![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mutations
Mutations in a DNA sequence can occur spontaneously where errors occur during DNA replication, or they can be induced.
Mutations can affect a single DNA building block (base pair) or a large segment of a chromosome that includes multiple genes.
|
Types of mutations
• Point Mutations • Insertion • Deletion • Translocation • Duplication • Mis-sense/Nonsense Mutations |
|
|
Point Mutations A point mutation is where a mutation occurs, and only affects one or very few nucleotides in a gene sequence and can have one of three effects.
There are two types of point mutations: 1. Base substitution - where one base is switched out with another. 2. Frame shift mutation - where one base is added or removed.
|
Example:
Original - THE TOY WAS OLD AND RED Mutated stand - THE BOY WAS OLD AND RED
|
|
|
Insertion Insertion is where one or more nucleotide base pairs are added into a DNA sequence. This usually occurs due to the DNA polymerase slipping.
An insertion mutation can be small where a single base pair is involved or large where a piece of chromosome is involved.
|
Example:
Original - THE TOY WAS OLD AND RED Mutated strand - THE GGG AGT OYW ASO LDA NDR |
|
|
Deletion Deletion is basically the loss of genetic material. It is where part of a DNA sequence becomes missing and occurs when part of a DNA molecule is not copied during DNA replication.
A deletion mutation can be small where a single base pair is missing or large where a piece of chromosome is missing. |
Example:
Original - THE TOY WAS OLD AND RED Mutated strand - THE OYW ASO LDA NDR
(the letter T has been deleted) |
|
|
Translocation Translocations are a type of chromosome mutations where the chromosome segments change positions. Translocations which don't involve a loss or gain or genetic material often show no harmful effects.
Intrachromosomal - within a chromosome Interchromosomal - between chromosomes
|
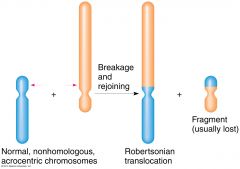
<---- Example
|
|
|
Duplication Duplication is where a portion of genetic material or a chromosome is replicated which results in multiple copies of that DNA strand.
Duplication is the opposite of deletion and is important in the evolution of the genomes of many organisms. |
Example:
Original - THE TOY WAS OLD AND RED Mutated strand -THE TOY WAS OLD AND THE TOY WAS OLD AND THE TOY WAS OLD AND RED |
|
|
Mis-sense mutations
A mis-sense mutation is where single base pairs change which causes there to be a substituted different amino acids instead of the protein.
Although, this substitution may have no effect there is a possibility that it may cause the protein to become unfunctionable.
|
Nonsense mutations
This is where a 'STOP' codon is produced too early on in the DNA sequence and therefore the DNA sequence ends in the incorrect space.
Due to this, there is a possibility that the protein cannot be created at all. |

