![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sexual dysfunction in men refers to
|
persistent inability to achieve normal sexual intercourse
|
|
|
Sexual dysfunction in women refers to
|
persistent lack of sexual satisfaction
|
|
|
prevalence of sexual concerns and problems
|
10-70%
|
|
|
% of sexual difficulties with an organic cause?
|
25-30%
(remainder are emotional or psychogenic in origin) |
|
|
What is the cause of the majority of sexual difficulties?
|
emotional or psychogenic
|
|
|
Sexual desire problems due to
|
low libido
|
|
|
Sexual arousal problems due to
|
erectile impotence
failure of arousal in women |
|
|
Sexual orientation/activity problems due to
|
homosexuality
fetishism |
|
|
Orgasm problems due to
|
premature ejaculation
retarded ejaculation orgasmic dysfunction in women |
|
|
Problems with sexual dysfunction in males are due to
|
low libido
erectile difficulties premature ejaculation failure to ejaculate, or retarded ejaculation |
|
|
Problems with sexual dysfunction in females are due to
|
low libido
failure of arousal vaginismus orgasmic difficulties dyspareunia |
|
|
What are some opportunities for the GP to provide sexual education?
|
antenatal and postnatal care
contraceptive requests parents concerned about their children's sex play serious illness—medical and surgical adolescent problems menopause problems |
|
|
which medical problems can present with underlying sexual issues
|
chronic backache, pelvic pain, vaginal discharge, tiredness, insomnia and tension headache
|
|
|
Medical conditions affecting sexual performance
|
Cardiovascular:
previous myocardial infarction angina pectoris peripheral vascular disease hypertension and its treatment Respiratory: asthma COPD Endocrine: diabetes mellitus hypothyroidism hyperthyroidism Cushing syndrome Neurological: multiple sclerosis neuropathy spinal cord lesions Parkinson disease Musculoskeletal: arthritis Depression Kidney: kidney failure Urological problems: prostatectomy phimosis Peyronie disorder priapism Hepatobiliary: cirrhosis Surgical: vaginal repair hysterectomy others Trauma: motor vehicle accidents Cancer Klinefelter syndrome |
|
|
Drugs affecting sexual arousal and function
|
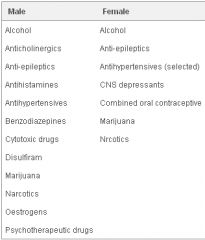
|
|
|
which is more common, chlamydia or gonorrhoea?
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
The symptoms of chlamydia usually appear
|
2 weeks after intercourse, although the incubation period can be as long as 3 weeks and as short as 5 to 10 days
|
|
|
Symptoms of chlamydia in men
|
a burning sensation when passing urine
a discharge (clear, white or yellow) from the penis. The first noticeable symptom is a slight tingling or burning at the tip of the penis, usually first thing in the morning. The pain sometimes becomes quite severe. The discharge soon follows. It is usually clear at first, but if untreated can become heavier and yellowish. Sometimes there is no discharge, just pain. Most often the symptoms are trivial. 40% have no symptoms |
|
|
Symptoms of chlamydia in women
|
usually causes no symptoms at all (this applies to about 70%) but may cause vaginal discharge. Some may notice burning on urination.
|
|
|
Complication of untreated chlamydia in men
|
The infection can spread to the prostate gland and testicles.
|
|
|
Complication of untreated chlamydia in women
|
If untreated, as is often the case, it can infect the Fallopian tubes.
This is the most common form of PID which can result in infertility ('silent' epidemic) |
|
|
Chlamydia diagnostic Ix in men
|
swab the urethra
OR PCR on first void urine |
|
|
Chlamydia diagnostic Ix in women
|
swab the urethra & cervix
OR PCR on first void urine |
|
|
how is chlamydia transmitted?
|
vaginal/oral/anal sex
|
|
|
chlamydia treatment
|
1
azithromycin 1 g po stat 2 doxycycline 100 mg po BD for 7 days |
|
|
Chlamydia prevention?
