![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
One of two or more versions of a gene. |
ALLELE |
|
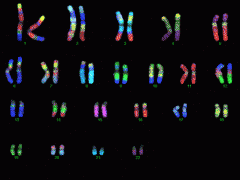
22 pairs of human chromosomes which not determine gender. |
Autosomal/nonsex chromosomes |
|
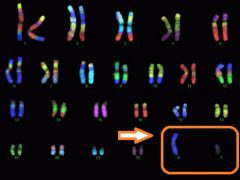
A pair of chromosomes which specify gender and determine whether you are male or female. The sex chromosomes are labeled X and Y. |
Sex chromosomes: Females do not have a Y chromosome. Instead, they have two X chromosomes.
|
|
A compact and efficient storage unit which contains the DNA packaged. Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of each cell. |
CHROMOSOME |
|
|
Chromosomes are the carriers of the genetic material, abnormalities in chromosome number or structure can result in disease. |
Chromosome abnormalities |
|

Trisomy 21 -a common disorder that occurs when a person has three copies of chromosome 21 |
Down syndrome |
|
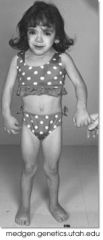
A common disorder that occurs when a person has ONLY ONE copies of chromosome 45, X |
Turner syndrome |
|
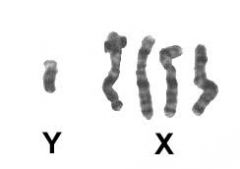
A common disorder that occurs when a person has three copies of chromosome 47, XXY. |
Klinefelter syndrome |
|
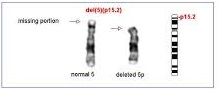
A common disorder that occurs when a person has three copies of chromosome 46, XX or XY, 5p. |
Cat cry syndrome |
|
|
The treatment of chromosomes to reveal characteristic patterns of horizontal bands like bar codes. The banding patterns lend each chromosome a distinctive appearance so the 22 pairs of human nonsex chromosomes and the X and Y chromosomes can be identified and distinguished without ambiguity. Banding also permits the recognition of chromosome deletions (lost segments), chromosome duplications (surplus segments) and other types of structural rearrangements of chromosomes. |
Chromosome banding |
|
|
A disease caused by an abnormality in an individual's genome. Most genetic diseases are the direct result of a mutation in one gene. However, one of the most difficult problems ahead is to find out how genes contribute to diseases that have a complex pattern of inheritance, such as in the cases of diabetes, asthma, cancer and mental illness. In all these cases, no one gene has the yes/no power to say whether a person has a disease or not. |
GENETIC DISEASE |
|
|
an individual's collection of genes. The term also can refer to the two alleles inherited for a particular gene. The genotype is expressed when the information encoded in the genes' DNA is used to make protein and RNA molecules. |
GENOTYPE |
|
|
a set of DNA variations, or polymorphisms, that tends to be inherited together. A haplotype can refer to a combination of alleles or to a set of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) found on the same chromosome. |
HAPLOTYPE |
|
|
the nickname of the International HapMap Project, an international project that seeks to relate variations in human DNA sequences with genes associated with health. The HapMap describes common patterns of genetic variation among people. |
HapMap: (short for "haplotype map project") |
|
|
The reception of genetic qualities by transmission through genes that have been passed from parent to offspring (children). All of the genetic characters or qualities transmitted from parent to offspring. |
Genetic inheritance |
|
|
a type of individual which contains different alleles of a gene. We can say that the individual is heterozygous for that gene. |
Heterozygous |
|
|
a type of individual which contains the same two alleles of a gene. We can say that the individual is homozygous for that gene. |
Homozygous |
|
|
An organized profile of a person's chromosomes. Two chromosomes specify gender — XX for female and XY for male. The rest are arranged in pairs, numbered 1 through 22, from largest to smallest. |
Karyotype |
|
|
The individual's observable traits produced by the expression of the genotype. |
Phenotype |
|
|
A a laboratory technique used to amplify DNA sequences. The method involves using short DNA sequences called primers to select the portion of the genome to be amplified. The temperature of the sample is repeatedly raised and lowered to help a DNA replication enzyme copy the target DNA sequence. The technique can produce a billion copies of the target sequence in just a few hours |
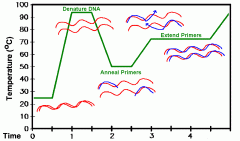
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) |

