![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
124 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
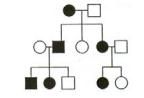
Name the type of inheritance
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
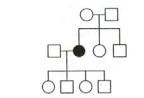
Type of Inheritance
|
Autosomal recessive
|
|
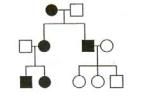
Type of Inheritance
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
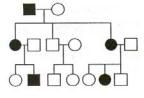
Type of Inheritance
|
X Linked Dominant
|
|
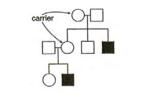
Type of Inheritance
|
X linked Recessive
|
|
|
Autosomal dominant CHARACTERISTICS
|
Both sexes equally affected
Vertical transmission Father-to-son transmission Affected individuals transmit trait to ~50% offspring |
|
|
Autosomal recessive CHARACTERISTICS
|
Both sexes equally affected Usually no prior family
history Consanguinity Mating between two carriers transmits trait to ~25% offspring |
|
|
X-linked dominant CHARACTERISTICS
|
Vertical transmission
NO father-to-son transmission Females twice as likely to be affected as males Affected males cannot transmit disease to sons, but transmit it to 100% daughters. |
|
|
X-linked recessive CHARACTERISTICS
|
Disease can skip generations by carrier females.
NO father-to-son transmission. Males are much more frequently affected than females. |
|
|
Mitochondrial CHARACTERISTICS
|
Both males and females can be affected.
Only females can transmit the disease. |
|
|
What two models for understanding Multifactorial inheritance?
|
Additive polygenic model for quantitative traits.
Threshold model for qualitative traits. |
|
|
Autosomal dominant diseases (5)
|
Huntington disease
Achondroplasia NF type 1 Marfan syndrome Familial hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
Autosomal recessive diseases 3
|
Hurler syndrome
Hereditary hemochromatosis Cystic fibrosis |
|
|
X-linked dominant diseases
|
Fragile X syndrome
|
|
|
x linked recessive diseases
|
Hemophilia A and B
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Duchenne muscular dystrophy Becker muscular dystrophy Red-green color blindness Severe combined immunodeficiency OTC deficiency |
|
|
Mitochondrial
diseases |
CPEO
LHON MELAS MERFF Kearns-Sayre syndrome Leigh syndrome Pearson syndrome |
|
|
Multifactorial diseases
|
Diabetes
Coronary artery disease Obesity Alcoholism Infantile autism Schizophrenia Cancer Cleft lip/palate Pyloric stenosis Club foot Spina bifida |
|
|
Mode of Inheritance Huntington Disease
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in
Scickle cell |
B-globin
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in tay-Sachs
|
HexA
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in B-thalassemia
|
B globin
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in cystic fibrosis
|
CFTR
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in
a-thalassemia |
a globin
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in
hurler syndrome |
a-L-iduronidase
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in hereditary hemochromatosis
|
HFE
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Neuofibromatosis Type 1?
|
NF1
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in CHarcot Marie Tooth disease/
|
PMP22
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Huntington Disease
|
HTT
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in achondroplasia
|
FGFR-3
fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 |
|
|
What is the gene defect in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
|
LDL Receptor
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Osteogenisis Imperfecta
|
Chrom 17, ColA1 or
Chrom 7 ColA2 |
|
|
What is the gene defect in Retinoblastoma
|
Chromosome 13 q14.1-2
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Myotonic dystrophy
|
DMPK gene, codes for
myotonic dystrophy protein kinase |
|
|
What is the gene defect in Male Pattern Baldness
|
DHT
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Hemophilia B
|
Factor 9
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Hemophilia A
|
Factor 8
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Red-Green Color Blindness
|
Opsin
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
|
Dystrophin
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Becker Muscular Dystrophy
|
Dystrophin
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Fragile X syndrome?
|
FMR1
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Prader-Willi Syndrome
|
Chromosome 15 q11-13 deletion from father
SNRPN |
|
|
What is the gene defect in Angelman Syndrome
|
Chromosome 15 q11-13 deletion from mother
UBE3A |
|
|
What is the MOI for Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Myoclonic epilepsy w/ragged red fiber disease (MERFF)
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Kern-Sayre
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Leigh Syndrome
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, stroke like episodes (MELAS)
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Pearson syndrome
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia?
|
Mitochondrial
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Tay-Sachs
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Sickle Cell disease?
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for B-Thalassemia
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Cystic Fibrosis
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for a-thalassemia
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Hurler Syndrome
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Male Pattern Baldness
|
Autosomal Dominant in Males
Autosomal Recessive in Females |
|
|
What is the MOI for Neurofibromatosis Type 1?
