![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Fossil |
the remains or impression of a prehistoric organism preserved in petrified form or as a mold or cast in rock.
|

|
|
|
mold fossil |
fossil formed when an animal, plant, or other organism dies and is covered by sediment, its flesh decays and bones deteriorate due to chemical reactions, and a cavity remains below the ground surface. |

|
|
|
Cast fossil |
fossil formed when an animal, plant, or other organism dies, its flesh decays and bones deteriorate due to chemical reactions; minerals gradually enter into the cavity, resulting in a cast, also called a mold fossil, which is in the general form of the original organism.
|

|
|
|
Petrified fossil |
the process by which organic material is converted into a fossil through the replacement of the original material and the filling of the original pore spaces with minerals.
|

|
|
|
Preserved fossil |
a fossil is the preserved remains from a prehistoric organism that have been preserved inside rock.
|

|
|
|
Carbonized fossil |
Carbonization is the process where only the residual carbon of the organism remains. In nature this usually happens over time when the organism is subject to heat and pressure.
|

|
|
|
Trace fossil |
Carbonization is the process where only
|

|
|
|
Law of superposition |
a basic law of geochronology, stating that in any undisturbed sequence of rocks deposited in layers, the youngest layer is on top and the oldest on bottom, each layer being younger than the one beneath it and older than the one above it.
|
|
|
|
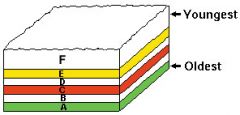
Relative age |
the relative order of past events the age of an object in comparison to another without necessarily determining their absolute age
|
|
|
|
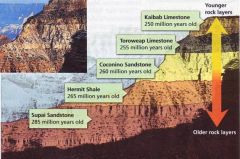
Absolute age |
Absolute age is the true age of a rock or fossil. Absolute age tells scientists the number of years ago a rock layer formed. What is meant by absolute. age? Radioactive elements give off particles and energy which causes the elements to decay.
|
|

