![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which are more common causes of environmental diseases?
a. major disasters b. chronic exposure to low levels of contaminants c. occupational injuries and illnesses |
b and c
|
|
|
How can initially non-toxic xenobiotics become toxic?
|
metabolism in the body --> becomes toxic
|
|
|
Where are most xenobiotics detoxified? what enzyme?
|
in the Liver by cytochrome P450 enzyme system
|
|
|
What is the most common toxic xenobiotic?
|
Drugs
|
|
|
How does ozone affect human body acutely? chronically?
|
Acute - oxidizes lipids to H2O2 and aldehyldes --> irritative and proinflammatory
chronic - pulmonary dysfunction |
|
|
A patient is exposed to smog particulates and shows following symptoms: inflammation, arrhtymia, and increase in BP.
are these fine or ultrafine particulates? |
ultrafine particulates.
Both cause inflammation via cytokine release from alveolar macrophages Only ultrafine particulates enter blood stream --> thicken blood and arrhythmia. |
|
|
List 3 most common indoor pollutants.
|
1. carbon monoxide
2. Radon 3. Nitrogen dioxide |
|
|
what is the mechanism behind CO poisoning?
Chronic symptoms of CO poisoning? Acute symptoms of CO poisoning? How is CO poisoning similar to Cyanide poisoning? |
mechanism - binds to hemoglobin --> carboxyhemoglobin --> hypoxia
Chronic (low levels, persistent exposure) - CNS ischemia Acute - high levels of carboxyhemoglobin --> cherry red hue to skin both cyanide and CO poisoning result in cherry red hue to skin |
|
|
What is the leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers?
|
Radon
|
|
|
What is radon?
Where can you find this in residential areas? |
radioactive gas, decay product of uranium
widely distributed in soil and concentrates in basements |
|
|
List 6 common heavy metals that can cause toxicity.
List common sources of each metal. List main diseases from each metal |
Mercury - contaminated fish, dental amalgrams; renal tubular necrosis, fetal toxicity (CNS)
Arsenic - soil, water, wood preservatives, herbicides; GI, CV, CNS disturbances Cadmium - plants (food); renal tubular damage, obstructive lung disease, lung cancer Cobalt - hard metal from grinding, polishing, cutting; asthma and fibrosing lung disease Chromium/Nickel - soil; lung cancer Lead - occupational (adults), paints and soil (children); CNS, PNS toxicity, anemia, renal fialure, and deposits ephyses of children's bones |
|
|
List 3 major manifestations of lead poisoning.
|
1. CNS, PNS toxicity
2. anemia 3. renal tubular damage b/c excreted by kidney |
|
|
High levels of petroleum products (gasoline and Kerosene) can cause?
|
CNS depression
|
|
|
High levels of aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene) can cause?
|
Leukemia
|
|
|
Exposure to vinyl chloride can cause?
|
hepatic angiosarcoma
|
|
|
List 3 toxic components in the insecticides.
|
1. organochlorines
2. organophosphates 3. carbamates |
|
|
What are Dioxins?
Dioxins can cause? |
Herbicides
Teratogenesis, immunosuppression, carcinogenesis |
|
|
what is paraquat?
Causes? |
Herbicides
Can cause acute lung injury (pulmonary fibrosis) |
|
|
List 3 non-CV, non-neoplastic diseases caused by tobacco.
|
COPD
insulin resistance osteoporosis |
|
|
What is third-hand smoke?
|
Ingestion of residual nicotine (esp. on indoor surfaces) and reaction with nitrogen dioxide --> forming Tobacco-specific nitrosamines ( TSNA)
|
|
|
Smokeless tobacco is associated with what cancers.
It is syngergistic with? |
Any upper aerodigestive cancer.
Especially oral cancer. Alcohol |
|
|
Name 4 enzymes that are involved in metabolizing ethanol.
|
1. CYP2E1
2. Alcohol dehydrogenase 3. catalase 4. aldehyde dehydrogenase |
|
|
Mallory hyaline is associated with what environmental agent?
|
ethanol
|
|
|
Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff psychosis are associated with what environmental agent?
|
Ethanol
|
|
|
What is the ultimate metabolic product of methanol? Ethylene glycol?
