![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Neither 2 alleles are dominant |
Co-dominance, blood groups (A,B,AB)
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Nature and severity of phenotype vary from 1 individual to another. |
Incomplete Penetrance
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
1 gene has >1 effect on an individual's phenotype. |
Pleiotropy, PKU.
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Differences in phenotype depend on whether the mutation is of maternal or paternal origin. |
Imprinting, Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome.
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Severity of the illness gets worse or age of onset of disease is earlier in succeeding generations. |
Anticipation, Huntington's disease
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
If the pt inherits or develops mutation in a tumour suppressor gene, the completmentory allele must be deleted or mutated before the Ca develops. |
Loss of heterozygosity, Retinoblastoma
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Exerts a dominant effect. A heterozygote produces a non-functional altered protein that also prevents the normal gene product from functioning. |
Dominant negative effect, Mutation of Tx factor in its allosteric site (mutated form binds DNA preventing functioning protein from binding.
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Tendency for certain alleles at 2 linked loci to occur together more often than expected by chance. Measured in the population,not in the family & varies with populations. |
Linkage disequilibrium, -.
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Cells in the body differ in genetic make up due to postfertilisation loss of genetic material. |
Mosaicism, lyonization (random X inactivation in females).
Can be GERMLINE MOSAIC, which may produce disease that is not carried by the parent's somatic cells. |
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Mutations at different loci can produce the same phenotype. |
Locus heterogeneity, Marfan's, MEN 2B, homocystinuria.
Albinism. |
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Presence of both normal and mutated mtDNA, resulting in variable expression in mitochondrial inherited disease. |
Heteroplasmy
|
|
|
What is the genetic term? Give an Example?
Offspring receives 2 copies of a chromosome from 1 parent and no copies from the other parent. |
uniparental disomy.
|
|
|
What is the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium equation?
|
p^2 + 2pq +q^2 = 1 and p+q=1
in X-linked recessive disease - males = q and females = q^2 |
|
|
What disease? What genetic defect?
Mental retardation, hyperphagia, obesity, hypogonadism, hypotonia. |
Prader-willi syndrome.
Has normal inactivated maternal allele. Paternal allele is deleted in chromosome 15 or unipaternal disomy (both Maternal). |
|
|
What disease? What genetic defect?
Mental retardation, seizures, ataxia, inappropriate laughter ("the happy puppet") |
Angelman's Syndrome.
Has normal inactivated paternal allele. Maternal allele is deleted in chromosome 15 or unipaternal disomy (both Paternal). |
|
|
Which inheritance pattern?
Often due to defects in structural genes. Many generations, both male and female, affected. |
Autosomal dominant
|
|
|
Which inheritance pattern?
25% of offspring from 2 carrier parents are affected. Often clue to enzyme deficiencies. Usually seen in only 1 generation. |
Autosomal Recessive
Commonly more severe than AD diseases, pt often present in chilhood. |
|
|
Which Inheritance Pattern?
Sons of heterozygous mothers have a 50% chance of being affected. No male-to-male transmission. |
X-linked recessive.
Commonly more severe in Males, females must be homozygous to be affected. |
|
|
Which Pattern of inheritance?
Transmitted through both parents. Either male or female offspring of the affected mother may be affected, while all female offspring of the affected father are diseased. |
X-linked dominant.
|
|
|
Which pattern of inheritance?
Transmitted only through mother. All offspring of affected females may show signs of disease. Often clue to failures in oxidative phosporylation. |
Mitochondrial inheritance.
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Hypophosphatemic rickets?
What patttern of inheritance is seen? |
inherited disorder resulting in increased phosphate wasting at the proximal tubule. results in rickets like presentation.
|
|
|
Mitochondrial myopathies types?
What pattern of inheritance? |
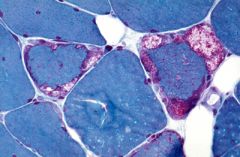
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (acute loss of central vision), myoclonic epilepsy, mitochondrial encephalopathy.
"ragged red fibers" on microscopy. Mitochondrial inheritance. |
|
|
Which disease & mode of inheritance?
