![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the spinal cord segment for the Musculocutaneous nerve? |
C5, C6 (also C7, but not listed in little book) |
|
|
what muscles does the musculocutaneous nerve innervate? |
coracobrachialis biceps brachii brachialis |
|
|
What is the sensory distribution of the musculocutaneous nerve? |
anterolateral surface of the forearmw |
|
|
what are the features of musculocutaneous peripheral nerve paralysis? |
loss of elbow flexion when supinated weakened supination |
|
|
What are the spinal cord segments for the Axillary nerve? |
C5, C6 |
|
|
What muscles does the axillary nerve innervate? |
deltoid and teres minor |
|
|
What is the sensory distribution supplied by the axillary nerve? |
lateral arm over lower portion of deltoid |
|
|
what are the motor features of axillary nerve paralysis |
loss of shoulder abduction weakened shoulder ER |
|
|
What are the spinal cord segments for the Radial nerve? |
C5, C6, C7, C8, T1 (T1 has inconsistent contribution. *Note little book does not say C5) |
|
|
What muscles does the radial nerve innervate? |
triceps, anconeus, brachioradialis, supinator, wrist, finger and thumb extensors |
|
|
what is the sensory distribution of the Radial nerve? |
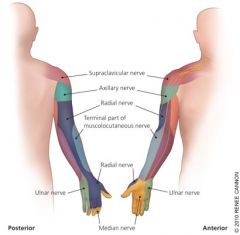
posterior arm, forearm and radial side of hand and digits 1-3 up to DIP and radially half of 4th up to DIP |
|
|
what are the motor features of radial nerve paraysis? |
loss of elbow, wrist, finger, and thumb extension (every mm with extensor word in it. & Abductor Pollicis longus) |
|
|
What are the spinal cord segments of the Median nerve? |
C5, C6, C7, C8, T1 (T1 has inconsistent contribution. *Note little book does not say C5) |
|
|
what muscles are innervated by the median nerve? |
pronators, wrist and finger flexors on radial side, most of thumb muscles -FCR -PT -PL -FDS -FPL -FDP (of digits 2 and 3) -PQ -APB -OP -FPB -Lumbricals 1 & 2 |
|
|
what is the sensory distribution of the median nerve? |
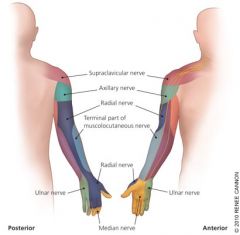
palmar aspects of the thumb-3rd digit and radial half of palmar aspect of the 4th digit and Distal tips of digits 1-3 and radial half of distal tip of 4th digit |
|
|
what are the motor features of median nerve paralysis? |
loss of forearm pronation thumb opposition thumb flexion and abduction (lateral pinch instead of pad-to-pad) Carpal tunnel syndrome thenar eminence atrophy |
|
|
what spinal cord segments does the ulnar nerve arise from? |
C8-T1 |
|
|
What muscles are innervated by the ulnar nerve? |
FCU FDP (4&5) Dorsal and Palmar Interossei lumbricals of 4 and 5 Adductor Pollicis ADM ODM FDMB
|
|
|
what is the sensory distribution of the ulnar nerve? |
medial half of the palmar and dorsal surfaces of the 4th digit 5th digit medial palmar and dorsal surfaces of hand |
|
|
What are motor features of ulnar nerve paralysis? |
loss of wrist ulnar deviation weakened wrist and finger flexion weakened fourth and 5th DIP flexion loss of thumb adduction loss of most intrinsic hand muscles (claw hand) |
|
|
What are the spinal cord segments of the sciatic nerve? |
L4-S3 |
|
|
what muscles does the sciatic nerve innervate? |
Hamstrings Adductor Magnus |
|
|
what is the sensory distribution of the sciatic nerve? |
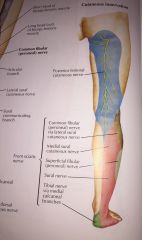
posterior/lateral calf, ankle and heel |
|
|
what are the motor features of sciatic nerve paralysis? |
loss of knee flexion weak hip adduction loss of all muscle function below the knee |
|
|
What are the spinal cord segments of the femoral nerve? |
L2, 3, 4 |
|
|
What are the muscles innervated by the femoral nerve? |
sartorius quadriceps iliacus pectineus |
|
|
what is the sensory distribution of the femoral nerve? |
middle anterior thigh and anterior medial leg and medial calf distal to knee (see pg. 538 of Netters) |
|
|
what are the motor features of paralysis for the femoral nerve? |
loss of hip flexion and knee ext |
|
|
what are the cord segments of the tibial nerve? |
L4-S3
|
|
|
what are the muscles innervated by the tibial nerve? |
gastrocnemius soleus (superificial posterior compartment) plantaris popliteus tibialis posterior FDL FHL (i.e. deep posterior compartment) |
|
|
what is the sensory distribution of the tibial nerve? |
posterior/lateral calf, ankle and heel tibial nn. specifically: plantar surface of foot (except margins of posterior medial and lateral side) & posterior distal heel pg. 540 of netter's |
