![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Weight reduction and reducing intake of fatty foods may sometimes reduce symptoms of _________________. |
gallbladder disease |
|
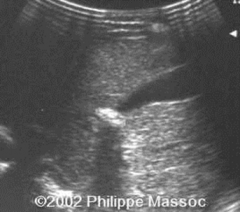
Which artifact is this? |
Acoustic shadowing |
|
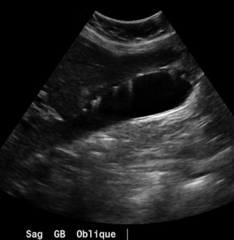
Which artifact is this? |
Ring down |
|
|
When not sure whether shadowing from the gallbladder is due to bowel gas or gallstones, rolling the patient into a ____________________ position is helpful in making this distinction. |
left lateral decubitus |
|
|
When imaging the gallbladder in a transverse orientation, a long shadow seen at both edges of the gallbladder is due to which artifact? |
The refraction artifact |
|
|
The most classic symptom of gallbladder disease is what? |
Right upper quadrant pain |
|
|
Other common symptoms of gallbladder disease include? |
1. Positive Murphy's sign 2. With inflammation, pain radiates to the right shoulder. 3. Intolerance of fatty foods or dairy |
|
|
The gallbladder is evaluated for? |
1. Increased size 2. Wall thickness 3. Presence of internal reflections within the lumen (the inside of it) 4. Posterior acoustic shadowing |
|
|
_____________ is characterized by the presence of bile in the tissues with resulting yellow-green color of the skin, most likely developing from tiny gallstones obstructing the bile ducts. |
Jaundice |
|
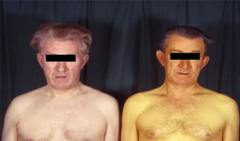
The patient on the right would be presenting with which pathology? |
Jaundice |
|
|
Nonshadowing, echogenic bile that consists of calcium and cholesterol crystals is known as what? |
Sludge |
|
|
The most frequent cause of sludge (or thick bile) is what?
|
Cholestasis (when the bile cannot flow from the gallbladder to the duodenum)
|
|
|
Sludge is a common precursor to _____________? |
gallstones |
|
|
Sludge is gravity dependent, meaning it should ___________ when the patient is moved around. |
shift |
|
|
Some gallbladders are so packed with thick bile (sludge) that it may appear as though the gallbladder is __________ and may often be confused for liver parenchyma. |
isoechoic |
|
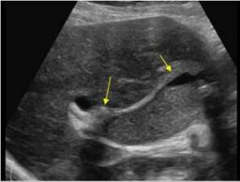
This gallbladder has become so full of _________ that it has become isoechoic. |
sludge |
|
|
Sludge creates a ______________ level, which is an interface created when two fluids have different acoustic properties. |
fluid-fluid |
|
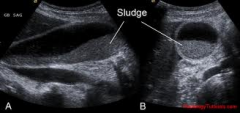
This gallbladder is partially filled with normal bile and sludge, which has created an interface between both fluids. This interface is known as what? |
A fluid-fluid level |
|
|
When sludge forms into the shape of a ball, stone or mass, it is called what? |
A sludge ball |
|
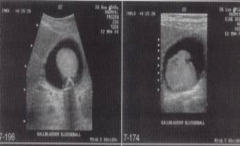
These would be an example of what? |
Sludge balls |
|
|
Although sludge balls can resemble pathologies such as ___________, they are avascular, meaning they lack _______________. |
tumors; blood flow |
|
|
A __________ gallbladder is defined as a large, round distended, non-inflamed gallbladder due to total obstruction of the cystic duct.
|
hydropic
|
|
|
A ___________, is a mucus filled gallbladder, that arises when the neck of the gallbladder becomes obstructed by gallbladder stones.
|
mucocele
|
|
|
Treatment of a mucocele (a mucus-filled gallbladder) consists of what? |
A cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) |
|
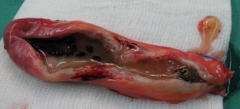
This would be an example of which pathology? |
A mucocele |
|
|
Hydropic gallbladder is consistent with a transverse measurement of what? |
5.3 cm |
|
|
When detecting a dilated, non-tender GB (hydropic gallbladder), you should look for mass where? |
At the head of the pancreas |
|
|
A common cause of a small gallbladder is that the patient has ______________.
