![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
177 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
apoptosis requires _
|
ATP
|
|
|
intrinsic pathway of apoptosis mechanism (3)
|
changes in levels of anti- and pro- apoptotic factors
--> -- ^ mitochondrial permeability -- release of cytochrome c |
|
|
when does apoptosis intrinsic pathway happen? (4)
|
embryogenesis
hormone induction e.g. menstruation atrophy e.g. endometrial lining in menopause injurious stimuli e.g. --radiation --toxins --hypoxia |
|
|
extrinsic pathway of apoptosis mechanism
|
--FasL binding to Fas (CD95)
--killer T cell release of perforin and granzyme B |
|
|
both intrinsic & extrinsic apoptosis pathways lead to
|
activation of cytosolic caspases -->
cellular breakdown |
|
|
apoptosis histopathology
3 + 4 |
--cell shrinkage
--membrane blebbing --apoptotic bodies which are phagocytosed nuclear: --shrinkage --pyknosis --karyorrhexis --karyolysis |
|
|
pyknosis
|
irreversible condensation of chromatin in the nucleus
--> basophilia |
|
|
karyorrhexis
|
pyknotic nuclear fragmentation
|
|
|
karyolysis
|
nuclear fading
|
|
|
types of necrosis
|
coagulative
liquefactive caseous fatty fibroid gangrenous |
|
|
coagulative necrosis is @
|
heart
liver kidney |
|
|
liquefactive necrosis is @
|
brain
bacterial abscess pleural effusion |
|
|
caseous necrosis is @
|
TB
systemic fungi |
|
|
fatty necrosis is @
and involves |
pancreas
saponification |
|
|
fibroid necrosis is @
involves |
blood vessels
immune-mediated damage |
|
|
gangrenous necrosis is @
types |
limbs
GI tract dry (ischemic) wet (bacteria) |
|
|
necrosis involves (4)
|
exogenous injury -->
enzymatic degradation, protein denaturation intracellular components extravasate inflammatory process |
|
|
intrinsic apoptosis:
_ is pro-apoptotic _ is anti-apoptotic |
Bax
Bcl-2 |
|
|
cell injury that's reversible with O2 (6)
|
v ATP synthesis
cellular swelling chromatin clumping v glycogen fatty change ribosomal detachment (v protein synthesis) |
|
|
cell injury that's irrreversible (7)
|
nuclear
--pyknosis --karyolysis --karyorrhexis ca2+ influx --> caspase activation membrane damage lysosomal rupture mitochondrial permeability |
|
|
red infarcts occur when/where?
|
loose tissues with collaterals e.g.
liver lungs intestine or following reperfusion |
|
|
reperfusion injury is due to damage by
|
free radicals
|
|
|
pale infarcts occur where/when?
|
solid tissues with single blood supply e.g.
heart kidney spleen |
|
|
atrophy is _
|
reduction in size or number of cells
|
|
|
6 causes of atrophy
|
v hormones (uterus/vagina)
v innervation (motor neurons) v blood flow v nutrients ^ pressure (nephrolithiasis) occlusion of secretory ducts (cystic fibrosis) |
|
|
inflammation:
abscess-- |
fibrosis surrounding pus
|
|
|
inflammation:
granulation tissue-- |
highly vascularized
fibrotic |
|
|
mediators of
acute vs. chronic inflammation |
neutrophil
eosinophil antibodies mononuclear cells |
|
|
chronic inflammation characterizations/associations
|
persistent destruction & repair
vessel proliferation fibrosis granulomas |
|
|
leukocyte extravasation steps (4)
|
rolling
tight binding diapedesis migration |
|
|
leukocyte extravasation
vasculature/stroma vs. leukocyte molecules involved in rolling |
e-selectin
p-selectin sialyl lewis |
|
|
leukocyte extravasation
vasculature/stroma vs. leukocyte molecules involved in tight binding |
ICAM-1
LFA-1 ("integrin") |
|
|
leukocyte extravasation
vasculature/stroma vs. leukocyte molecules involved in diapedesis |
PECAM-1
PECAM-1 |
|
|
leukocyte diapedesis is
|
leukocyte travels between endothelial cells and exits blood vessel
|
|
|
leukocyte migration is
|
travels through interstitium
to injury or infection site guided by chemotactic signals |
|
|
leukocyte extravasation
vasculature/stroma vs. leukocyte molecules involved in |
--bacterial products
"CILK" C5a IL-8 LTB4 Kallikrein ---------------------------- various |
|
|
free radicals damage cells via (3)
|
membrane lipid peroxidation
protein modification DNA breakage |
|
|
free radical injury is initiated by (6)
|
radiation
phase I metabolism of drugs transition metals redox rxns NO leukocyte oxidative burst |
|
|
free radicals --> pathologies...