|
|
What are the motor features of tibial nerve paralysis? |
loss of PF and supination |
|
|
What are the cord segments of the superficial peroneal (fibular) nerve? |
L5-S2 |
|
|
what muscles are innervated by the superficial peroneal nerve? |
peroneus longus and brevis |
|
|
what is the sensory distribution of the superficial peroneal nerve? |
anterior/medial distal lower leg and ankle most of dorsum of foot except web space between 1st and 2nd digit and lateral border of the 5th metatarsal (sural nn) |
|
|
what are motor features of superificial peroneal nerve paralysis? |
loss of eversion |
|
|
What are the the cord segments of the deep peroneal nerve? |
L4-S2 |
|
|
what muscles are innervated by the deep peroneal nerve? |
tibialis anterior EHL EDL peroneus tertius 1st and 2nd dorsal interossei EDB EHB |
|
|
What is the sensory distribution of the deep peroneal nerve? |
web space between first and 2nd toes on dorsum of foot |
|
|
what are motor features of paralysis of the deep peroneal nerve? |
loss of DF (drop foot) weakness in the foot intrinsics |
|
|
Name the cranial nerves. |
Olfactory CN I Optic CN II Oculomotor CN III Trochlear CN IV Trigeminal CN V Abducens CN VI Facial VII Vestibulocochlear VIII Glossopharyngeal IX Vagus X Spinal Accessory XI Hypoglossal XII |
|
|
What is the function of CN I? and what does damage cause? |
function: smell damage: anosmia (loss of sense of smell)
|
|
|
What is the function of Optic nerve (CN II)? and what does damage cause? |
function: sight/vision, pupillary reflexes damage: monocular blindness, loss of pupillary constriction, absence of blink reflex |
|
|
What is the function of Oculomotor CN III? and what does damage cause? |
function: moves the eye and elevates the upper eyelid damage: ptosis (drooping eyelid) dilation of pupil/loss of accomodation of the light reflex |
|
|
What is the function of the Trochlear CN IV? and what does damage cause? |
function: innervates the superior oblique mm (moves eye out and down, test by looking down and in) damage: diplopia, head tilt up and inclined to the opposite side |
|
|
What is the function of Trigeminal CN V? and what does damage cause? |
Function: motor innervation of mm of mastication and sensory nerve for the head damage: loss of facial sensation, weakness of mm of mastication, deviation of opened jaw to ipsilateral side
|
|
|
What is the function of Abducens CN Vi? and what does damage cause? |
Function: abducts the eye via nerve supply to lateral rectus mm Damage: diplopia, convergent squint (medial strabismus), abductor paralysis of ipsilat eye |
|
|
What is the function of Facial nerve (CN VII)? and what does damage cause? |
Function: facial expression, speech articulation, winking, ingestion of food and drink, taste, salivary and nasal secretions Damage: ipsilat facial paralysis loss of taste on anterior 3rd of tongue (Bell's Palsy) |
|
|
What is the function of Vestibulocochlear CN VIII? and what does damage cause? |
Function: maintenance of equilibrium and hearing Damage: vertigo, nystagmus, dysequilibrium, tinnitus, loss of hearing |
|
|
What is the function of Glossopharyngeal CN IX? and what does damage cause? |
Function: taste, elevates pharynx, salivary secretions (testing: say 'ahh' and watch for symmetrical elevation) Damage: slight dysphagia, partial dry mouth, loss of taste on posterior 3rd of tongue |
|
|
What is the function of Vagus CN X? and what does damage cause? |
Function: phonation, visceral sensations and reflexes, cardiac depressor, bronconstrictor, GI tract peristalis and secretion Damage: palpitation, tachycardia, vomiting slowing of respiration UMN: uvula deviates toward lesion; ipsilat paralysis of soft palate and larynx LMN: uvula deviates contralat to lesion hoarseness anesthesia of larynx |
|
|
What is the function of Accessory CN XI? and what does damage cause? |
Function: swallowing (deglutition) and phonation movements of head and neck (SCM and Trapes) Damage: weakness in shrugging ipsilat shoulder and turning head to contralat side |
|
|
What is the function of Hypoglossal CN XII? and what does damage cause? |
Function: movements of tongue Damage: unilat paralysis of tongue LMN (nuclear or peripheral lesion) deviation to the ipsilat side during protrusion UMN: tongue deviates contralat to side of lesion |

