![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is LASER |
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
|
|
|
What is Light? EM Wave Spectrum of Light |
Light is an EM Wave from 400nm - 700nm.
Red to Violet.
White light is made of a range of colours/wavelengths. |
|
|
How to get white light? How to get different colours of light? |
White Light: Obtained through heating an object.
Colours: Pass white light through prism onto a screen to get diffracted light. |
|
|
What are absorption lines? |
Dark lines appear in the band of diffracted light after it is passed through certain elements.
The photons of a certain energy is absorbed by electrons of the element, and not passed on to the screen, hence they are 'missing'. |
|
|
What are emission lines? |
Pass an electric current through a gas. Only a few discrete wavelengths are emitted. |
|
|
What is a photon? |
Photon is a particle of light with no mass and energy E = hf.
E = hf E = hc/λ |
|
|
Converting Energy in joules to Electron Volts |
Divide E by (1.602 x 10^-19)
SI unit is eV |
|
|
Bohr's quantum model of the Atom |
Electrons could only exist on 2 specific orbits.
Electrons can jump levels when gaining a specific level of energy (E = hf) |
|
|
What is the effect of light on an atom, using Bohr's model? |
Photons of the right energy is absorbed by electrons, which goes to a higher level of orbit.
When the electron loses its energy, it releases photons to go back to its Ground State.
Electrons that jump back down emit specific photons. |
|
|
What are the ways an excited atom can decay? |
Spontaneous emission: Excited atom goes back to Ground State with an emission of an atom. (~10^-18 seconds after excitation)
Phosphorescence: Atoms that remain excited for hours. Emit light long after initial photons have excited the atoms.
Fluorescence: Atom returns to Ground State via intermediate levels. Emitted photons are of lower energy (and frequency)
Stimulated Emission: Atom returns to a lower energy state faster than normal. |
|
|
What is Stimulated Emission? |
An incoming photon of the correct energy stimulates an atom (which is already in an excited state) to emit a 2nd photon.
Electron will go to a lower state of excitation faster than it would normally take.
The 2 emitted photons are in phase and travel in the same direction. |
|
|
Can we create an artificial system in which stimulated emission is prevalent? |
1. Population Inversion Situation when more atoms are in excited state than ground state.
2. Increase the number of photons with the correct energy to stimulate the excited states (Increase photon density). |
|
|
Conditions of Laser Action |
1. Population Inversion 2. Metastable State (Phosphorescent?) 3. Photons need to stay in the system long enough so that photon density is built up to further stimulate photon emission. |
|
|
How does the body react to light? |
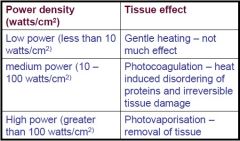
Photocoagulation and Hemostatic Properties.
Low Power: No real dmg. Medium Power: Starts to break down tissue. High Power: Water in tissue boil and vaporize. |
|
|
How is laser used in medicine? |
Laser light is used to transfer energy to tissue in a controlled way by varying:
1. Size of the beam 2. Intensity 3. Colour (wavelength) 4. Duration of exposure |
|
|
What is photocoagulation? |
Break down of proteins and tissue by photons. |
|
|
How do proteins function? |
Most major structural and functional chemicals in the body are proteins. Eg, muscles, connective tissues and blood vessels.
Made of large complex molecules, mainly with C, O, H.
Proteins must fold their complex 3 dimensional structures.
When heated above body temperature (37°C), proteins destabilize.
At >50°C, protein structures uncoil and form tangled networks (Coagulation). |
|
|
What happens when human meat is photocoagulated? |
Tissue is 'cooked'. Cells in the region is killed. Proteins are destroyed.
Excellent Hemostatic Properties: Blood vessel subjected to photocoagulation is pinched due to shrinkage of proteins in the blood vessels (Blood is clotted). |
|
|
What is Photovaporisation? |
>100°C Tissue is removed through vaporisation.
Used for incisions or removal of thin layers of tissue.
Small laser spots: Precise incisions. Large laser spots: Vaporising larger areas in a controlled manner. |
|
|
What happens with Photovaporization? |
Coagulation occurs in the surrounding region because of transference of heat. Not hot enough to vaporise, but is coagulated. |
|
|
What is Photoablation? |
Use of high power UV lasers to cause damage to chemical structures without heating damage.
Mainly for eye treatments. |
|
|
How to solve a Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion? |
A blockage of the portion of circulation that drains the retina of blood. Blockage leads to pressure in the capillaries, leading to haemorrhage and fluid leakage on the retina.
Eye repairs itself with angiogenesis (growth of new arteries). This can grow over the retina and impair vision.
Laser is used to seal the tip of the growing blood vessel and stop growth. Hopefully, the new artery grows behind/around the retina. |
|
|
Use of Pulsed Lasers |
More efficient use of lasers. Short pulses but high power, with similar average laser power. (TBC FROM HERE) |

