![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Conscious |
The subjective awareness of internal and external events |
|
|
|
Attention |
Internal process used to set priorities for mental functions. |
|
|
|
Dichotic listening |
Different auditory messages presented to each ear at the same time then the subject must repeat aloud one message while ignoring the other |
|
|
|
Automaticity |
Fast and effortless processing that requires little to no focused attention |
|
|
|
Biological rhythms |
Circadian rhythm |
body temp, blood pressure, hormone secretion, activates in a 24 hour cycle |
|
|
Biological Clock |
Brain structures that schedule resonance variations in bodily function by triggering them at the appropriate times. |
|
|
|
EEG |
Monitors the electrical activity of the brain |
|
|
|
Four categories of brain wave patterns |
Beta, Alpha, Theta, Delta |
|
|
|
Sleep stage 1 |
Theta waves, drifting thoughts, slow breathing |
|
|
|
Sleep Stage 2 |
Sleep spindles & K complexes. Asleep but may respond to some external signals. |
|
|
|
Sleep Stage 3 & 4 |
Deeper sleep state, delta activity & lack of responsiveness if woken. Moving from light to deep sleep. |
|
|
|
REM Sleep |
Rapid eye movement, 70 to 90 minutes in to sleep & electrical activity resembles that of awake. Vivid dreams; if awoken usually remember 80% |
|
|
|
Sleep deprivation |
Slurred speech, declines in mental ability, development of paranoia and or hallucination |
|
|
|
REM rebound |
Tendency to increase time spent in REM sleep after REM deprivation |
|
|
|
Dyssomnias |
Problems connected with the amount, timing & quality of sleep. |
|
|
|
Parasomnias |
Abnormal disturbances that occur during sleep. I.E. Nightmares, night terrors, sleepwalking |
|
|
|
Epiphenomenon |
Non crucial effect |
|
|
|
Insomnia |
Difficulty starting or maintaining sleep. Must be chronic (Last at least a month). |
|
|
|
Hypersomnia |
Chronic condition marked by excessive sleepiness |
|
|
|
Narcolepsy |
Sudden extreme sleepiness |
|
|
|
Psychoactive Drugs |
Drugs that affect behavior and mental process through alterations of conscious awareness. |
|
|
|
Drug actions |
Some drugs duplicate the actions of neurotransmitters. Some depress or block the action of neurotransmitters. |
|
|
|
Categories of psychoactive drugs |
Depressants, stimulants, opiates, hallucinogens |
|
|
|
Drug Effects |
Tolerance, Drug Dependency & Withdraw. |
|
|
|
Depressants |
Slows or depresses the ongoing activity of the central nervous system. Produce feelings of relaxation. I.E. alcohol, barbiturates, tranquilizers. |
|
|
|
Stimulants |
Increase central nervous system activity, increase alertness. Dilated pupils, extreme anxiety & convulsions. I.E. Caffeine, Nicotine, Cocaine, Methamphetamine. |
|
|
|
Opiates |
Depresses nervous system, reduces anxiety and elevates mood. Linked to endorphins. Strong withdraw. I.E. Opium, heroin, morphine. |
|
|
|
Hallucinogens |
Disrupt normal mental / emotional functioning, distort perception in altering reality. Perception is fractured & the world becomes awash in colors, sounds & tactile sinsations. I.E. LSD, marijuana, DMT, psilocybin mushrooms, 2CI & many more. |
|
|
|
Hypnosis |
Social interaction that produces a heightened state of suggestibility in willing participants. |
|
|
|
Fun theory |
People are more likely to do something if they think the activity is fun |
|
|
|
Motivation |
The force that moves people to behave think and feel the way they do |
|
|
|
Yerkes-Dodson Law |
Level of arousal shares a common curve in relation to task performance |
|
|
|
2 motivation types |
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation |
|
|
|
2 things goals should be |
Specific, difficult yet reachable |
|
|
|
Anorexia nervosa |
Relentless pursuit of thinness through starvation can literally starve themselves to death |
|
|
|
Bulimia nervosa |
Follows a binge and purge eating pattern |
|
|
|
Masters and Johnson set out to answer the question |
What physical reactions develop as people respond to sexual stimulation why do people behave as they do to the stimulation if treatment for sexual inadequacy was possible possibilities must be answered |
|
|
|
The sexual response cycle |
Stage 1 excitement stage 2 Plateau stage 3 orgasm stage 4 resolution |
|
|
|
What is self regulation |
Delayed gratification. Self-regulatory failure equals prominent concern! Can lead to poor emotional control, alcohol abuse, smoking, over eating, hostility, debt, behavioral problems |
|
|
|
TOTE |
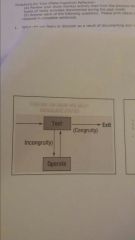
Test operate test exit with a feedback loop associated with the TO function |
|
|
|
What is learning |
A relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs through experience |
|
|
|
Behaviorism |
Theory of learning that focuses solely on observable acts |
|
|
|
Types of learning |
Associative learning and observational learning |
|
|
|
Ivan Pavlov |
Associated with classical conditioning |
|
|
|
Who is little Albert |
Watson and Rayner. Conditioned an orphaned toddler to loud noises to oppose white rats inadvertently causing opposition all furry animals |
|
|
|
BF Skinner |
Operant conditioning |
|
|
|
Operant conditioning instrumental conditioning |
Learn that our own actions not the conditioned stimulus led to outcomes |
|
|
|
Edward L Thorndike |
Correlated with BF Skinner, used cats |
|
|
|
Albert Bandura |
Social learning theory |
|
|
|
Social learning theory |
Associated with Thorndike |
|
|
|
Pandora's four-step model |
Attend, remember, enact, expect |
|
|
|
Martin EP Seligman |
Associated with learned helplessness used dogs |
|

