![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
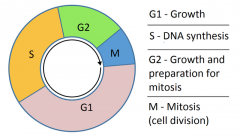
Cell Cycle |
A cell cycle is orders of events that takes place in cell. Takes place in a cell as it grows and divides. |
|
Interphase |
Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. |
|
|
G1 or Gap 1 |
The G1 phase, or Gap 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequent steps leading to mitosis. |
|
|
S-Phase (synthesis phase) |
S-phase (synthesis phase) is the part of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Precise and accurate DNA replication is necessary to prevent genetic abnormalities which often lead to cell death or disease. |
|
|
G2 |
G2 phase. : the period in the cell cycle from the completion of DNA replication to the beginning of cell division — compare g1 phase, m phase, s phase. |
|
|
G0 |
The G0 phase, G zero phase, or 'resting phase' is a period in the cell cycle in which cells exist in a quiescent state. G0 phase is viewed as either an extended G1 phase, where the cell is neither dividing nor preparing to divide, or a distinct quiescent stage that occurs outside of the cell cycle. |
|
|
Cancer |
Cancer is an abnormal growth of cells caused by multiple changes in gene expression leading to regulated balance of cell proliferation and cell death and ultimately evolving into a population of cells that can invade tissues and metastasize to distant sites, causing significant morbidity and, if untreated, death of the host. |
|
|
Mitosis |
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth. |
|
|
Cell Division |
The division of a cell into two daughter cells with the same genetic material. |
|
|
Parent Cell |
Parent Cell is a cell that is the source of other cells, as a cell that divides to produce two or more daughter cells, or a stem cell that is a progenitor of other cells or is the first in a line of developing cells. Also called mother cell. |
|
|
Daughter Cell |
Either of the two cells formed when a cellundergoes cell division by mitosis. Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell because they contain the same number and type of chromosomes |
|
|
Checkpoint |
A point in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the cycle may continue if specific conditions are present or will stop if conditions are not right. |
|
|
Prophase |
The first stage of cell division, before metaphase, during which the chromosomes become visible as paired chromatids and the nuclear envelope disappears. The first prophase of meiosis includes the reduction division. |
|
|
Metaphase |
The second stage of cell division, between prophase and anaphase, during which the chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers. |
|
|
Anaphase |
The stage of meiotic or mitotic cell division in which the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle. |
|
|
Telophase |
The final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed. |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
The cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells. |
|
|
Cell Plate |
A cell plate is a plate that develops at the midpoint between the two groups of chromosomes in a dividing cell and that is involved in forming the wall between the two new daughter cells. |
|
|
Chromatin |
Chromatin is the material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria (i.e., eukaryotes) are composed. It consists of protein, RNA, and DNA. |
|
|
Centrioles |
Centrioles is a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division. |
|
|
Microtubules |
Microtubules is a a microscopic tubular structure present in numbers in the cytoplasm of cells, sometimes aggregating to form more complex structures. |
|
|
Nuclear envelope/membrane |
A nuclear membrane, also known as thenuclear envelope, nucleolemma or karyotheca, is the double lipid bilayer membrane which surrounds the genetic material and nucleolus in eukaryotic cells. The nuclear membrane consists of two lipid bilayer—the inner nuclear membrane, and the outer nuclear membrane. |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Nucleolus is a small dense spherical structure in the nucleus of a cell during interphase. |
|
|
Poles |
An extremity of the main axis of a cell, organ, or part. |
|
|
Spindle Fibers |
Spindle fibers form a protein structure that divides the genetic material in a cell. The spindle is necessary to equally divide the chromosomes in a parental cell into two daughter cells during both types of nuclear division: mitosis and meiosis. |
|
|
Metaphase Plate |
Metaphase Plate is a plane cell section in the equatorial plane of the metaphase spindle having the chromosomes oriented upon it. |
|
|
Cleavage Furrow |
In cell biology, the cleavage furrow is the indentation of the cell's surface that begins the progression of cleavage, by which animal and some algal cells undergo cytokinesis, the final splitting of the membrane, in the process of cell division. |
|
|
Meiosis |
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores. |
|
|
Gametes (examples) |
Gametes is a mature haploid male or female germ cell that is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote. (example 1) Eggs and sperm cells are called gametes, and they have only one set of 23 chromosomes, which is called a haploid, or n. (example 2) When two haploid gametes (one egg and one sperm cell) fuse during fertilization, is a diploid cell is produced. |
|
|
Somatic Cells (examples) |
A somatic cell is any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells. (example 1) For example, in mammals, somatic cells make up all the internal organs, skin, bones, blood, and connective tissue, while mammalian germ cells give rise to spermatozoa and ova which fuse during fertilization to produce a cell called a zygote, which divides and differentiates into the cells of an embryo. |
|
|
Haploid |
Haploid (of a cell or nucleus) having a single set of unpaired chromosomes. |
|
|
Diploid |
Diploid (of a cell or nucleus) containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. |
|
|
Zygote |
Zygote is a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum. |
|
|
Meiosis 1 |
Meiosis 1 is a cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; the nucleus divides into for nuclei each containing half the chromosome number (leading to gametes in animals and spores in plants) |
|
|
Meiosis 2 |
Meiosis 2 is the second stage of meiosis. During this stage, sister chromatids separate to form haploid cells with just one chromatid per chromosome. |
|
|
n |
n is the number of chromosomes in a gamete of an organism. |
|
|
2n |
2n is having a pair of each chromosome characteristic of a species (2n or, in man, 46). |
|
|
Homologous Chromosomes |
A homologous pair of chromosomes consists of one chromosome from each parent. During most of the cell cycle, homologous chromosome pairs are unreplicated. When the chromosomes replicate, each chromosome of the pair becomes doubled; each "half" of the doubled chromosomes is called a chromatid. |
|
|
Independent Assortment |
Independent Assortment is a formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of each diploid pair of homologous chromosomes into each gamete independently of each other pair. |
|
|
Crossing Over |
Crossing over is the exchange between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics of offspring. |
|
|
Biodiversity |
Biodiversity is the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem. |
|
|
Genetic Diversity |
Genetic Diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It is distinguished from genetic variability, which describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to var |

