![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
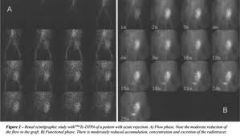
What is the imaging protocol that was probably used to obtain the above images?
a. consecutive 1 sec images for 15 sec b. consecutive 3 sec images for 45 sec c. 15 consecutive 10 sec images d. 15 consecutive 15 sec images |
b
|
|
|
Normal glomerular filtration rate is:
d. 125 mL/min |
d. 125 mL/min
|
|
|
12. For visualizing intraparenchymal lesions in the kidneys, the radiopharmaceutical from the list below is:
a. 99mTc DMSA b. 99mTc DTPA c. 99mTc MAG3 d. 131 I OIH |
a
|
|
|
15. If after administration of furosemide, a patient still has activity in the renal calyces, there is probably:
a. poor renal function b. renal artery occlusion c. renal infartion d. collection system obstruction |
d
|
|
|
19. Torsion of the testicle:
a. is synonmous with epididymitis b. is not painful c. is a surgical emergency d. may be treated with antibiotics |
c
|
|
|
20. The adult dose of 99mTc pertechnetate for imaging the testicles is:
a. 1-2 mCi b. 2-4 mCi c. 5-10 mCi d. 10-20 mCi |
d
|
|
|
21. The kidneys are normally perfused via the iliac artery.
a. true b. false |
b
|
|
|
22. Radionuclide cystography is most often performed to:
a. determine transplant function b. evaluate renal perfusion c. detect vesicoureteral reflux d. visualize space occupying lesions in the bladder |
c
|
|
|
28. In normal patients, a volume of up to 1.5 ml may reflux into the ureters and kidneys at maximum bladder filling.
a. true b. false |
b
|
|
|
30. Which of the following is not true regarding glomerlar filtration rate?
a. it usually becomes abnormal before serum creatinine levels become abnormal b. it is typically obtained through the use of 99mTc DTPA c. it can be determined only by taking blood or urine specimens d. it is the measure of the ability of the kidneys to clear insulin from the plasma e. all except b |
c
|
|
|
31. Which radiopharmaceuticals can be used to determine effective renal plasma flow?
a. 99mTc MAG3 b. 131 I OIH c. 99mTc DTPA d. a and b only e. a and c only |
d
|
|
|
32. An advantage of GFR and ERPF measurements over other indicators of renal function such as BUN and creatine is that the kidney can be determined seperately.
a. true b. false |
a
|
|
|
33. Which saline bottle would be sufficient to fill the bladder of an 8 year old during radionuclide cystography?
a. 125 ml b. 250 ml c. 400 ml d. none of the above |
c
|
|
|
34.Which renal imaging agent requires the highest administered dose?
a. 99mTc DTPA b. 131 I OIH c. 99mTc MAG3 d. 99mTc DMSA |
a
|
|
|
35. A technologist prepares a radiopharmaceutical for renal imaging at 8am. The patient arrives late at 10am and therefore a new kit has to be made. The radiopharmaceutical used is:
a. 99mTc MAG3 b. 99mTc DMSA c. 99mTc DTPA d. 99mTc GH |
b
|
|
|
37. Following the injection of 131 I NP-59, imaging for adrenal lesions is performed:
a. 6 hrs later b. 24-48 hrs later c. 48-72 hrs later d. 5-7 days later e. none of the above |
d
|
|
|
41. On otherwise normal static images of the kidneys, the lower poles of the kidneys appear slightly decreased in intensity relative to the upper poles. Why is this?
a. there is probably an obstruction of the collecting system b. there are bilateral space occupying lesions in the lower poles c. the adrenal glands are attenuating the activity from the lower poles d. the lower poles of the kidneys are situated slightly anterior to the upper poles |
d
|
|
|
42. In a patient with renal artery stenosis:
a. a post captopril study will show increased GFR b. a post captopril study will show decreased GFR c. a post captopril study will show GFR to be unchanged |
b
|

