![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who is Erwin Chargaff? |
Discovered that DNA the number of guanine units equals the number of cytosine units, and the number of adenine units equals the number of thymine units. The ratio of of A & T and G&C is equivalent. I.e. Human Genome A- 29 T-31 and C-18 G-18 |
|
|
What are the characteristics of DNA? |
1. Double stranded molecule 2. DNA alphabet: A,T,C,G 3. Used for longterm information (reference material in a library) 4. Deoxyribose sugar on C2 an H (Hydrogen) is bound. 5. Deox= oxygen missing from the structure on C2 |
|
|
What are the characteristics of RNA? |
1. Single stranded (the molecule can base pair with itself ; like sticky rope) 2. RNA nucleotides: A,U,C,G 3. Used to store short term information 4. Ribose on C2 an OH (hydroxyl group) 5. Has an extra oxygen on the second C. |
|
|
Who are Franklin and Wilikins? |
use of x-ray crystallography photographs to determine the structure of a molecule. Radar or Sonar technique that aids in trying to discover the approximation of the structure by bouncing "objects" off the desired structures i.e Photo 51 |
|
|
What is the structure of DNA backbone? |
The phosphate group bound to the 5th Carbon of the sugar and a nitrogenous base bound to the 1st Carbon of sugar. |
|
|
What are purines? |
A and G. Lager nucleotide molecules |
|
|
What are pyrimidines? |
C, U and T. Smaller nucleotide molecules |
|
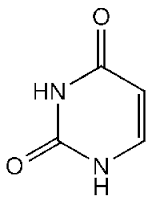
|
Uracil |
|
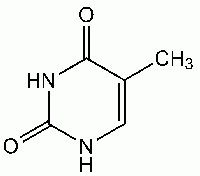
|
Thymine |
|
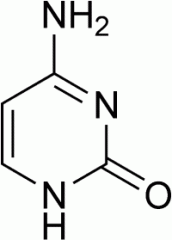
|
Cytosine |
|
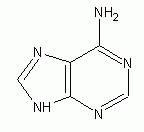
|
Adenine |
|
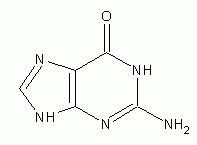
|
Guanine |
|
|
What does N mean in a genomic sequence? |
Any nitrogenous bases (A,T,G,C,U) |
|
|
How does DNA or RNA arranged? |
5' to 3': phosphate group at the begin attached to the 5' Carbon and the 3' Carbon naked at the end of the molecule. |
|
|
Semi-Conservative |
produce two copies that each contained one of the original strands and one new strand. |
|
|
Conservative |
leave the two original template DNA strands together in a double helix and would produce a copy composed of two new strands containing all of the new DNA base pairs. |
|
|
Dispersive |
produce two copies of the DNA, both containing distinct regions of DNA composed of either both original strands or both new strands. |
|
|
How many Hydrogen bonds are between the nitrogenous bases? |
3 hydrogen bonds between G and C
2 hydrogen bonds between A and T or U |
|
|
What is the Central Dogma? |
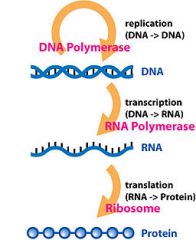
|
|
|
How are the DNA strand arranged? |
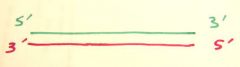
Antiparrell |
|
|
What does PCR stand for? |
Polymerase Chain Reaction |
|
|
What are the steps for PCR? |
A. Denaturation at 94 C for 45 seconds: breaks down or separates the hydrogen bonds between nucleotides. B. Annealing at 60 C for 45 seconds: primers are finding their compliment base pair (18-25 bp) on the DNA strand. C. Extension at 72 C for 60 seconds: primer extends the desired amplification region. Add nucleotides one at a time. |
|
|
When does elongation stop? |
The primer knows to stop when the temperature rises up to 94 C (denaturation step). The primer will then bind to a new region of DNA. |
|
|
Where are the new nucleotides added? |
At the 3' end of the strand. |
|
|
Primer Dimers |
consists of primer molecules that have attached (hybridized) to each other because of strings of complementary bases in the primers. Typically occur lower than 100 bps. |
|
|
Gradient PCR |
Varying thermal annealing in order to find the perfect annealing temperature for both primers. |
