![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Its characterized by mass and quantity |
Matter |
|
|
|
Described as matter's energy equivalence |
Mass |
|
|
|
Force exerted by a body under the influence of gravity |
Weight |
|
|
|
Is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distuinguished by its atomic number |
Element |
|
|
|
How many elements has been identified? |
112 |
|
|
|
How many elements that are identified naturally occuring? |
92 |
|
|
|
Where does the 20 manmade elements been produced? |
High energy accelerators |
|
|
|
Composed of two or more element that are chemically linked in definite proportion |
Compounds |
|
|
|
Smallest unit which chemical element can be broken down without losing its chemical identity |
Atom |
|
|
|
Ability to do work |
Energy |
|
|
|
The ability to do work by virtue of position |
Potential energy |
|
|
|
It is possessed by all matters in motion |
Kinetic energy |
|
|
|
Is the energy released by the way of chemical reaction |
Chemical energy |
|
|
|
Represents the work that can be done when an electron or an electronic charge moves through a electric potential |
Electrical energy |
|
|
|
Is the energy in motion at the atomic or molecular level and in this regard can be viewed as kinetic energy of atoms |
Thermal energy |
|
|
|
Is the type of energy in xray |
Electromagnectic energy |
|
|
|
Attraction toward the nucleus and the centrifugal forces associated with the fast electrons |
Electrostatic attraction or force |
|
|
|
Relativity of protons |
1.836 |
|
|
|
Relativity of electron |
1 |
|
|
|
Relativity of neutron |
1.838 |
|
|
|
Weight of electron |
1.109x10^-31 kg |
|
|
|
Weight of protons |
1.673x10^-27 kg |
|
|
|
Weight of neutron |
1.675x10^-27 kg |
|
|
|
Atomic Mass Unit of electron |
0.000549 AMU |
|
|
|
Atomic Mass Unit of proton |
1.00728 |
|
|
|
Atomic Mass Unit of neutron |
1.00867 |
|
|
|
Has the same mass as an electron but carries a positive charge |
Positron |
|
|
|
A combination of one proton and one neutron |
Deuteron |
|
|
|
Two proton and two neutron form a stable combination known as? |
Alpha particle |
|
|
|
What principle says that no two orbital electrons in an atom move with exactly the same motion |
Pauli's exclusion principle |
|
|
|
Equation to compute for electron limit per shell |
2n² |
|
|
|
Physicist called the shell number as |
Principal quantum number |
|
|
|
The removal of orbital electron from the atom |
Ionization |
|
|
|
Any type of radiation capable of removing or ejecting electron from the atom with which it interacts is called |
Ionizing radiation |
|
|
|
The strenght of attachment of an electron to a nucleus |
Electron binding energy |
|
|
|
Alphabetical abbreviation of elements |
Chemical symbol |
|
|
|
In a chemical symbol, "A" is a abbreviation for? |
Atomic Mass Number |
|
|
|
Abbreviation for Atomic Mass Number |
"A" Capital |
|
|
|
It is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons |
Atomic Mass Number - A |
|
|
|
Z+N |
A - Atomic Mass Number |
|
|
|
Z+N |
A - Atomic Mass Number |
|
|
|
Other term for Atomic Mass Number |
Nucleon number |
|
|
|
Symbol for atomic number |
"Z" Capital |
|
|
|
Indicates the number of protons in nucleus |
Atomic Number - "Z" |
|
|
|
It is also the number of electrons in a neutral atom |
Atomic Number - "Z" |
|
|
|
Number of atomic mass number minus the number of neutrons. |
Atomic number - "Z" |
|
|
|
A-N= |
"Z" - Atomic Number |
|
|
|
Neutron Number symbol |
"N" |
|
|
|
Number of atomic mass number minus the the atomic number |
Neutron Number - "N" |
|
|
|
Equation to get the atomic mass number "A" |
Atomic number "Z" + Neutron number "N" |
|
|
|
Equation to get the neutron number |
Atomic mass number "A" - Atomic number "Z" |
|
|
|
Equation for atomic number |
Atomic Mass Number - Atomic Number |
|
|
|
A specific nuclear species with a given proton and neutron number |
Nuclide |
|
|
|
Nuclide that has the same atomic number but different atomic mass number |
Isotope |
|
|
|
Nuclide that have the same neutron number but different number of proton. |
Isotones |
|
|
|
Nuclide that have the same atomic mass number but different atomic number |
Isobar |
|
|
|
Nuclides that have the same atomic number and same atomic mass number but different in physical state |
Isomers |
|
|
|
Force that attracts only |
Gravitational force |
|
|
|
Acts in a mass through an associated gravitational field |
Gravitational force |
|
|
|
Gravitational force is expressed by what law? |
Newton's Law |
|
|
|
Forces that attracts and repels |
Electrostatic force and magnetic force |
|
|
|
Electrostatic force acts in a associated *blank* |
Electric field |
|
|
|
Force that acts in a pole through an associated magnetic field |
Magnetic force |
|
|
|
Associated with alpha and beta decay |
Gamma decay |
|
|
|
Alpha and beta decay usually leaves the product nucleus in excited state.These go down to there ground state by emitting what? |
Gamma rays |
|
|
|
Transfer of energy to an orbital electron, causing it to be ejected from the atom. |
Internal conversion |
|
|
|
A decay involving neither the emission nor the capture of a particle. |
Isometric transition |
|
|
|
In isometric transition, the nucleus simply changes from a higher to lower energy level by emitting what? |
Gamma proton |
|
|
|
The period of time required for a quantity of radioactivity to be reduced to one half of it's original value |
Physical half-life or radioactive half-life |
|
|
|
The time required for the body to eliminate one half of the dose of any substance by the regular process of elimination |
Biological half-life |
|
|
|
The time required for the radioactivity from a given amount of radioactive element deposited in the tissues or organs to diminish 50% as a result of the combined action of radioactive decay and loss of material by biological elimination |
Effective half-life |
|
|
|
Equation for effective half-life and biological half-life |