what are the other causes for a small gallbladder |
●Eaten
-biliary obstruction -chronic cholecystitis -liver disease that destroys liver parenchyma and there for decreases production of bile - congenital hypoplasia of gallbladder (extremely rare) |
|
|
When a gallbladder is contracted and filled with many stones, it may hardly be visible and have a lot of shadowing posterior to it, forming what? |
The wall-echo-shadow (WES) sign |
|
|
"Dirty" shadowing from bowel gas is more ___________ than "clean" shadowing from gallstones. |
echogenic (snowstorm color) |
|
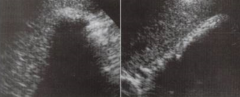
This gallbladder is contracted but also full of stones, causing major shadowing. The ___________ helps us confirm the identification of this gallbladder. |
WES (wall-echo-shadow) sign |
|
|
A _________________ gallbladder is an enlarged gallbladder caused by an obstruction of the distal portion of the common bile duct, usually because of a mass found at the head of the pancreas. |
Courvoisier |
|
|
Thickening of the gallbladder wall may or may not be associated with gallbladder ___________ in general. |
disease |
|
|
The gallbladder walls should measure less than ____ to be considered normal. |
3mm |
|
|
The most common cause of gallbladder wall thickening is ____________________? |
cholecystitis |
|
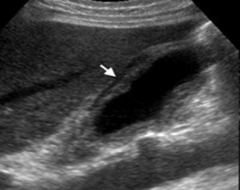
The arrow would be pointing to what? |
Pericholecystic fluid |
|
|
Should the gallbladder walls be measured in longitudinal or transverse? |
Transverse |
|
|
Excess free fluid in the peritoneal cavity is known as what? |
Ascites |
|
|
Two non-biliary reasons for diffuse wall thickening of the gallbladder are ____________ and ___________________. |
ascites and acute hepatitis |
|
|
Inflammation of the gallbladder wall with decreased gallbladder function is known as? |
Cholecystitis |
|
|
There are seven sonographic criteria that define acute cholecystitis. They include? |
1. Cholelithiasis (especially in the cystic duct) 2. Positive Murphy's Sign 3. Gallbladder wall thickening of greater than 3mm 4. Gallbladder dilatation 5. Sludge 6. Pericholecystic fluid 7. Increased color flow to the cystic artery (which is only visible when pathology is present) |
|
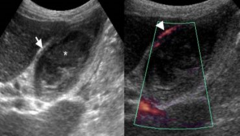
On the picture on the right, the arrow is pointing to hypervascularity of which artery? |
The cystic artery |
|
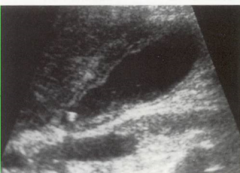
This patient's gallbladder is exhibiting thickened walls, a stone lodged in the cystic duct, sludge, and there appears to be edema within the thickened walls. This would most likely be an example of which pathology?
|
Acute cholecystitis
|
|
|
Another name for pus in the gallbladder would be? |
Empyema of the gallbladder |
|
|
Gas-forming bacteria within the wall and lumen of the gallbladder that eat away at the gallbladder is known as what? |
Emphysematous Cholecystitis |
|
|
Emphysematous cholecystitis is a ____________________? |
surgical emergency |
|
|
When the gallbladder becomes so diseased that its blood supply is cut off and it literally dies, this condition is known as what? |
Gangrenous Cholecystitis |
|
|
Will you have a positive Murphy's sign in a gangrenous gallbladder? |
No.. the gallbladder is dead. |
|
|
Localized fluid collection within the gallbladder fossa caused by the gallbladder "bursting" open and releasing its contents is known as what?
|
Gallbladder perforation
|
|
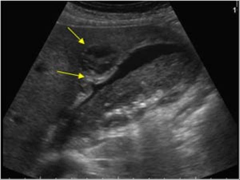
The top yellow arrow is pointing to a localized fluid collection within the gallbladder fossa caused by the gallbladder bursting open. This condition is known as what? what is its mortality rate _________
|
Gallbladder perforation
19-24% |
|
|
In the fasting patient, the most common cause for nonvisualization of the gallbladder is contraction of the gallbladder due to ________________________? |
chronic cholecystitis |
|
|
Recurrent or chronic inflammatory changes of the gallbladder is known as what? |
Chronic cholecystitis |
|
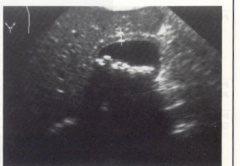
This patient's gallbladder has experienced recurrent episodes of gallbladder attacks, it's full of stones, and its walls are enlarged. They are intolerant to fattty foods and fried foods. This patient most likely has what pathology?