Cell signaling defect of FGF-receptor 3. Pt presents with dwarfism; short limbs; BUT head and trunk are normal. Associated with advanced paternal age. |
Achondroplasia
|
|
|
Which disease & mode of inheritance? gene mutated?
Pt presents with flank pain, haematuria, HTN, progressive renal failure. Bilateral, massive enlargement of kidneys due to multiple cysts. |
Autosomal Dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).
Gene: PKD1 (90%), chromosome 16. Associated with berry aneurysm, polycystic liver disease, mitral valve prolapse. |
|
|
Which disease & mode of inheritance? Gene (& chromosome)?
Colon becomes covered with adematous polyps after puberty. progresses to Colon cancer unless resected. |
Familial adematous polyposis, AD.
Gene: APC gene (chromosome 5) |
|
|
Which disease & mode of inheritance?
Elevated LDL due to defective or absent LDL receptor. Heterozygotes (1:500) have cholestrol of approx 300mg/dl. homozygotes have 700mg/dl, early severe atherosclerotic disease and tendon xanthomas. Mi may develop before age 20. |
familial hypercholestrolemia, AD.
|
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern?
inherited disorder of the blood vessels. pt presents with telangiectasia, epistaxis, skin discolouration and Arteriovenous malformations. |
Hereditary Hemorrhagic telangiectasia (osler-weber-rendu syndrome
|
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern?
Spheroid erythrocytes due to spectrin or ankyrin defect; hemolytic anemia; increased MCHC. Splenectomy is curative. |
Hereditary Spherocytosis
|
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern? Chromosome?
Pt presents with depression, progressive dementia, choreiform movements, caudate atrophy, and Decreased levels of GABA and ACh in the brain. Symptoms manifest in affected individuals between the ages of 20 and 50. |
Huntington's disease, AD/
Chomosome 4, trinucleotide CAG repeats |
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern?
Fibrillin gene mutation causing a connective tissue disorder affecting skeleton, heart, and eyes. Findings: tall with long extremities, pectus excavatum, hyperextensive joints, and long, tapering fingers and toes (arachnodactyly); cystic medial necrosis of aorta resulting in aortic incompetence and dissecting aortic aneurysms; floppy mitral valve. Subluxation of lenses. |
Marfan's Syndrome
|
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern? What gene mutation is associated with the Type 2?
Characterized by familial tumors of endocrine glands, including those of the pancreas, parathyroid, pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal medulla. |
Multiple endocrine neoplasias (1, 2A, 2B)
2A and 2B associated with the ret gene. |
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern? Chromosome?
pt with cafe-au-lait spots, neural tumors, Lisch nodules (pigmented iris hamartomas). Also marked by skeletal disorders (e.g., scoliosis) and optic pathway gliomas. |
Neurofibromatosis type I (Von Recklinghausen's syndrome)
Chromosome 17 = no. letters in "von Recklinghausen" |
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern? Gene & Chromosome affected?
Bilateral acoustic schwannomas, juvenile cataracts. |
Neurofibromatosis 2.
NF2 gene on chromosome 22. |
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern?
Pt with facial lesions (adenoma sebaceum), hypopigmented "ash leaf spots" on skin, cortical and retinal hamartomas, seizures, mental retardation, renal cysts and renal angiomyolipomas, cardiac rhabdomyomas, increased incidence of astrocytomas. |
Tuberous sclerosis.
Incomplete penetrance, variable presentation. |
|
|
Which disease & inheritance pattern? Gene & Chromosomes affected?
Pt with hemangioblastomas of retina/cerebellum/medulla; about half of affected individuals develop multiple bilateral renal cell carcinomas and other tumors |
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease AD
VHL gene on chromosome 3. |
|
|
List the autosomal recessive diseases. (10)
|
1. Albinism
2. ARPKD 3. Cystic Fibrosis 4. glycogen storage diseases 5. Haemochromatosis 6. mucoppolysaccaridoses (except Hunter's) 7. phenylketonuria 8. sickle cell anaemia 9. Sphingolipidoses (except Fabry's) 10. thalassemias. |
|
|
List the X-linked recessive diseases (10).
|
Be Wise, Fool's GOLD Heeds Silly Hope.
