![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Protons |
*Postive (+e) *In nucleus of atom *# of protons=atomic number (Z) |
|
|
Neutrons |
*Neutral *In nucleus of atom *Mass only slightly larger than a proton's |
|
|
Electron |
*Negative (-e) *Move through the space surrounding nucleus *Associated with varying levels of energy *Much smaller mass than proton's and neutron's |
|
|
Valence electrons |
*Electrons furthest from the nucleus *Have strongest interactions with surrounding environment and weakest with nucleus *Involved in bonds with other atoms *Determine the reactivity of the atom |
|
|
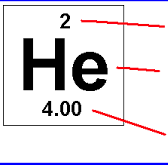
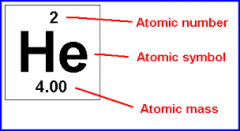
Atomic number (Z) |
equals the number of protons found in an atom (number above the atom letter in the periodic table and the number in the lower left corner for written atom letters) |
|
|
Mass number (A) |
sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom (number in upper left corner of written atom) |
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Isotope |
*Atoms that share an atomic number but have different mass numbers *Same number of protons (so same atom), but different number of neutrons *Name isotopes with element name followed by mass number (ex. carbon-12, iodine-131) |
|
|
Atomic mass |
nearly equal to the mass number, the sum of protons and neutrons |
|
|
protium |
*Isotope of hydrogen *One proton |
|
|
deuterium |
*Isotope of hydrogen *One proton and one neutron |
|
|
tritium |
*Isotope of hydrogen *One proton and two neutrons |
|
|
Atomic weight |
*Weighted average of an atom's different isotopes *Reported on periodic table under element *No atoms have this exact mass (it's an average) |
|
|
Avogadro's number |
NA=6.022x10^23 particles |
|
|
Planck's relation (for quantized energy) |
E=hf |
|
|
Planck's constant |
h=6.626x10^-34 Js |
|
|
Equation for the energy of the electron orbiting a hydrogen nucleus |
E= -RH/n^2 |
|
|
Rydberg unit of energy (RH) |
2.18x10^-18 J/electron |
|
|
Does the energy of an electron increase or decrease the further out from the nucleus that it's located? |
Increases |
|
|
Does the energy of an electron become more or less negative the further out from the nucleus that it's located? |
Becomes less negative (Energy increases) |
|
|
What color do we see for compounds? |
We see the color of the light that is NOT absorbed by the compound |
|
|
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle |
It's impossible to determine, with perfect accuracy, the momentum and the position of an electron |
|
|
Pauli exclusion principle |
No two electrons in a given atom can possess the same set of four quantum numbers |
|
|
Maximum number of electrons within a shell |
2n^2 |
|
|
Maximum number of electrons within a subshell |
4l+2 |
|
|
principal quantum number (n) |
Shells |
|
|
Angular momentum quantum number (l) |
the shape of subshells (n-1) (0=s, 1=p, 2=d, 3=f) |
|
|
Magnetic quantum number (ml) |
the orbital within a subshell where the electron is most likely to be found (between -l and +l, including 0) |
|
|
Electron configuration for Chromium (Z=24) and other elements in its group |
[Ar]4s^1 3d^5...... (would have normally been [Ar]4s^2 3d^4 but want 3d subshell to be half-filled for extra stability) |
|
|
Electron configuration for Copper (Z=29) and other elements in its group |
[Ar]4s^1 3d^10...... (would have normally been [Ar]4s^2 3d^9 but want a full d subshell for extra stability) |
|
|
paramagnetic |
*Materials composed of atoms with unpaired electrons *A magnetic field will cause parallel spins in unpaired electrons and therefore cause an attraction |
|
|
diamagnetic |
materials composed of atoms with only paired electrons (will be slightly repelled by a magnetic field) |
|
|
Balmer series |
transitions from upper levels (n>2) to n=2 |
|
|
Lyman series |
transitions from upper levels (n>1) to n=1 |
|
|
Hund's rule |
Within a given subshell, orbitals are filled such that there are a maximum number of half-filled orbitals with parallel spins |

