![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
182 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 major proc resp for gen variat?
|
1. mutat
2. recombinat |
|
|
mutation ______________ playing cards, and ___________________ recombination ____________ playing cards
|
mutat introduces
recombinat shuffles them |
|
|
mutagens
|
cause mutations
|
|
|
excision repair
|
damamged dna strand is cut out, oth strand is used as templ to remake the damaged one
|
|
|
what is the minimum mutat that can be induced?
|
point mutation
|
|
|
t or f
its easier to have a loss of funct mutat than a gain of funct mutation |
t
|
|
|
new mutat are categorized as/
|
1. induced
2. spontaneous |
|
|
what is rate of spont mutat?
|
one c in 10^5 to 10^8
|
|
|
mutagenesis
|
prod of mutat thr expos to mutagens
|
|
|
an organ that has gone thr mutagenesis has been?
|
mutagenized
|
|
|
mutagens have a ______________ dose response
|
linear
|
|
|
there is always a ___________ level of mutations, even when you are inducing mutations on purpose
|
background level
|
|
|
2 main types of point mutat are?
|
1. base subst
2. base addit or delet |
|
|
base substit are what 2 kinds?
|
1. transition
2. tranvservion |
|
|
transition point mutat is?
|
replacement of A with G
or T with C |
|
|
replacing a purin with a purin in a mutat is?
|
transition mut
|
|
|
replac a pyrimidine w a pyrimidine is a?
|
transition mut
|
|
|
transversion point mutat is?
|
replac of purine w a pyrimidine
|
|
|
purines are?
|
A and G
|
|
|
pyrimidines are?
|
C and T
|
|
|
indel mutat are?
|
insertion deletion mutat
|
|
|
addit or delet mutat are actually?
|
addit or mutat of nucleotide pairs
|
|
|
mutat at prot level
a mutat that leads to a diff codon that encodes the same original AA is? |
a synonymous mutation
|
|
|
synonymous mutat are also called?
|
silent mutat
|
|
|
missense mutation is?
|
codon for one aa is changed to a codon for another aa
also called nonsynonymous mutat |
|
|
nonsense mutat are?
|
codon for one aa is ch to a stop codon
|
|
|
synonymous mutat never alter?
|
the aa seq of polypeptide chain
|
|
|
conservative substit (from a missense mutat)
|
when an aa is repl wit a chemically similar one
|
|
|
nonconservative substitution (from a missense mutat) is
|
when an aa is repl w a chem non similar other aa
|
|
|
nonconservat are more likely to prod _______________- in prot struc and funct
|
severe changes
|
|
|
the closer a nonsense mutat is to the ______________ end of open reading frame the _____________
|
3' end
more likely that result prot will stil have some biolog activit |
|
|
nonsense mutat lead to?
|
premat terminat of translat
|
|
|
indel mutat _________ the reading frame
|
changes
|
|
|
indel mutation leads to a ___________
|
frameshift mutation
|
|
|
frameshift mutat is caused by?
|
an indel mutat
|
|
|
t or f
you can also have mutations in noncoding an regulatory dna like promoters |
t
|
|
|
you can have mutat in regulatory regions of dna that can change the level?
|
of express of a g
|
|
|
just bec you have a mutat on the genotypic leve does not mean you will have one?
|
on the phenotypic lev
|
|
|
northern blot looks at?
|
rna
|
|
|
western blot looks at
|
protein
|
|
|
mutational specificity
|
mutag tend to do a cert kind of mutat and at a certain spot called hot spot
|
|
|
hot spot
|
place where a cert mutag tends to makes its mutations
|
|
|
mutagents
3 mech? |
1. replace a base
2. alter a base 3. damage a base |
|
|
base analogs
|
chemic comp that are so similar to normal nitr bases of dna they are accid incorp into dna struct
|
|
|
tautomers of bases
|
the diff forms of dna bases that they can naturally take
|
|
|
tautomers of bases
what are the diff forms? |
1. keto
2. imino 3. enol |
|
|
keto, imino, enol
which one is the most common? |
keto
|
|
|
what is the change of one tautomer into another called?
|
tautomeric shift
|
|
|
when a dna base bec ionized it can?
|
cause a mispair
|
|
|
if A bec its rare imino form it could accid pair w?
|
C instead of T
|
|
|
name 2 mutagens that alter a base?
|
EMS and NG
|
|
|
EMS is?
|
ethylmethanesulfonate
|
|
|
NG is?