|
Chronic cholecystitis
|
|
|
Chronic cholecystitis is assocated with _____________ 90% of the time. |
gallstones |
|
|
An abnormal (man-made) passage between two internal organs or structures is known as a what? |
Fistula |
|
|
______________________ is an acute inflammation of the gallbladder without the presence of gallstones. |
Acalculous cholecystitis |
|
|
Sludge-like material with a high concentration of calcium found in the gallbladder and usually associated with chronic cholecystitis is known as?
|
Limy Bile syndrome (or Milk of Calcium)
|
|
|
Calcification of the gallbladder walls, strongly associated with chronic cholecystitis, is known as? |
Porcelain gallbladder |
|
|
Patients who have a porcelain gallbladder (calcification of the gallbladder walls) are most at risk for which other pathology? |
Gallbladder carcinomas |
|
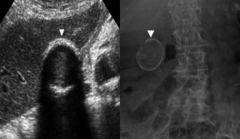
This patient's gallbladder's walls are calcified, causing shadowing. This condition is known as what? |
Porcelain gallbladder |
|
|
Stones within the gallbladder are known as what? |
Cholelithiasis |
|
|
The three characteristics for diagnosing gallstones within the gallbladder are?
|
1. Echogenic foci
2. Posterior acoustic shadowing 3. Gravity dependent (they move around when patient position is changed ☆ remember that patient may be asymptomatic or have RUQ pain |
|
|
To reduce shadowing produced by stones or bowel gas, you should decrease/increase the frequency of the transducer? |
Increase |
|
|
Gallstones form when ______________ concentration in the gallbladder is greater than the ability for the bile to make it soluble. |
cholesterol |
|
|
Gallstones produce ____________ shadowing. |
clean (the dark type of shadow) |
|
|
Gallstones less than ____ in size will usually not produce shadowing. |
3mm |
|
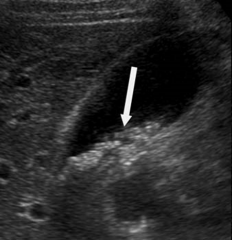
The arrow is pointing to very tiny gallstones in this gallbladder. These gallstones are not producing shadowing, meaning they are probably less than ____ in size. |
3mm |
|
|
Cholesterol gallstones with a significantly lower calcium salt content are known as what? |
Floating gallstones |
|
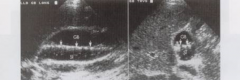
These gallstones are known as what? |
Floating gallstones |
|
|
An accumulation of lipids within the gallbladder wall is known as what? |
Cholesterolosis |
|
|
Small, well-defined soft tissue projections attached to the gallbladder wall by a stalk are known as? |
Gallbladder polyps |
|
|
____________ are the most common "pseudo"tumors of the gallbladder. |
Polyps |
|
|
What differentiates polyps from gallstones is the fact that polyps do not cause __________? and they are attached to GB wall vs. stones which attach to the dependent portion of GB
|
shadowing
|
|
|
Polyps do/do not move when changing patient position. |
do not |
|
|
Gallbladder polyps greater than _____ in size are usually related to malignant polyps. another reason is multiplicity (many polyps)
|
10mm
|
|
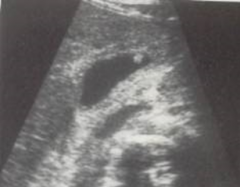
This would be an example of what? It does not shadow. |
Gallbladder polyp |
|
|
Overgrowths of the gallbladder wall is known as? |
Adenomyomatosis |
|
|
Adenomyomatosis involves overgrowths of the RAS within the gallbladder wall, which stands for? |
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses |
|
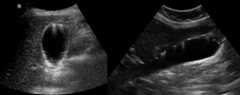
This pathology causes "comet-tails" or ring-down artifacts to form within the gallbladder. This pathology is known as? |
Adenomyomatosis |
|
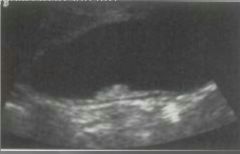
_____________ are benign neoplasms (growths) of the gallbladder with a potential to become malignant.
|
Gallbladder adenomas
|
|
|
An irregular mass that contains low-level echoes within the gallbladder would probably be considered what?
and what is its mortality rate |
A gallbladder carcinoma
almost 100 |
|
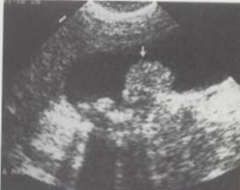
The arrow is pointing to an irregular, heterogenous mass within the gallbladder. This would best represent which pathology?
