![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
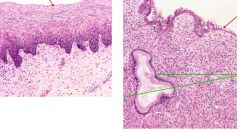
These are slides of normal cervix. Which one is Endocervix? Ectocervix?
How do you know? |
Left - Ectocervix (stratified squamous epithelium)
Right - Endocervix (columnar epithelium with endocervical glands) |
|
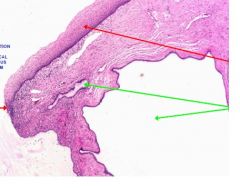
This is a slide of endocervix. What is represented by the LONG RED ARROW?
Describe what happened. |
Squamous metaplasia: from columnar to stratified squamous epithelium.
Transformation of cell type due to an adaptive response to chronic, persistent tissue insult. May undergo further transformation to neoplasia via dysplasia |
|
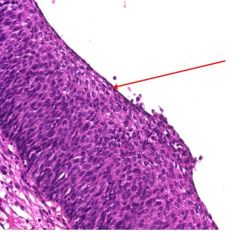
This is a slide of endocervix that underwent dysplasia.
Do you see carcinoma-in-situ? How do you know? |
Yes
Dysplasia in full thickness of epithelium. |
|
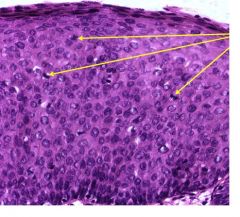
This is a carcinoma-in-situ dysplasia of endocervix.
What do the arrows indicate? what is the significance of these arrows? This can further progress into what specific malignancy? What pathogen promotes this growth? What are 2 virulent proteins of this pathogen. |
The arrows indicate mitoses signifying anaplasia.
This can further progress into cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Human Papilloma Virus (types 16 and 18) can promote this growth. E6 and E7 are virulent proteins of HPV that inhibit apoptosis. |
|
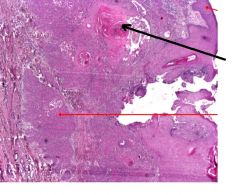
This is a slide of skin.
What type of malignancy is this? What does the black arrow indicate? What does the upper red arrow indicate? What does the lower red arrow indicate? |
Squamous cell carcinoma
Black arrow - Keratin pearl; a feature of squamous cell carcinoma Upper red arrow - normal squamous epithelium Lower red arrow - invading carcinoma |
|
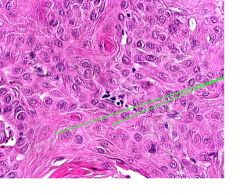
This is a slide of squamous cell carcinoma.
What do the GREEN ARROWS indicates? |
Intercellular bridges
|
|
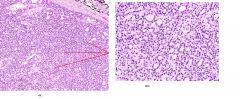
These are slides of thyroid.
Is this tumor benign or malignant? How do you know? What is the name of this growth? |
Benign. No histological features of anaplasia
Thyroid follicular adenoma |
|
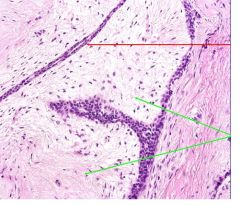
This is a slide of breast tissue.
Name this neoplasia. What does the red arrow indicate? Green arrow? |
Breast fibroadenoma.
Red arrow - glandular element; compressed duct by the neoplasm Green arrow - intralobular stroma; neoplastic element of fibroadenoma |
|
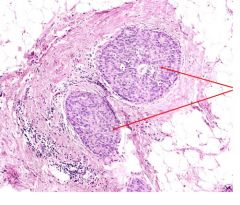
This is a slide of breast tissue.
What is the name of the neoplasia? Malignant or benign? If malignant, invading or non-invading. |
Ductal carcinoma in situ
Malignant but non-invading. |
|
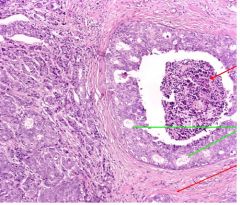
This is a section of breast tissue.
Name this neoplasia. Invading or non-invading? |
Infiltrating duct carcinoma (invading)
|
|
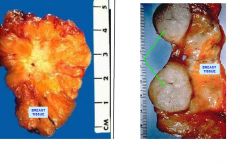
These are biopsies of breast neoplasms.
which one is malignant? name each. |
Left - infiltrating duct carcinoma (malignant)
Right - fibroadenoma |
|
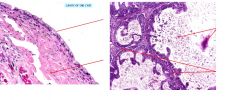
These are slides of neoplasms in the ovary.
Name them. |
Left - Mucinous cystadenoma
Right - Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma |
|
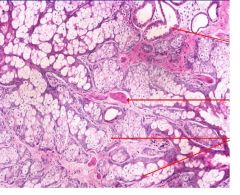
This is a neoplasm in the ovary.
Name it. What do these arrows represent? |
Cystic teratoma
Upper arrow - sweat gland Middle arrow - smooth muscle bottom 2 arrows - sebaceous glands |
|
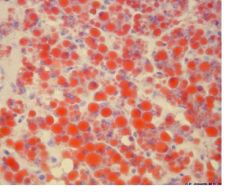
What type of stain is this?
What does it stain? What type of neosplams would this be? |
Oil Red O stain
Stains for fat Lipoma |
|
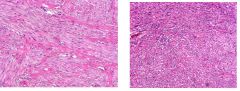
These are sections of neoplasms in the uterus.
Name them. |
Left - Leiomyoma
Right - Leiomyosarcoma |
|
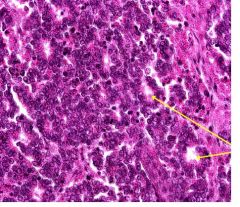
This is a slide of metastatic neuroblastoma in the kidney.
What is indicated by the YELLOW ARROWS? Which serum markers do you expect to find in the serum? |
Yellow arrows indicate true rosettes.
Neuron-specific enolases (NSE) |
|
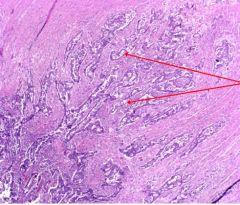
This is a section of the muscular wall of the colon.
What type of cells are indicated by red arrows? What is the significance of these cells? |
Red arrows - glandular epithelium or adenocarcinoma
They indicate metastasis because you don't expect to find epithelium in this layer |