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Charcot-Marie Tooth
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Huntington Disease
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Achondroplasia
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Familial Hypercholesteroemia
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Osteogenisis Imperfecti
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Retinoblastoma
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Myotonic Dystrophy
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Hemophilia B
|
X Linked recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Anhydrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
|
X Linked Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Hemophilia A
|
X Linked recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Red-Green Color Blindness
|
X- Linked Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
|
X- Linked Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Becker Muscular Dystrophy
|
X- Linked Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Fragile X Syndrome
|
X- Linked Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Prader-Willi
|
Other
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Angleman Syndrome
|
Other
|
|
|
Name 3 Pleiotropic Diseases
|
Cystic Fibrosis
Marfan Syndrome von Gierke |
|
|
What diseases fall under the category of Point mutation?
|
hemophilia b
tay sachs NF1 Sickle Cell B-thalasemia |
|
|
What diseases fall under the category of missense
|
Sickle-cell anemia
|
|
|
What diseases fall under the category of nonsense
|
Neurofibromatosis
type 1 |
|
|
What diseases fall under the category of Splice site mutation
|
Tay-Sachs
|
|
|
What diseases fall under the category of Deletion
|
a thalassemia
Cystic Fibrosis |
|
|
What diseases fall under the category of Insertion
|
Tay-Sachs
Charcot Marie Tooth |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
New (de novo) mutation |
Achondroplasia
NF type 1 |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Germline mosaicism |
Osteogenesis imperfecti
Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Delayed age of onset |
Huntington disease
Hereditary hemochromatosis |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Reduced penetrance |
Retinoblastoma (90%)
Fragile X in Females |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Variable expression |
NF type 1
|
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Pleiotropy |
Cystic fibrosis
Diabetes Marfan syndrome von Gierke disease |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Heterogeneity |
Osteogenesis imperfecti
|
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Genomic imprinting |
Prader-Willi syndrome
Angelman syndrome |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Anticipation |
Myotonic dystrophy
Fragile X syndrome Huntington disease |
|
|
What diseases exhibit the following complication?
Consanguinity |
Rare autosomal recessive diseases
|
|
|
What is the gene defect in Marfan Syndrome?
|
FBN1
|
|
|
What is the MOI in Marfan Syndrome
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
What is the MOI of Severe combined immunodeficiency?
|
X-Linked Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI of OTC deficiency?
|
X-Linked Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for severe combined immunodeficiency?
|
X-Linked Recessive
|
|
|
What is the MOI for Lesch -Nyhan?
|
X-Linked Recessive
|
|
|
Mode of Inheritances for PKU?
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
What is the occurrence risk/recurrence risk like for germline mosiacism?
|
Both high. Mutation is in germ cells.
|
|
|
What is the occurrence risk/recurrence risk like for geonomic imprinting?
|
Both Low. Genomic imprinting is like a "new deletion" so it would be extremely rare for a second child to exhibit the disease.
|
|
|
What is the exception to the rule that X linked dominant diseases are more prevalent in females?
|
Fragile X
|
|
|
What three dieases show antcipation?
|
Huntington
Fragile-X Myotonic Dystrophy |
|
|
What does concordance measure?
|
The presence of the same PHENOTYPE in two twins.
|
|
|
What does low HGB indicate?
|
Anemia
|
|
|
What does a low or within range CR count indicate?
|
Anemia do to insufficient blood production.
|
|
|
What does a high CR count indicate?
|
Anemia due to destruction or loss of cells.
|
|
|
What does a low MCV indicate?
|
Microcytic cells due to impared HGB synthesis most likely due to iron insufficiency.
|
|
|
What does a HIGH MCV indicate?
|
Macrocytic cells due to limited DNA synthesis, most likely due to folate or Vitamin b12 deficiency
|
|
|
What are examples of anemia due to distruction or loss?
|
Premature RBC Destruction
Premature "Blase" Destruction Acute blood loss |
|
|
What would cause premature RBC destruction?
|
sickle cell anemia
G6PD Deficiency |
|
|
What would cause Premature blast destruction?
|
Thalassemias
(usually microcytic, hypochromic) |
|
|
When do you use the multiplication rule?
|
For "and" occurrences
|
|
|
When do you use the addition rule?
|
For "or" occurrences
|
|
|
AR diseases can be predicted using what probability equation?
|
chance of mother having one disease allele x chance of baby inheriting from mother x chance that father is carrying one allele for the disease x chance of inheriting defective gene from the father
|
|
|
formula for mcv
|
hct/rbc x10
|
|
|
formula for mch
|
hgb/rbc x10
|
|
|
rule of 3's
|
rbc x 3 = hgb
hgb x 3 = hct |
|
|
formulas for MCHC (2)
|
hgb/hct x 100
or MHC/MCV x 100 |
|
|
Solve for CR
|
pt HCT/mean "normal" HCT x or
|
|
|
Average RBC count
|
5 x 10^6 uL
|
|
|
Average HGB
|
15g/dL
|
|
|
Average HCT
|
45%
|
|
|
What is Hematocrit
|
The portion of blood volume that is RBC's
|
|
|
List the 3 Trisomies, their chromosomal name, common name and man characteristics
|
21-Downs Syndrome: Facial Features
18-Edwards; crossed fingers, clenched fists 13-Patau: (cleft) palate, polydactyly |