The common signs and symptoms are nausua, vomiting, intolerance to fatty foods or it could be asymptomatic. |
Gallbladder carcinoma
|
|
|
These are cysts that cause cystic dilatation and are usually an outpouching of the common bile duct. They are known as what? |
Choledochal cysts |
|
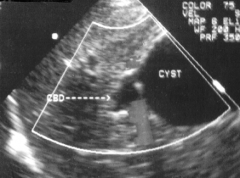
This image represents a cyst located next to the common bile duct. It would most likely be associated with which pathology? |
Choledocal cyst |
|
|
A rare congenital abnormality that causes the liver to have multiple cystic structures that communicate with the intrahepatic ducts is known as what? |
Caroli's Disease |
|
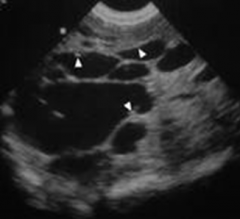
This would be an example of what? |
Caroli's Disease |
|
|
Intrapancreatic obstruction causes the entire ______________ duct to be dilated. |
extrahepatic |
|
|
In a suprapancreatic obstruction, an obstruction located between the _____________ and the porta ___________, the pancreatic duct _________ become dilated. |
pancreas and the porta hepatis; does not |
|
|
The most common cause of porta hepatic obstructions would be from? |
Neoplasms |
|
|
In porta hepatic obstructions, the ____________ ducts dilate, but the CBD remains ____________. |
intrahepatic; normal |
|
|
The presence of gallstones within the bile ducts would be known as? |
Choledocholithiasis |
|
|
Inflammation of the bile ducts is known as? |
Cholangitis |
|
|
A specific type of cholangiocarcinoma that occurs at the bifurcation of the common hepatic duct into the left and right hepatic ducts is known as? |
Klatskin's Tumor |
|
|
When a gallstone becomes impacted in the cystic duct causing the extrahepatic biliary system to obstruct, this condition is known as what? |
Mirizzi Syndrome |
|
|
Names such as "parallel channels" or "shotgun signs" should remind you of what? |
Dilated intrahepatic ducts |
|
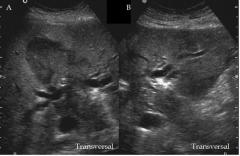
This would be an example of what? |
Dilated intrahepatic ducts |
|
|
A patient presents with RUQ pain, fever, and elevated white blood cell count. The gallbladder appears enlarged with echogenic debris. This most probably represents which pathology? |
Empyema of the gallbladder |
|
|
In the fasting patient, what is a common cause for sonographic nonvisualization of the gallbladder? |
Contraction of the gallbladder due to chronic cholecystitis |
|
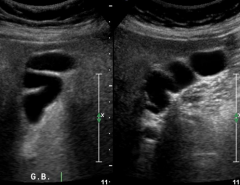
This would be an example of a gallbladder with? |
Septations |
|
|
The most common sonographic sign of gallbladder carcinomas is?
|
A fungating, irregular mass that produces low-level echoes within the gallbladder
|
|
|
what are the complications of acute cholecystitis
|

|
|
|
what are the sonographic finding for a GB perforation
|
1. pericholecystic fluid
2. intraperitoneal collection |
|
|
perforations are found in patients with
|
1. acute or chronic cholecystitis
2. gangrenous gb |
|
|
What are the complications of perforation
|
1. peritonitis
2. Pericholecystic abscess 3. Biliary fistula |
|
|
What is most consistent with gallbladder perforation
|
Pericholecystic fluid seen in conjunction with gallstones and thickened gallbladder wall is most consistent with acute cholecystitis and gallbladder wall perforation
|
|
|
what are the lab values for acute cholecystitis
|
Elevated AST, ALT, alkaline phosphate, and increase of direct Serum bilirubin
|
|
|
sonographic finding of chronic cholecystitis
|

|
|
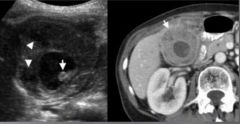
what condition is this
|
xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
|
|
|
focal gallbladder wall thickening in Association with non shadowing soft tissue masses is defined as
|
Metastatic disease of the gallbladder
|