|
nitrosoguanidine
|
|
|
EMS does what to the DnA bases?
|
it adds an ethyl gr
|
|
|
EMS and NG both add?
|
alkyl gr to differ positions on the bases
|
|
|
base alteration
when is a mutat most likely to occur? |
when the alkyl gr is added to the oxy at posit 6 of guanine to make o-6-alkylguanine
|
|
|
adding an O to posit 6 of guanine leads to what transition?
|
G C ---> A T
|
|
|
T or F
alkylating agents can ch incoming bases during DNA synth |
T
|
|
|
name 3 types of incalating agents?
|
1. proflavin
2. acridine orange 3. ICR compounds |
|
|
intercalating agents do what?
|
flat planar molecules that mimic base pairs and can slip betw nitrogen bases
|
|
|
an intercalating agent like acridine orange
|
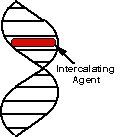
what caused this to happen
|
|
|
acridine orange, ICR-191, proflavin can cause ___________ in the DNA
|
single nucleotide pair insertions or deletions
|
|
|
if a mutag damages a DNA base it can ___________ DNA synthesis
|
block
|
|
|
E COli uses what system to bypass a damaged DNA base?
|
SOS system
|
|
|
t or f
SOS is used only as a last resort |
t
|
|
|
DinB , UmuC, and UmuD' are ?
|
error prone DNA polymerases
|
|
|
EP polymerases are also called?
|
sloppy copiers or error prone polymerases
|
|
|
the eukaryote system _____________ is similar to E Coli SOS system
|
translesion DNA synthesis
|
|
|
how do EP polymerases overcome the block in replica?
|
they add nucleotides to the strand opposite the damaged bases
|
|
|
t or f
error prone polymerases are always present in euk cells |
t
|
|
|
error prone polym in E Coli only appear when?
|
they are induced to by UV damage
|
|
|
SOS mechan
UV light induces the synth of what protein? |
RecA
|
|
|
REC A is a key player in?
|
mechan of DNA repair and recombination
|
|
|
e coli
dna damage DNA polymerase ________ stalls at site of dna damage |
III
|
|
|
e coli
dna ahead of DNA pol III is unwound and bound by ______, and then ___________- |
SSB
and then RecA |
|
|
Rec A and SSB join to form?
|
protein DNA filament
|
|
|
nist carcinogens like uv and aflatoxin B1 are ___________ mutagens
|
SOS dependent
|
|
|
name one uv light generated photoproduct?
|
cyclobutyl ring that unites adj pyrimidines
|
|
|
UV light makes what alterations in DNA?
|
photoproducts
|
|
|
what is most freq transition causes by UV light?
|
C ---> T
|
|
|
Aflatoxin B1 comes from?
|
a fungus assoc w peanuts
|
|
|
apurinic site is where?
|
in DNA, where the base and the sugar backbone have been separated..
happens with aflatoxin |
|
|
aflatoxin B1 causes what kind of mutation?
|
G -C --> T-A transversion
|
|
|
Luria and Delbruck tested?
|
e coli to with phage T1 to see if any would bec resistant
|
|
|
luria and delbruck
were testing to see if? |
the mutations were random or induced by the phage
|
|
|
who came up with the "fluctuation test"
|
luria and delbruck
|
|
|
luria and delbruck
their experiment suggested that? |
resistant e coli cells are select by environm agent (the phage) but not produced by it
|
|
|
replica plating reveals mutant colonies on a __________ thr their behavior on __________
|
master plate
selective replica plates |
|
|
replica plating can be used to screen for mutants that?
|
fail to grow under selective regime
|
|
|
spontaneous lesions are?
|
naturally occuring damage to dna
|
|
|
what are 2 most freq spont lesions?
|
depurination and deamination
|
|
|
which is the more common spont lesion , depurination or deamination?
|
depurination
|
|
|
deamination of cytosine yields?
|
uracil.
|
|
|
deamination of 5-methylcytosine generates?
|
thymine. making a C to T transition
|
|
|
DNA analysis of "hot spots" for mutations freq show what base is there?
|
5-methylcytosine residues
|
|
|
what is another type of spont lesion?
|
oxidatively damaged bases
|
|
|
name 3 active oxygen species?
|
O2-, H2O2, and OH radicals
|
|
|
errors in dna replicat can cause?
|
base substitut
base insert and deletion |
|
|
in e coli indel can occur at?
