![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
-Taxinomy and Nomenclature
|
- |
|
|
Microbial world includes? (4)
|
1.Acellular organisms (viruses),
2.Unicellular organisms without a nucleus (prokaryotes/bacteria), 3.Unicellular organisms WITH a nucleus (eukaryotes/fungi and some parasites), 4.Multicellular organisms all have nuclei (eukaryotes/parasites) |
|
|
Eukaryotes comprises (4)
|
1.Fungi (Yeasts, moulds and pneumocystic jiroveci),
2.Plants, 3.Parasites, 4.Animals |
|
|
Prokaryotes are _ organisms
|
Single cell (1.No nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, 2.Free-standing DNA, 3.Extra-chromosomal DNA [plasmid])
|
|
|
Prokaryote morphology (4)
|
1.Coccus (Spherical),
2.Bacillus (Rod shape), 3.Sphirochete (Cork-screw shape), 4.Vibrio (Comma) |
|
|
Clusters of cocci in grapes? Clusters of cocci in chains?
|
Grapes: STAPHYLOCOCCI, chains: STREPTOCOCCI
|
|
|
Helical Form of spirochete?
|
Helicobacter Pylori
|
|
|
Name 1 Vibrio
|
Vibro Cholerae
|
|
|
Eukaryotes are _ organisms
|
Single cell OR multi-cell organisms (Have nucleus, mitochondria and membrane bound organelles)
|
|
|
Guinea worm?
|
Draculunculus Medinensis (Rod of Ascelpius)
|
|
|
Reproduction in the microbial world: Prokaryotes
|
Binary fission (asexual, no mitosis) -> CLONAL EXPANSION
|
|
|
Reproduction in the microbial world: Viruses
|
Fission (asexual, use host apparatus) -> CLONAL EXPANSION
|
|
|
Reproduction in the microbial world: Eukaryotes
|
1.Binary fission [Yeasts and some protozoa] -> CLONAL EXPANSION,
2.Sexual Reproduction (mitosis) -> not clonal |
|
|
What is Bacterial Sex/Bacterial conjugation?
|
Usage of pillus for exchange of gentic material (i.e tranmists plasmid, Abx resistance, etc.) between 2 bacteria. THERE ARE NO DAUGHTER CELLS
|
|
|
How do we name microbes?
|
Genus + Species (Staph + aureus or Staph + epidermidis)
|
|
|
2 ways to name viruses?
|
1.Scientifically (family, subfamily, genus, species and/or genus name),
2.Colloquial name (influenza, measles, HIV, etc.) |
|
|
How do we name influenza?
|
1.Virus type (A,B,C),
2.Geographic Location, 3.Strain number, 4.Year of Isolation, 5.Virus subtype (Hemagglutinin, Neuraminidase; H#, N#) |
|
|
When is the human microbiome colonized?
|
At birth (maternal vaginorectal and skin flora) - Colonization occurs in stage throughout infancy and based on environmental contact (Food, social interactions)
|
|
|
1.1 Bacteriology - BASIC CONCEPT AND KEY DIVISIONS
|
- |
|
|
2 key families of bacteria?
|
1.Pathogen vs non-pathogen [vs opportunistic pathogen],
2.Aerobes vs anaerobes [vs facultative anaerobes] |
|
|
Most basic division which reflects and determines lab Identification, Clinical Tx and Virulence?
|
GRAM'S STAIN (what color is the bacteria under the microscope?)
|
|
|
What are the 4 ingredients of Gram's stain?
|
1.CRYSTAL VIOLET (blue - purple),
2.Iodine fixator, 3.Acid and Alcohol or Acetone decolorization, 4.SAFRANIN (red) |
|
|
Bacterial cell wall synthesis
|
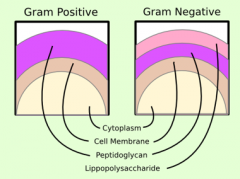
Polymers of NAM and NAG with chains of amino acids are linked then bound together through penicillin-binding-proteins (penicillin interferes with the ability of penicillin binding protein to link a.a chains together)
|
|
|
Gram positive bacteria have _ cell wall than the gram negative
|
Thicker -> stains blue (blue doesn't decolorize even after the addition of Acid/alcohol or acetone decolorization)
|
|
|
Gram positive: Color? Suffix?
|
BOY: BLUE -> 1.Coccus, 2.Bacillus, 3Iium, 4.Onostoc, 5.Myces
[EXCEPTION: 1.Listeria, 2.Nocardia, 3.Gemella] |
|
|
Gram negative: Color? Suffix?
|
GIRL: RED -> 1.Ella, 2.Eria, 3.Ichia, 4.Inia, 5.Encia [EXCEPTION:
1.PseudoMONAS, 2.AeroMONAS, 3.AcinetoBACTER, 4.EnteroBACTER, 5.CitroBACTER, 6.CampyloBACTER, 7.Bacteroides, 8.Haemophilus, 9.Vibrio, 10.Proteus] |
|
|
3 examples of bacteria without cell walls
|
1.Mycoplasma (pneumoniae, hominis), 2.Chlamydia (trachomatis),
3.Chlamydophila (pneumonia, psittaci) |
|
|
1.2 Bacteriology - BACTERIAL VIRULENCE FACTORS
|
- |
|
|
3 examples of bacterial physical defense barriers and adherence virulence factors?
|
1.Capsule (i.e strep. coccus -> can't get opsonized by Abs),
2.Biofilms (staph epidermidis), 3.Fimbrae (E coli -> adhesion) |
|
|
Lipopolysaccharides are found on _ bacteria. What do they lead to (3)?
|
Gram-NEGATIVE (endotoxin) -> Immune response -> 1.Cytokine Release, 2.Fever, 3.Shock
|
|
|
Bacterial toxins -> Systemic effects
|
Superantigens: Activate 10% of lymphocyte pool (directly bind MHCII on T cell) -> TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME
|
|
|
Bacterial toxins -> GI distress (4)
|
1.Shiga & shiga-like toxin,
2.Toxins A & B (C. Difficile), 3.Cholera toxin, 4.Food poisoning (staph enterotoxin, CPE enterotoxin) |
|
|
Bacterial toxins -> Neurotoxins (3)
|
1.Bolinum toxin -> (paralysis, C. Botulinum), 2.Tetanospasmin (teatnus, C Tetani),
3.Shigatoxin -> seizures |
|
|
Bacterial toxins -> Respiratory Distress (4)
|
1.Diphteria toxin (URTI, Resp obstruction), 2.Pertussis toxin (Whooping cough, Insulin-induced hypoglycemia),
3.Botulinum toxin (Through paralytic effect), 4.Necrotizing pneumonia (Panton Valentin Leukocidin, S. aureus) |
|
|
Bacterial toxins -> Tissue changes (5)
|
1.Alphatoxin (Gas gangrene, C perfrigens), 2.Anthrax toxin (Edema factor, B anthracis), 3.Exfoliatin (staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, S. aureus),
4.Panton Valentin Leukocidin (leukocytes and epithelial cell lysis; Community MRSA), 5.Pyogenic exotoxin (superantigen, necrotizing fascilitis) |
|
|
Bcaterial Toxins -> Renal failure (3)
|
1.Shiga toxin,
2.Verotoxin (hemolytic uremic syndrome), 3.E Coli O157 H7 (enterohemorrhagic E coli) |
|
|
Listeriolysin O causes?
|
Lysis of phagosomes -> allows the bacterium to replicate intracellularly (evade the immune system)
|

