![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Submergent Coastline |
Coastline that is now underwater from rising sea levels or the land being lowered; its in process of being eroded back |
|
|
Emergent Coastline |
Coastline that has been exposed from sea levels retreating; can occur when reefs build up and begin growing seaward; can occur through uplift of seafloor |
|
|
Signs of Emergent Coastlines |
Wide beaches, spit, exposed marine terraces, well developed marshes |
|
|
Signs of Submergent Coastlines |
Estuaries (drowned river valley), wave cut cliffs, headland, barrier islands, stack, tied island, narrow beaches, deep bays |
|

|
Braided channel |
|

|
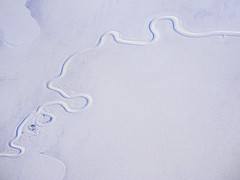
Sinuous Channel (sinuosity of 1.3-1.5) |
|
|
Meandering Channel (sinuosity over 1.5) |
|

|
Straight Channel (sinuosity below 1.3) |
|
|
Sinuosity=? |
(length of stream measured along path of water)/(length measured along straight distance) |
|

|
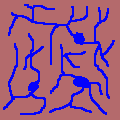
Dendritic drainage: common where a stream cuts into flat lying layers of rock or sediment, or where a stream cuts into homogenous rock |
|
|
Deranged drainage: random pattern of stream channels that seem to have no relationship, underlying rock types or geologic structures |
|

|
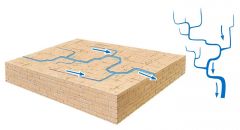
Radial drainage: channel flow outward from a central area resembling spokes on a wheel; happens on conical mountains such as volcanoes or structural domes |
|
|
Rectangular drainage: network of channels with right angel bends that form a pattern of interconnected rectangles and squares; often develops over rocks that are fractures or faulted in 2 main directions which are nearly perpendicular |
|
|
Annular drainage |
long channels form a pattern of concentric circles connected by short radial channels; develop on eroded domes or folds with resistant and non resistant rock |
|
|
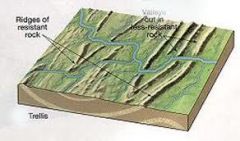
Trellis drainage: pattern of channels resembling a vine with a trellis; develops where tilted layers of resistand and nonresistant rock form parallel ridges and valleys; the main stream cuts through the ridges and the main tributaries flow parallel to the ridges and at a right angle to the main stream |
|
|
Centripetal drainage |
opposite of radial; flows into a central low point in a basin often a lake or dry lake bed |
|
|
compressional stress + brittle rocks= |
reverse faults |
|
|
compressional stress + ductile rocks= |
folding |
|
|
tensional stress + brittle rocks= |
normal faults |
|
|
tensional stress + ductile rocks= |
stretching and thinning |
|
|
shear stress + brittle rocks= |
strike slip faults |
|
|
shear stress + ductile rocks= |
bending along internal surfaces |
|
|
berm crest |
highest part of the beach; separates the foreshore from backshore |
|
|
washover fan |
fan shaped land ward deposit of sand and gravel during a washover of the land during a storm or high tide |
|
|
estuary |
river flooded by a rise in the level of an ocean or lake; a submergent feature |
|
|
delta |
sediment deposit at the mouth of a ricer where is enters a lake or ocean |
|
|
headland with cliffs |
projection of land that extends into an ocean or lake and generally has cliffs along its water boundary; submergent feature |
|
|
barrier island |
a long narrow island that parallels the mainland coastline and is separated from the mainland by a lagoon, tidal flat, or salt marsh; submergent feature |
|
|
spit |
a sand bar extending from the end of a beach into the mouth of an adjacent bay; usually emergent |
|
|
tidal flat |
muddy or sandy area that is covered with water at high tide and exposed at low tide; best developed at emergent coastlines |
|
|
salt marsh |
a march that is flooded by ocean water at high tide; best developed at emergent coastlines |
|
|
wave cut cliff |
a seaward facing cliff along a steep shoreline produced by wave erosion; best developed at submergent |
|
|
wave cut platform |
shelf at sea level or lake level along a steep shore and formed by wave erosion; best developed at submergent |
|
|
marine terrace |
elevated wave cut platform thats now higher up on the shore; emergent coastline |
|
|
stack |
isolated rocky island near a headland cliff; best developed at submergent |
|
|
tombolo |
sand bat that connects an island with the mainland or another island; best developed at submergent |
|
|
tied island |
island conneted to the mainland by a tombolo |
|
|
sea wall |
embankment of boulders reinforced with concrete against a shoreline to prevent erosion by waves or current |
|
|
breakwater |
off shore wall constructed parallel to the shoreline to break waves, the current is halted behind the wall and the sand accumulates there, and the beach widens |
|
|
groin |
a short wall constructed perpendicular to shoreline in order to trap sand and make or build up a beach; the sand accumulates of the up shore side in relation to the longshore current |
|
|
jetties |
long walls extending from shore and the mouths of harbors and used to protect the harbor entrance from filling with sand or being eroded by waves and currents |
|
|
VERTICAL EXAGGERATION=? |
HORIZONTAL SCALE/VERTICAL SCALE |

