![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Air Masses |
large volumes of air that have distinctive characteristics oftemperature and moisture. |
|
|
cP, cT, mP, mT |
Continental Polar, Continental Tropical, Maritime Polar, Maritime Tropical Continental: Dry Maritime: Wet Polar: Cold Tropical: Warm |
|
|
Cold Front |
The colder air is pushing intothe area occupied by the warmer air mass. This is characterized by cumulus clouds, shorter rain duration, intense weather. |
|
|
Warm Front |
The warmer air pushing into the areas occupied by colder air. This is characterized by stratus clouds, longer period of rain, more chill. |
|
|
Occluded Front |
A cold front will overtake a warm front and the result is that the whole warm frontis lifted off the ground. |
|
|
Dryline |
When two fronts have the same temp but different moisture, they don't mix. In lubbock, it tends to be dryer on the west side of the dryline and wetter on the east. |
|
|
Cyclones & Anticyclones |
Zones of low pressure are called cyclones and zones of highpressure are anticyclones |
|
|
Polar Front |
Where warm tropical air and cold polar air converge. |
|
|
Rossby Waves |
The undulations of the Polar Fronts |
|
|
Polar Jet Stream |
The insanely strong winds along the Polar Fronts. |
|
|
Cyclogenesis |
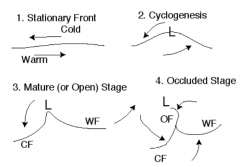
The formation of a cyclone. |
|
|
Thunderstorms |
Rapidly rising air forming cumulonimbus clouds that thunder and lightning and rain heavily. |
|
|
Köppen System |
Identifying climate regions based on temperatureand precipitation over the year. |
|
|
A Climates |
Found roughly between about 20° northand south. Very hot, little variation between seasons, equator, yo. |
|
|
B Climates |
Arid and semiarid regions are, obviously, areas of little water. Deserts and the like. |
|
|
C Climates |
Mesothermal climates: moderate temperatures, hence thename, and occur in the mid-latitudes. More than half of human population lives in C climates |
|
|
D Climates |
Microthermal climates are characterized by long and cold wintersand short summers. Poleward of C climates. |
|
|
E Climates |
The Polar climates: Ice Cap and Tundra Climates |
|
|
H Climates |
Highland Climates found at any place on earth if there is high enough mountains. |
|
|
Continentality |
A measure of the difference between continental and marine climates characterized by the increased range of temperatures that occurs over land compared with water. |