|
|
What is the Wallace Equation? |
TM = 4(G+C) + 2(A+T) |
|
|
What process only needs one primer? |
RT: Reverse Transcription |
|
|
What process uses two primers? |
PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction |
|
|
What are the degenerate letters? |
Y: T or C R: G or A N: A, T, U, G, C |
|
|
What does a nucleotide contain? |
5' carbon sugar or 3' carbon sugar, a phosphate group and one out of the four nitrogen bases. |
|
|
What is the leading strand? |
3' to 5'. The top strand being replicated. |
|
|
What is the lagging strand? |
5' to 3'. The bottom strand being replicated. |
|
|
What is the function of the Hhelicase enzyme? |
Unwinds the DNA structure separating a desired region/section into two halves. Breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases. |
|
|
What is the replication fork? |
a site on a DNA molecule at which unwinding of the helices and synthesis of daughter molecules are both occurring. |
|
|
How are the primer dimers arranged? |

|
|
|
What would you do if the PCR produced too many bands? |
increase the annealing temperature and decrease the magnesium concentration. |
|
|
What would you do if the PCR produced no bands? |
decrease the annealing temperature and increase the magnesium concentration. |
|
|
What does starting material does DNA polymerase need to begin sequence? |
The polymerase needs DNA as a template. |
|
|
Who is Kary Mullis? |
Developed the PCR technique in 1983 |
|
|
What is the salt adjustment for the %GC Method? |
usually 0.05 Na+ |
|
|
Where does the leading and lagging strand synthesized? |
These processes occur on both sides of the replication fork. |
|
|
What are the components apart of the replication of DNA? |
A. DNA Polymerase B. Topoisomerase C. DNA Polymerase III & I D. Ligase E. Primase |
|
|
What is topoisomerase? |
An enzyme that regulate the overwinding or underwinding of DNA. regulation of DNA supercoiling is essential to DNA transcription and replication, when the DNA helix must unwind to permit the proper function of the enzymatic machinery involved in these processes. Topoisomerases serve to maintain both the transcription and replication of DNA. |
|
|
What is Helicase? |
An enzyme used to separate strands of a DNAdouble helix or a self-annealed RNA molecule using the energy from ATP hydrolysis, a process characterized by the breaking of hydrogen bonds between annealed nucleotide bases. |
|
|
What are DNA Polyermerase III & I? |
III: makes the chain in a 5 to 3 direction and it proofreads with a 3 to 5 exonuclease, so it goes both ways doing something different
I: breaks down the RNA primer with a 5 to 3 exonuclease. |
|
|
What is ligase ? |
is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond. |
|
|
What is primase? |
enzyme that synthesizes short RNA sequences called primers. These primers serve as a starting point for DNA synthesis. |
|
|
Who discovered that eukaryotic genes are composed of intron and exons? |
Robert and Sharp |
|
|
What provides the primer for the replication? |
RNA Polymerase; 5' to 3' (leading) |
|
|
What copies a series of segments of the lagging strand? |
RNA primase starts to encode short RNA segements. DNA Polymerase III works backwards to replicate. And DNA Polymerase I replaces RNA U nucleoides with DNA T nucleotides. |
|
|
What adds complementary nitrogenous bases in replication of DNA? |
DNA Polymerase III |
|
|
What does the reverse transcriptase? |
An enzyme used to convert RNA back into DNA |
|
|
What is reverse transcription? |
used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template. It is mainly associated with retroviruses. |

