![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hernia |
Protusion of viscus/part of viscus through a defect in the wall of the cavity which it is normally contained |
|
|
Hernia terminology |
Irreducible (cant be pushed back) Obstructed (bowel obstruction) Strangulated (ischaemic emergency) Incarceration (contents of hernia stuck by adhesions) |
|
|
Groin hernia aetiology |
Inguinal : 96% cases, M>F 9:1, Femoral : 4% cases, F>M 4:1, old + weight-loss, high risk strangulation |
|
|
Types of inguinal hernia |
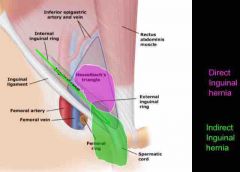
Indirect : thru internal inguinal ring to external inguinal ring Direct : forward thru posterior wall of inguinal canal to defect in abdominal wall (Hesselbach’s triangle) |
|
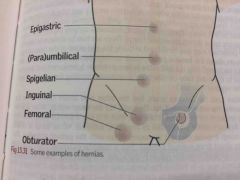
Other hernias |
Richter’s (bowel wall only, not whole lumen) Spegellian (thru linea semilunaris lateral rectus sheath) Epigastric (thru linea alba above umbilicus) Paraumbilical (omentum/bowel thru rectus sheath around umbilicus) |
|
|
Hernia Risk Factors |
Surgery, chronic cough, prostatism, constipation, heavy lifting/labour, weightloss, connective tissue disorders |
|
|
Indications for (hernia) surgery |
Symptomatic (pain, obstruction) Risk of incarceration Interfering with QOL Compromise testicular blood supply |
|
|
Surgical options (hernia) |
Mesh repair (Lichtenstein) Primary repair (Suture - Totally extra peritoneal TEP) Laparoscopic (Open - Transabdominal pre peritoneal TAPP) |
|
|
Bowel obstruction cardinal features |
Vomiting (nausea, anorexia), colic (early sign), constipation (absolute/partial), abdominal distension (+tinkling bowel sounds) |
|
|
Small (SBO) vs Large Bowel Obstruction (LBO) Signs |
Small: vomiting early, less distension, pain higher abdomen Large: constant pain, more distension, less vomiting |
|
|
Ileus vs Mechanical Obstruction Signs |
Ileus: Less pain, bowel sounds absent Mechanical: More pain, bowel sounds present |
|
|
Simple obstructed bowel |
One obstructing point & no vascular compromise |
|
|
Closed-loop obstructed bowel |
Obstruction at 2 points (eg sigmoid volvulus) forming a loop of grossly distended bowel at risk of perforation |
|
|
Strangulated obstructed bowel |
Blood supply is compromised and pt is critical (mesenteric ischaemia) despite seeming otherwise. Signs: Sharper, more constant & localized pain, fever, high WCC. Cardinal sign: Peritonism |
|
|
SBO causes |
Hernias, adhesions (from previous abdominal surgery/ secondary to infection, radiation, inflammatory disease eg Crohn's), |
|
|
LBO causes |
Colon ca, constipation, diverticular stricture, sigmoid volvulus, caecal volvulus |
|
|
Rare SBO/LBO causes |
Crohn's stricture, TB, foreign body More common in SBO: gallstone ileus, intussusception |
|
|
Bowel obstruction Mx |
Drip & suck (NGT+IV fluids), analgesia If strangulation: Emergency surgery (open, endoscopic decompression if closed loop, stenting if palliative) |
|
|
Breast cancer RF |
Family hx, age (>35yrs), nulliparity, early menarche, late menopause, HRT, obesity, BRCA genes, not breastfeeding, past breast ca |
|
|
Breast ca Main types |
Non-invasive ductal carcinoma in-situ (DCIS): premalignant, non-invasive lobular CIS: rare, invasive ductal carcinoma 70%, invasive lobular carcinoma 10-15%, medullary ca ~5% young, colloid/mucoid ~2% old Others: Papillary, tubular, adenoid-cystic, Paget's disease |
|
|
Breast ca genetics |
60-70% oestrogen receptor +ve (better prognosis), ~30% over-express HER2 growth factor receptor gene (aggressive + poorer prognosis) |
|
|
Paget's disease |
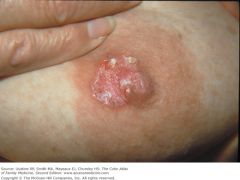
An intra-epidermal spread of intraduct cancer which can look like eczema |
|
|
Breast ca Triple Assessment Ix |
1. Clinical exam 2. Radiology (US <35yrs, mammography >35yrs) 3. Histology/cytology (FNA/core biopsy: US-guided core biopsy for new lumps) |
|
|
Breast ca Mx |
Surgery (WLE/mastectomy), radiotherapy, chemotherapy (epirubicin + CMF), ER blocker agents (tamoxifen), ovarian ablation/GnRH analogues eg goserelin (young ER+ve), |
|
|
Sentinel node biopsy |
Procedure to assess metastases, decrease needless axillary clearances in lymph node of -ve pt. 1. Inject dye to tumour/periareolar area 2. Probe to identify sentinel node 3. Biopsy + further clearance if +ve |
|
|
Intussusception |
In-folding of the walls of the colon leading to a telescoping effect (most common at ileocolic junction) |
|
|
Volvulus |
When part of a colon twists on its mesentery, resulting in acute, subacute, or chronic colonic obstruction. Most common sigmoid & caecal (because mobile) |
|
|
Breast Ca staging & Mx options |
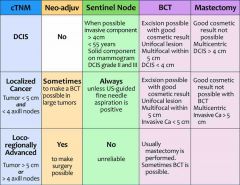
Back (Definition) |