What symptom is caused by the product of methanol? product of ethylene glycol? |
methanol --> formic acid --> can cause blindness
Ethylene glycol --> oxalic acid --> can cause acute renal failure |
|
|
Oral contraceptives are associated what diseases?
|
thromboembolic disease
CV diseases hepatic adenoma |
|
|
Estrogen HRT is highly associated with what cancer?
|
endometrial carcinoma
|
|
|
High dose of acetaminophen can cause what? how?
|
high dose of acetamiphen --> accumulation of unconjugated NAPQI --> hepatic injuries
liver failure hepatocyte necrosis |
|
|
what is the most common side effect of chloramphenicol?
|
marrow hypoplasia
|
|
|
Which is more dangerous? hyperthermia or hypothermia?
why? |
Hyperthermia
Humans are more efficient at generating heat |
|
|
which layers are penetrated in full thickness burn?
|
subcutaneous tissue (3rd degree)
muscle (4th degree) |
|
|
What is the #1 organism associated with severe burn patients?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
Define following terms:
Heat cramps Heat exhaustion Heat stroke |
Heat cramps - sweating --> electrolyte loss
Heat exhuastion - more sweating --> hypovolemia Heat stroke - thermoregulatory failure (no sweating) heat stroke is the worst type. |
|
|
Define systemic hypothermia.
|
core temperature ≤ 95oF
|
|
|
How does ethanol exacerbate hypothermia?
|
dilation of superficial blood vessels --> lose heat
|
|
|
Define frostbite.
|
freezing of intracellular water + circulatory changes--> pallor
|
|
|
define trench (immersion) foot.
|
vasoconstriction + increase in vascular permeability
--> edema, atrophy, fibrosis |
|
|
What is result of electrical shock on high resistant tissue? low resistant tissue?
|
high resistant - thermal effects
low resistant - cardiorespiratory failure |
|
|
What type of embolism can arise form pressure injuries?
|
air/gas embolism
|
|
|
What are the symptoms associated with acute mountain sickess?
What is chronic mountain sickness? |
1. hypoventilation but compensates with increased respiratory rate
2. increased hematocrit (from adaptation) 3. mild CNS symptoms (headache, weakness, insomnia) CMS - continued acute mountain sickness symptoms due to lack of adaptation and/or decompensation Symptoms - chronic hypoventilation, symptomatic polycythemia. |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis behind high-altitude pulmonary edema?
|
hypoxia --> pulmonary vasoconstriciton + intravascular thrombosis --> pulmonary hypertension (also increased vascular permeability) --> right ventricular overload and pulmonary edema
|
|
|
What is the pathogenesis behind high-altitude cerebral edema?
|
cerebral hypoxia --> inhibition of Na/K pump --> intracellular edema
|
|
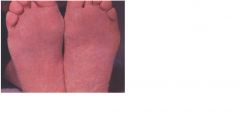
this patient is showing cherry red hue to skin. what are some possible poisons that can cause this?
|
CO and cyanide
|
|
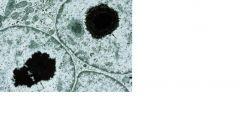
This is an electron microscope slide of the renal tubule. What are the dark stains?
|
Lead inclusions
|
|
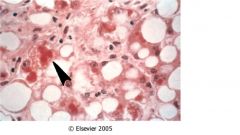
This is a slide of liver from and chronic alcohol abuser. What is the item indicated by the arrow called?
|
mallory hyaline
|
|
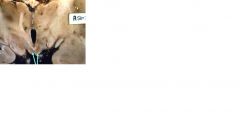
This brain exhibits mammilary body hemorrhage (indicated by the arrows).
What can cause this? what is this called? List 3 symptoms of Wernicke encephalopathy. |
ethanol
Wernicke encephalopathy due to mammilary body hemorrhage 1. ataxia 2. ophthalmoplegia 3. deranged mentation (normal human brain fxn) |
|
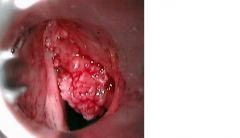
This is a carcinoma of the vocal cord. What environmental substance can cause this?
|
ethanol
|

