![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What gives the cell shape?
a) nuclear membrane b) cell membrane c) cell wall |
Cell membrane |
|
|
What holds the cytoplasm?
a) cell membrane b) endoplasmic reticulum c) cell wall |
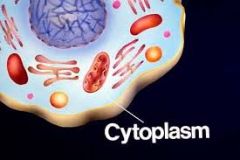
Cell membrane
Surrounds the cell |
|
|
What helps control what moves in and out of the cell?
a) ribosomes b) cell wall c) cytoplasm |
Cell membrane |
|
|
Helps control what moves out of the cell
|
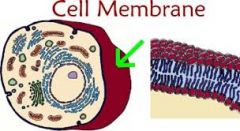
Cell membrane |
|
What is the cells "brain"? |
Nucleus |
|
|
This part of the cell determines how proteins will be made. |
Nucleus
|
|
|
Determines when proteins will be made |
Nucleus |
|
|
Passes traits from parents to offspring |
Nucleus
|
|
|
Separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell
|
Nuclear membrane
Surrounds the nucleus |
|
|
Helps make ribosomes
|
Nucleolus
Inside the nucleus |
|
|
Determine what traits a living thing will have
|
Chromosomes
Inside the nucleus |
|
|
Makes up most of the cell
|
Cytoplasm
Between the cell membrane and the nucleus |
|
|
Help move material around inside the cell
|
Network of canals
Contained in the cytoplasm |
|
|
Connect the nuclear membrane and the cell membrane
|
Network of canals
Contained in the cytoplasm |
|
|
Where proteins are made |
Ribosomes |
|
|
Package and store chemicals to be released from the cell |
Packaging structures
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
Produce energy from food that has been digested
|
Mitochondria
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
Chemicals made in these break down large molecules
|
Sacs that contain digestive chemicals |
|
|
Chemicals made in these get rid of disease-causing bacteria that enter the cell
|
Sacs that contain digestive chemicals
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
Chemicals made in these destroy worn-out cell parts
|
Sacs that contain digestive chemicals
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
Chemicals made in these form products that can be used again
|
Sacs that contain digestive chemicals |
|
|
Stores food
|
Vacuoles
Within the cytoplasm |
|
|
Stores water |
Vacuoles |
|
|
Stores minerals
|
Vacuoles
Within the cytoplasm |
|
|
Store wastes until the cell is ready to get rid of them
|
Vacuoles
Within the cytoplasm |
|
|
The fluid inside these helps to support a plant
|
Vacuoles |
|
|
Help with cell reproduction
|
Centrioles
Within the cytoplasm, located near the nucleus in animals cells but not in plant cells |
|
|
Contain chlorophyll, which traps energy from the sun
|
Chloroplasts
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
Give plants their green color
|
Chloroplasts
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
Protects the cell
|
Cell wall |
|
|
Supports the cell
|
Cell wall |
|
|
extremely thin, rather fluid membrane
|
plasma membrane
|
|
|
Plant's cell walls are composed of ________ .
|
cellulose |
|
|
Made up of: |
Cytoskeleton.
|
|
|
Maintains and changes cell shape
|
Cytoskeleton
|
|
|
Facilitates cell division
|
cytoskeleton
|
|
|
Which cell is larger? Eukaryotic or Prokaryotic |
Eukaryotic
|
|
|
isolates the nucleus from the rest of the cell
|
Nuclear envelope
|
|
|
contain genes
|
chromosomes
|
|
|
contains nuclear and plasma membranes |
cell membrane
|
|
|
produces lipids, detoxifies drugs, breakdown glycogen, synthesize lipids.
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
studded with ribosomes, produces proteins
|
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
sorts various proteins and lipids, packages and finished molecules
|
Golgi apparatus
|
|
|
water regulation, support, and storage
|
vacuole
|
|
|
capture energy stored in sugar
all Eukaryotic cells have this |
mitochondria |
|
|
Movement of particles from a high concentration to a low concentration:
a) diffusion b) equillibrium c) permeable transmission |
a) diffusion |
|
|
When substances and particles are equally spread it: a) homeostasis b) diffused temperate c) equallibrium |
c) equallibrium |
|
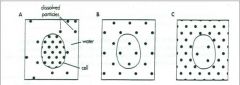
Which one is a hypotonic? |
A |
|
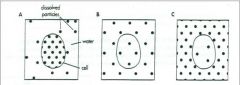
Identify the Hypertonic solution: |
c |
|
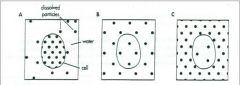
Identify the Isotonic Solution |
B |

