial activities become clustered in cities in order to share infrastructure and markets 2. social advantages -historical momentum -prestige -the need to locate near work |
|
|
The Causes of Decentralization |
-changes in accessibility -agglomeration -the need to locate near work -prestige |
|
|
The Costs of Decentralization |
-people who can't afford to live in the suburbs are forced to live in run down housing in the inner city, where there aren't many good jobs -vacant storefronts, empty offices, deserted factories -retain stores in central cities have steadily lost sales |
|
|
Checkerboard Development |
a mixture of farmlands and housing tracts |
|
|
Gentrification |
the displacement of lower-income residents by higher-income residents as buildings in deteriorated areas of city centers are restored |
|
|
The Costs of Gentrification |
-displacement of lower-income people, forced to leave their homes because of rising property values -gentrification contributes to racial and ethnic tensions |
|
|
Urban Heat Islands |
-an area of warmer temperatures at the center of a city, caused by the urban concentration of heat-retaining concrete, brick, and asphalt -urbanization affects precipitation -city heats comes from heating systems, automobiles, industry, human bodies, etc |
|
|
Features of Latin American Cities |
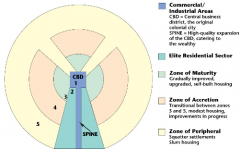
|
|
|
The Greek City |
-modest sized, approx. 5000 inhabitants -two distinctive functional zone 1. acropolis - temples of worship, storehouse of valuables, seat of power, sanctuary during siege 2. agora - province of the citizens; place for public meetings, education, social interaction, and judicial matters |
|
|
Medieval Ghettos |
-defined by ethnicity rather than occupation -began when Venetians decided to restrict Jewish settlement to the Ghetto Nuovo (new foundry) -Jews were forced to live in their own districts in most medieval cities |
|
|
The Renaissance City |
-city size increased rapidly -bureaucracies of regional power structures came to dominate cities -trade routes expanded -most planning measures were meant to benefit the privileged classes |