|
|
|
|
The number of nuclear transformation per unit time |
Activity |
|
|
|
Equation for activity |

|
|
|
|
Half-life equation |
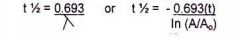
|
|
|
|
Decay constant |

|
|
|
|
Fixed or stationary electric charges |
Electrostatic |
|
|
|
The electric charge that is associated with electron and a proton have the _____ magnitude but _____ signs. |
Same, opposite |
|
|
|
All electric charges deals with? |
Negative electric charges |
|
|
|
An object is said to be electrified if it has an ____ or an ____ of electron |
Insufficient,excess |
|
|
|
It occurs because of the movement of negative electric charges |
Electrification |
|
|
|
What are the electrostatic laws? |
1. Unlike charges attract, like charges repel. 2. Coulomb's law. 3. Electric charge distribution. 4. Electric charge concentration. |
There are four |
|
|
Uncharged matter is ____ by charged matter |
Unaffected |
|
|
|
What law represents the magnitude of the electrostatic force? |
Coulomb's law |
|
|
|
This law states that the electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the electrostatic charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. |
Coulomb's law |
|
|
|
What is the Coulomb's law equation? |
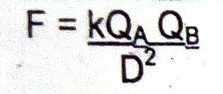
|
|
|
|
When a diffuse nonconductor object becomes electrified; the electric charges are distributed throughout the object. |
Electric charge distribution |
|
|
|
Some atoms exists in a abnormally excited state are characterized by an? |
Unstable nucleus |
|
|
|
If one or more of the orbital electrons are removed from an atom by radiant energy and the remaining part has a surplus of positive charge; this damage atom is called? |
Positive Ion |
|
|
|
If the removed electrons attach themselves to other neutral atoms or if they stay free, they are called? |
Negative Ion |
|
|
|
What are the 3 fundamental forces in nature? |
1. Gravitational Force 2. Electrostatic Force 3. Magnetic Force |
|
|
|
What process do atoms undergo to reach stability, where the nucleus spontaneously emits particles and energy and transforms itself into another atom? |
Radioactive Disintegration or Radioactive Decay |
|
|
|
What do you call the atoms that are involved in radioactive decay? |
Radionuclides |
|
|
|
Term for nuclear arrangement? |
Nuclide or nuclei |
|
|
|
It is the emission of particles and energy in order to become stable. |
Radioactivity |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of Radioactivity? |
1. Natural Radioactivity 2. Artificial Radioactivity |
|
|
|
What are the 3 modes of radioactive decay? |
1. Alpha Decay 2. Beta Decay 3. Gamma Disintegration Process |
|
|
|
Radioactive Decay results in emission of _,_,&_? |
1. Alpha Particle 2. Beta Particle 3. Gamma Rays |
|
|
|
Mode of Radioactive Decay that emits 2 protons and 2 neutrons? |
Alpha Decay |
Screenshot |
|
|
Mode of Radioactive Decay where neutron changes to proton when the nucleus has an excess of neutrons? |
Beta-Minus Decay |
Screenshot |
|
|
Mode of Radioactive Decay where proton changes to neutron when the nucleus has an excess of protons. |
Beta-Plus Decay |
Screenshot |
|
|
Mode of Radioactive Decay where the nucleus captures one of the orbital electrons (usually K-electron) which converts a proton into a neutron. |
Electron Capture |
Screenshot |

