![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Eggs Composition
|
65% Water
12% Protein 11% Fat 12% Ash (Mineral) |
|
|
Is egg yolk or egg white more nutritional
|
Egg yolk is more nutritional than the egg white. It has Vitamin A,D,E in it.
|
|
|
The structure of the inside view of a hen's egg
|
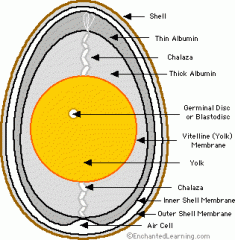
|
|
|
Functions of the parts of the egg
|
Anchors (chalazae) - It holds the egg yolk and keeps it in place
Air Space- If the egg was fertilized, the chick would have to have space to breathe. Yolk- It contains the most nutrients in it. |
|
|
Why does the shell contain pores?
|
Pores allow air to get through them and into the egg so if the egg was fertilised, the chick would be able to breathe properly.
|
|
|
How do the pores effect the keeping quality of the egg?
|
They allow the air to get into the egg. The longer you keep an egg, the more air goes through and the less fresh it becomes.
|
|
|
Functions of eggs + Example
Binding Coating |
Binding- Eggs bind and stick dry ingredients together. The egg provides moistness. The egg protein coagulates when heated. Beefburgers, fishcakes, Croquettes
Coating- The egg coagulates with heat and protects the ingredient during frying. Fried Fish, Fishcake with breadcrumbs, Croquettes |
|
|
Functions of eggs + Example
Glazing and Finishing Enriching |
Glazing and Finishing-Beaten egg is brushed over savoury pastries before baking. The egg protein coagulates with heat and forms a shiny surface on baked products. Cheese Straws, Bread
Enriching- Egg adds nutritional value and thickens and adds colour. Sauces, potatoes, pasteries |
|
|
Functions of eggs + Example
Thickening and setting Garnishing |
Thickening and Setting- The egg is a liquid food which contains protein and this thickens and coagulates with gentle heat. 1 Medium egg will set 125ml of milk or cream. Custards, savoury flans, quiches, soups
Garnishing- Hard boiled eggs can be sliced and chopped. Salads and Sandwiches |
|
|
Functions of eggs + Example
Trapping air-aeration Emulfisying |
Aeration- Eggs can trap air when they are whisked or beaten. Eggs whites trap air to foam. A stabiliser in egg white foam is the protein albumen. Aerating. Cakes, meringues, Choux pastry
Emulsifying- Egg yolk contains an emulsifying agent called lecithin which holds together oil and water. Mayonnaise-oil and vinegar, Ice cream, salad cream |
|
|
How to reduce the risk of food poisoning
|
Store eggs in the fridge, wash your hands before and after handling eggs, cook eggs thoroughly, don't use cracked eggs.
|
|
|
Lion quality mark
|
It is a red stamp and we should only buy eggs with this stamp because it means they are produced to highest standards of food safety.
|
|
|
What dies the Lion Quality mark tell you about eggs
|
1. Produced under British Standards
2. High quality eggs 3. Stored under correct standards 4. Transported at right temperature 5. Produced legally |
|
|
All about eggs
Nutrient Groups Vitamins and Minerals Sizes |
fat, protein
A,D,E Protein Small medium, Large |
|
|
Farming eggs in the UK
|
Cage- Hens are kept in a barn and are cramped together completely-fed more hormones
Barn- Hens are kept in a barn and never leave that barn-fed grains Free-range-- Hens can roam freely outside- fed healthy food |
|
|
Why Battery Hens are cheaper than Free Range
|
There are a lot of battery hens, they are given cheap chemicals to feed on and are worse quality than free range eggs.
|

