![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Mitosis |
Cell division (4 stages) |
|
|
|
Meiosis |
Process in which cells reduce their number by half |
|
|
|
Gross chromosomal abnormalities |
Alteration in chromosome number or structure |
|
|
|
Trisomy 21 |
Down syndrome |
Slanted eyes, shorter stature, heart abnormalities, varied intelligence levels, fissures tongue, perio/gingival issues, hypodontia, less caries. |
|
|
Cyclic neutropenia |
Decrease in the number of circulating neutrophils. Autosomal dominant. Occur in intervals 22-27 days, and may last 2-3 days. Oral lesions present as sever ulcerative gingivitis, ulcers, and perio disease. Treated between cycles. |
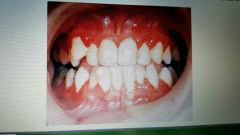
|
|
|
Gingival fibromatosis |
Gingival enlargement, smooth pu k tissue, firm, may have displaced teeth, may have delays in eruption. Treatment: gingivectomy |
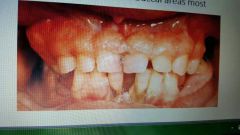
|
|
|
Cherubism |
Jaw increase rapidly until puberty but facial deformities remain. Autosomal dominant. Painless, biateral enlargement ifbthe mandible or maxillla. "Soap bubbles" in x-rays. |

|
|
|
Gardner syndrome |
Presence of osteomas in various bones. Teeth can exhibit hypercementosis and fail to erupt. Autosomal dominant |
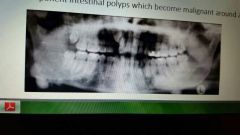
|
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
Bones fracutre easily, teeth resemble dentinogenesus imperfecta. Smaller teeth than usual. Autosomal dominant or recessive. |
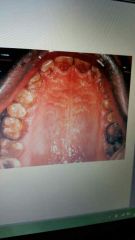
|
|
|
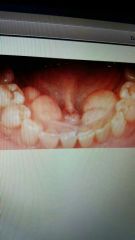
Torus mandibularis |
Excess bone on lingual mandible. Autosomal dominant. Could need surgically removed. |
|
|
|
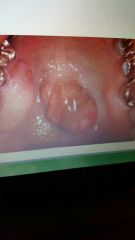
Torus palatinus |
Excess bone on hard palate. Autosomal dominant. May need removed. |
|
|
|
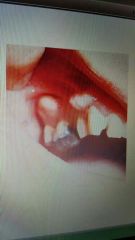
Maxillary exostosis |
Extra bone on buccal surface of the maxillary alveolar ridge. Autosomal dominant. |
|
|
|
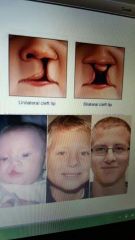
Cleft lip/palate |
Genetic pattern. Usually missing lateral incisors. Happens during fetus development. |
|
|
|
White sponge nevus |
Thick layer of keratin which produces a white velvety appearance. Bilateral buccal mucosa. Autosomal dominant. No treatment. |
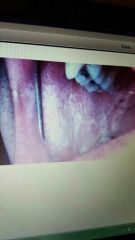
|
|
|
Hypoplastic (amelogenesis imperfecta) |
Type 1. Tootb enamel does not develop normal thickness. Can be sutosomal dominant or recessive. Ameloblasts fail to lay down enamel matrix properly. |
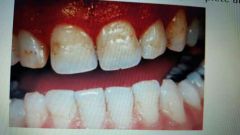
Pitted, smooth, rough, enamel ansence. |
|
|
Hypocalcified (amelogenesis imperfecta) |
Type 2. Yellow to orange enamel that is very soft and rapidly lost leaving exposed dentin. Can be autosomal dominant or recessive. |
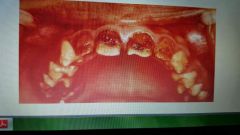
|
|
|
Hypomaturation (amelogensis imperfecta) |
Type 3. Snow capped. X likes recessive and sutosomal dominant. |
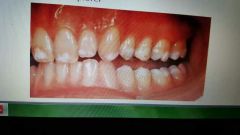
|
|
|
Hypoplastic-hypomaturation (amelogenesis imperfecta) |
Type 4. Thin yellow to brown pitted enamel. Related to taurodontism |
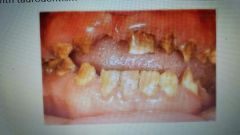
|
|
|
Dentinogenesus imperfecta |
Disturbance in dentin formation. Brown to brownish blue. Dentin very soft, enamel chips. Short, thin roots. No pulp chambers of root canals seen. |
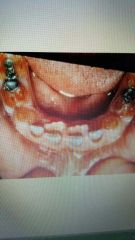
Type 1: associated with osteogenesis imperfecta Type 2: hereditary opalescent doninant Type 3: very rare (maryland) |
|
|
Pegged or absent maxilary laterals |
Small, pegged, or absent. Autosomal dominant |
|
|
|
Taurodontism |
Large pulo chambers. Can find with many syndromes. Dominant and recessive. |
|