Bruton's agammaglobinemia, Wiskott-aldrich syndrome Fabry's Disease G6PD Deficiency Ocular albinism Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Duchenne's MD Hunter's Syndrome Hemophilia A & B |
|
|
Which gene is affected in Cystic fibrosis?
|
CFTR gene often a deletion of Phe 508.
|
|
|
What would you expect in a patient with Duchenne's MD? How does it differ from Becker's?
|
Weakness begins in the pelvic girdle muscles progressing superiorly. Onset in those younger than 5y.o. Characteristic - Gower's sign reuqiring upper body assistance to stand.
Becker's is less severe and presents in adolescence or early adulthood. |
|
|
What is the pathology of Duchenne's MD?
|
X-linked frame shift resulting in deletion of the dystrophin gene. This results in accelerated muscle breakdown. Dystrophin helps anchor the muscle fibers, primarily in skeletal and cardiac muscle.
|
|
|
What Inheritance pattern and gene is affected in Fragile X Syndrome?
|
X-linked Trinucleotide repeat disorder (CGG) in the FMR1 gene.
|
|
|
Which Disease?
Macro orchidism, Long face with long jaw, large everted ears, autism, mitral valve prolapse. |
Fragile X syndrome.
2nd most common cause of mental retardation. |
|
|
Which Disease?
Trinucleotide repeat - CGG |
Fragile X syndrome
|
|
|
Which Disease?
Trinucleotide repeat - CAG |
Huntington's Disease
|
|
|
Which Disease?
Trinucleotide repeat - CTG |
Myotonic dystrophy
|
|
|
Which Disease?
Trinucleotide repeat - GAA |
Friedreich's Ataxia
|
|
|
What are the Findings in a pt with Down Syndrome?
What is the Genetic defect in Down Syndrome? |
mental retardation, flat facies, prominent, epicanthal folds, simian crease, Gap between 1st 2 toes, duodenal atresia, Congenital heart disease.
Trisomy 21. 95% due to meitotic nondisjunction |
|
|
What is associated with down's syndrome?
|
ALL, Alzheimer's disease.
|
|
|
What is the risk of having a Down syndrome baby at <20y.o.? At >45y.o.?
|
1:1500 ni a mother <20y.o
1:25 in a mother >45y.o |
|
|
What will an antenatal screen show in a mother with a Down syndrome Baby?
|
low a-fetoprotein, estriol.
High inhibin A, high B-HCG ultrasound shows increased nuchal translucency |
|
|
Which Disease & gene affected?
Severe mental retardation, rocker-bottom feet, micrognathia, low-set ears, clenched hands, prominent occiput, congenital Heart disease. |
Edwards syndrome, Chromosome 18 trisomy (1:8000)
|
|
|
What will antenatal test show in edward's syndrome
|
low aFP, B-hCG, estriol
normal inhibin A |
|
|
Which Disease & chromosome affected?
severe mental retardation, rocker bottom feet, micropthalmia, microencephaly, cleft lip/palate, holoprosencephaly, polydactyly, congenital heart disease. Death usually < 1 y.o. |
Patau's Syndrome, Trisomy 13 (1:15000)
|
|
|
Which Disease and chromosomal alteration?
Pt with microencephaly, moderate to severe mental retardation, high-pitched crying, epicanthal folds, cardiac abnormalities (VSD). |
Cri Du chat Syndrome, microdeletion of the short arm of chromosome 5.
|
|
|
Which disease & chromosomal alteration?
elfin facies, mental retardation, hypercalcemia, well-developed verbal skills, extreme friendliness w strangers, cardiovascular problems. |
Williams syndrome, microdeletion of the long arm of chromosome 7.
|
|
|
What are the 22q11 deletion syndromes?
|
Variable presentation - Cleft palate, Abnormal facies, Thymic aplasia, Cardiac defects, Hypocalcemia - 2ndry to Parathyroid aplasia.
Digeorge - thymic, parathyroid, cardiac defects. Velocardiofacial - palate, facial, cardiac defects. |