|
repeated seq in dna
|
|
|
e coli
longer repeats are hot spots for? |
deletions
|
|
|
common mech respons for genetic diseases is?
|
expansion of a 3 base pair repeat. called trinucleotide repeat disease.
|
|
|
what is an ex of a trinucleotide repeat disease?
|
fragile X syndrome
|
|
|
errors in dna replicat can cause?
|
base substitut
base insert and deletion |
|
|
in e coli indel can occur at?
|
repeated seq in dna
|
|
|
e coli
longer repeats are hot spots for? |
deletions
|
|
|
common mech respons for genetic diseases is?
|
expansion of a 3 base pair repeat. called trinucleotide repeat disease.
|
|
|
what is an ex of a trinucleotide repeat disease?
|
fragile X syndrome
|
|
|
fragile x syndrome results from?
|
changes in number of a (CCG)n repeat in a region of the FMR-1 gene
|
|
|
(CCG)n repeat in a region of the FMR-1 gene
parents and grandp have increased numb of the repeat so they have? |
premutations. cause they dont have the dis yet but they do have increased copy number
|
|
|
fragile X syndrome
(CCG)n repeat in a region of the FMR-1 gene if you have premutations what will happen? |
the repeats will increase a lot more in your offspring
|
|
|
fragile X syndrome
(CCG)n repeat in a region of the FMR-1 gene what is proposed mechanism? |
slipped mispairing in course of DNA synth
|
|
|
Huntington disease is assoc with?
|
expansion of trinucleotide repeats in a g. huntingtons dis has a repeated seq, often within prot coding regions
|
|
|
Huntington disease and Kennedy disease result from?
|
amplification of a 3 base pair repeat of CAG
|
|
|
fragile X syndrome
6-59 number of copies. phenotype? |
normal
|
|
|
fragile X syndrome
60-200 number of copies. phenotype ? |
largely normal. this is the premutation stage
|
|
|
fragile X syndrome
>200 number of copies. phenotype IS? |
AFFECTED
|
|
|
FMR-1 g, that are involved in fragile x syndrome, are freq ______ , which is assoc with silenced genes
|
hypermethylated
|
|
|
dna error free repair
what are 2 ways this happens? |
1. repair the damaged base
2. delete the damaged dna and use complem seq as template |
|
|
direct rev of damag dna
which dam can be revers? |
a photodimer caused by uv light
|
|
|
photolyase can repair?
|
a photodimer caused by uv light
|
|
|
light repair or photorepair uses what enzyme?
|
photolyase.
|
|
|
why is photolyase a photorepair enzyme?
|
bec you need cert wavelenghts of light for it to work and repair the damag dna
|
|
|
t or f
photolyase can not work in the dark |
t
|
|
|
name 2 dna repair enzymes
|
1. photolyase
2. alkyltransferase |
|
|
alkyltransferase is a ?
|
dna repair enzyme. they can remove alkyl gr from damaged dna
|
|
|
what are 3 types of repair with dam dna?
|
1. direct rev
2. base excision and replac 3. segm removal and replacement |
|
|
what are 2 types of homology depend repair systems?
|
1. excision repair
2. postreplication repair |
|
|
homolog dep repair syst
excision repair occurs? |
before replication
|
|
|
homolog dep repair systems
depend on _____________ of the DNA |
complementarity
|
|
|
excision is the ____________ of an entire base
|
removal and replacement
|
|
|
what enzyme carries out base excision repair?
|
DNA glycosylase
|
|
|
DNA glycosylase cleaves?
|
base-sugar bonds
|
|
|
DNA glycosylase generates ___________ sites
|
apurinic or apyrimidinic
|
|
|
dna glycosylase works with what enzymes?
|
ap endonuclease
deoxyribophosphodiesterase dna polymerase dna ligase |
|
|
what does ap endonuclease do?
|
it cuts the sugar phosphate backbone around the site lacking a base
|
|
|
base excision repair ends with _____________ sealing the repaired DNA
|
dna ligase
|
|
|
there are more ways to damage a base in dna than?
|
there are glycosylases to remove them. so instead you have to use nucleotide excision repair
|
|
|
nucleotide excision repair system detects?
|
distortions in the double helix
|
|
|
nucleotide excision repair
e coli 3 enzymes will? |
cut the damaged str at 2 sites flanking the lesion
|
|
|
nucleotide excision repair
e coli the uvr exinuclease cuts out? |
8 nucleotides from one side
and 4 from the other |
|
|
euk
yeasts nucleotide excision repair is done by? |
repairosome
|
|
|
euk
yeasts repairosome preferentially repairs ? |
the template, or transcribed DNA strand
|
|
|
euk
yeasts repairosome has subunits that are also subunits in the? |
basal rna transcription apparatus
|
|
|
name one post replication repair?