|
condoms
|
|
|
Gonorrhoea causative organism
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
body areas affected by gonorrhoea
|
urethra (especially in men), other genital areas, anus, throat
|
|
|
Gonorrhoea symptoms usually appear
|
2-10 days after vaginal, anal or oral sex, but the incubation period can be as long as 3 weeks
|
|
|
Gonorrhoea symptoms in men
|
The main symptoms (due to urethritis) are:
a burning sensation on passing urine a pus-like (white or yellow) discharge or leak. The first noticeable symptom is a slight discomfort on passing urine, which can later become very painful 'like passing razor blades' if it is not treated. A discharge of creamy pus from the tip of the penis follows. Sometimes there is no discharge, just pain, and sometimes there are no symptoms at all. |
|
|
Gonorrhoea symptoms in women
|
often causes no symptoms but can produce vaginal discharge or pain on passing urine
|
|
|
Symptoms of PID
|
pain and tenderness deep in the pelvis
lower abdominal pain and tenderness fever, an unwell feeling and painful periods dyspareunia |
|
|
Anal symptoms of gonorrhoea
|
may be a discharge (a feeling of dampness) around the anus
|
|
|
How is gonorrhoea spread?
|
vaginal, anal, oral sex
|
|
|
Complications of gonorrhoea
|
septic arthritis
men - infection of testicles, urethral stricture women - PID |
|
|
How is gonorrhoea prevented?
|
condoms
annual screening if high risk |
|
|
Gonorrhoea treatment
|
For uncomplicated urethral, cervical, pharyngeal and
anorectal gonorrhoea: • Ceftriaxone 500 mg IM in 2 ml of 1% lignocaine AND • Azithromycin 1g stat (due to penicillin, fluoroquinolone & doxycycline resistance) |
|
|
types of PID
|
endometritis, chorioamnionitis, salpingitis, tubo-ovarian abscess, pelvic cellulitis ± pelvic peritonitis
|
|
|
PID is usually polymicrobial and due to
|
sexually acquired pathogens ± endogenous vaginal flora particularly following mechanical disruption of the normal cervical barrier (eg. pregnancy termination, delivery, surgery, insertion of an intrauterine contraceptive device)
|
|
|
Investigations for PID ?
|
endocervical swab for Gram stain & culture ± susceptibility testing
Those likely to have a sexually transmitted infection should also have a first voided urine collected for nucleic acid test (NAT) for N. gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis and, if available, Mycoplasma genitalium. |
|
|
empirical treatment of PID?
|
antibiotics with activity against the major STI's & anaerobic bacteria
|
|
|
causative organism in Syphilis
|
Treponema pallidum
|
|
|
Diagnosis of active syphilis is made on the basis of
|
+ve nontreponemal rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test
AND +ve Treponema pallidum-specific antibody test |
|
|
What is "early syphilis" ?
|
Early syphilis (< 2 years based on serology):
primary or chancre (an anogenital or, less commonly, extragenital painless ulcer with indurated edges) secondary (an acute systemic illness with rash, anogenital condylomata lata [clusters of soft, moist lumps in skin folds], mucosal lesions, hepatitis, meningitis etc.) latent (asymptomatic). |
|
|
What is the antibiotic category of choice in syphilis?
|
penicillin
|
|
|
Treatment of early syphilis?
|
Benzathine penicillin G 1.8g IM single dose OR
• Procaine penicillin G 1.0g IM daily for 10 days OR • Doxycycline 100mg twice daily for 14 days (if allergic to penicillin and not pregnant) |
|
|
What is "late latent syphilis" ?
|
latent syphilis of >2 years or of indeterminate duration, in the absence of tertiary syphilis
|
|
|
Treatment of Late latent syphilis ?
|
Benzathine penicillin G 1.8 g IM, 3 doses given one
week apart OR • Procaine penicillin G 1.0g IM daily for 15 days OR • Doxycycline 100mg twice daily for 28 days (if allergic to penicillin and not pregnant) |
|
|
What is "tertiary syphilis" ?
|
long delayed cardiovascular or neuropsychiatric symptoms
|
|
|
Serological screening for syphilis in pregnancy?
|
Serological screening for syphilis should be performed routinely in ALL pregnant women at the 1st antenatal visit
Screening should be repeated at 28 weeks gestation in women at high risk |
|
|
Essential Questions to Ask for STI hx?
|
discharge
itching / stinging on urination sores, blisters, rashes |