|
mismatch- repair system
|
|
|
mismatch repair system has to do what 3 things?
|
1. recog mismatched base pairs
2. determ which base is the wrong one 3. excise the incorr base and carry out repair synth |
|
|
replication errors produce errors on which strand?
|
the new strand
|
|
|
t or f
normally bacterial dna is methylated |
t
|
|
|
post replicat repair
right after replication, the new bact dna is has not yet been? |
methylated
|
|
|
post replic repair
e coli adenine methylase does what? |
it methylates the dna strands.
|
|
|
post replicat repair
e coli mismatch repair system can work bec it can dist the old strand from the new one by? |
the methylation pattern
|
|
|
mismatch repair in hum
it repairs freq errors in what? |
short repeat seq (microsatellites)
|
|
|
humans
short repeat seq are also called? |
microsatellites
|
|
|
hMutSα and HMutLα fix what kinds of mismatch?
|
mispaired regions and loops
|
|
|
prok
mismatch repair system corrects errors in replication that are not corrected by? |
proofreading function of the replicative dna polymerase.
|
|
|
prok
mismatch repair system it only fixes the? |
newly synthesized strand
|
|
|
repair of ds breaks
how does this occur? |
if both str of double helix break at sites that are close to each other
|
|
|
making ds breaks is a normal part of what in a human?
|
generating antibod diversity
|
|
|
give 2 examples of normal ds breaks?
|
1. generating antibod divers
2. meiotic recombination |
|
|
what 2 mech are used to repair ds breaks?
|
1. non homologous end joining
2. homologous recombination |
|
|
why is ds repair so hard in a non dividing cell?
|
bec you dont have anything else to compare it to, like a sister chromatid
|
|
|
ds break
if you dont put the ends back together what could happen? |
they could initiate chromosomal rearrangements
|
|
|
non homologous end joining is?
|
putting the ends back together of a ds break
|
|
|
ds break
what is the proc? |
1. KU70, KU80, DNA dep prot kin bind
2 ends are trimmed 3. ends are joined 3 |
|
|
what 3 proteins bind ds in a ds break?
|
KU70
KU80 large DNA dependeint Prot kinase |
|
|
homologous recombination is error free bec?
|
it uses the sister chromatid to repair ds breaks
|
|
|
homolog recombinat
first step? |
trimming of 5' ends
|
|
|
homolog recomb
sec step? |
broken dna is coated with proteins including RAD51 (a RecA homolog)
|
|
|
RAD51 is involved in?
|
homolog recombination
|
|
|
RAD51-DNA filament does what after its formed?
|
searches for the undamaged sequence in its sister chromatid
|
|
|
homol recombin
when RAD51-DNA finds the complementary reg on the sister chrom, what forms? |
joint molecule betw the the damaged sister chrom and the undamag sister chromatid
|
|
|
what proteins are involved in repair by homolog recombinat?
|
1. RAD51
2. DNA Polymerase 3. DNA ligase |
|
|
In meiosis you can use
a. nonhomologous endjoining b. homologous recombination |
b. homolog recombination
|
|
|
meiosis
crossing over is initiated by? |
a ds break
|
|
|
molec mech of crossing over involves what 2 mech?
|
1. ds break
2. format of heteroduplex DNA |
|
|
heteroduplex dna is made up of?
|
one DNA str from one parent and one from another
|
|
|
first evidence for heteroduplex dna came from?
|
strange ratios in fungi.
in their ascus. You should have ratio of A:a of 4:4 but you sometimes got 6:2 2:6 |
|
|
what were the aberrant ratios seen in the fungi ascus?
|
6:2, 2:6
5:3, 3:5 |
|
|
when the ascus had extra copies it was said to have undergone?
|
gene conversion
|
|
|
ds break model of crossing over
what is the holiday structure? |
the formation of what looks like 2 single stranded cross overs
|
|
|
fungus
ascus ds model of break crossing over holiday structure are resolved in what ways? |
1. vetical breakage
2. horizontal breakage |
|
|
fungus
ascus ds break model if you had no A/a repair you would have a? |
5:3 octad
|
|
|
fungus
ascus ds break model if you had A/a repair you would have a? |
6:2 octad
|