(6) |
preemies:
--retinopathy of prrematurity --bronchopulmonary dysplasia CCl4 acetaminophen iron overload reperfusion |
|
|
CCl4 -->
|
liver necrosis (fatty change)
|
|
|
reperfusion free radical injury involves _
esp occurs when? |
superoxide
after thrombolytic rx |
|
|
granulomatous diseases (8)
|
tuberculosis
leprosy fungal infections (e.g. histoplasmosis) syphilis sarcoidosis berylliosis cat scratch fever Crohn's |
|
|
mechanism of granuloma formation/maintenance
|
Th1 cells: gamma-interferon -->
+ macrophages: TNF-alpha |
|
|
a bad juju that happens with anti-TNF drugs...
|
break down granulomas
--> disseminated disease |
|
|
a drug that can break down granulomas
|
anti-TNF
|
|
|
transudate vs. exudate
cellularity protein specific gravity |
hypocellular vs. cellular
poor vs. rich < 1.012 > 1.020 |
|
|
transudate vs. exudate
due to: |
^ hydrostatic pressure
v oncotic pressure Na+ retention lymphatic obstruction inflammation |
|
|
ESR: RBCs fall at a faster rate within the test tube because...
|
products of inflammation e.g. fibrinogen
coat RBCs --> aggregation |
|
|
a surprise cause of ^ ESR
|
pregnancy
|
|
|
(3) cause v ESR
|
sickle cell (altered shape)
polycythemia (too many) CHF |
|
|
iron poisoning epi
|
one of the leading causes of toxicologic fataly in children
|
|
|
iron poisoning moa
|
cell death 2^ peroxidation of membrane lipids
|
|
|
iron poisoning sxs
|
acute: gastric bleeding
chronic: --metabolic acidosis --scarring --> GI obstruction |
|
|
amyloidosis
--in a word |
beta-pleated sheet
|
|
|
amyloidosis
--lab |
apple-green birefringence of
Congo-red stain under polarized light |
|
|
amyloidosis
--gross clinical |
tissue has waxy appearance
|
|
|
primary amyloidosis
--protein --derived from |
AL
Ig light chains (multiple myeloma) |
|
|
secondary amyloidosis
--protein --derived from |
AA
serum amyloid-associated protein (chronic inflammatory disease) |
|
|
senile cardiac amyloidosis
--protein --derived from |
transthyretin
AF |
|
|
diabetes II amyloidosis
--protein --derived from |
amylin
AE |
|
|
medullary thyroid carcinoma amyloidosis
--protein --derived from |
A-CAL
calcitonin |
|
|
Alzheimer's amyloidosis
--protein --derived from |
beta-amyloid
amyloid precursor protein (APP) |
|
|
dialysis-associated amyloidosis
--protein --derived from |
beta-2 microglobulin
MHC class I |
|
|
types of amyloidosis
|
primary
secondary senile cardiac alzheimer's medullary thyroid carcinoma diabetes II dialysis-associated |
|
|
hypovolemic/cardiogenic vs. septic shock
|
low-output
^ TPR low cardiac output cold, clammy -- high-output -- v TPR -- dilated arterioles, high venous return -- hot |
|
|
neoplastic progression:
hyperplasia |
increase in number of cells
|
|
|
neoplastic progression:
dysplasia |
abnormal proliferation
loss of size shape orientation |
|
|
neoplastic progression:
carcinoma in situ/preinvasive |
--have not invaded basement membrane
--neoplastic cells encompass entire thickness --high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio --clumped chromatin |
|
|
neoplastic progression:
invasion of the basement membrane occurs by using _ |
collagenases
hydrolases |
|
|
metastasis, to occur, must survive
|
immune attack
|
|
|
metastasis molecular changes {{on the surface of cancer cells??}}
|
v cadherin
^ laminin, integrin receptors |
|
|
hyperplasia
|
^ number of cells
|
|
|
metaplasia (3)
|
one adult cell type is replaced by another
often 2^ irritation or exposure e.g. squamous metaplasia in trachea and bronchi of smokers |
|
|
dysplasia
|
abnormal growth
loss of orientation shape size |
|
|
reversible plasias vs. irreversible plasias
|
hyperplasia
metaplasia dysplasia anaplasia neoplasia desmoplasia |
|
|
anaplasia
|
"undifferentiated malignant neoplasms"
lacking differentiation, like that tissue's primitive cells little or no resemblance to tissue of origin |
|
|
neoplasia
|
clonal proliferation that's
uncontrolled and excessive |
|
|
desmoplasia
|
fibrous tissue formation
in response to neoplasm |
|
|
tumor grade vs. stage
|
diffferentiation
spread |
|
|
_ _ _ staging system
|
TNM
size of tumor node involvement metastasis |
|
|
_ is often more predictive of cancer prognosis than _
|
stage
grade |
|
|
epithelial tumors
benign malignant |
adenoma
papilloma adenocarcinoma papillary carcinoma |
|
|
blood vessel tumors:
benign malignant |
hemangioma
angiosarcoma |
|
|
skeletal muscle tumors:
benign malignant |
rhabdomyoma
rhabdomyosarcoma |
|
|
tumors with
> 1 cell type |
benign:
--mature teratoma (women) malignant: --immature teratomas --mature teratoma (men) |
|
|
_ implies epithelial origin of a malignant tumor
_ implies mesenchymal origin of a malignant tumor |
carcinoma
sarcoma |
|
|
neoplasms associated with
down syndrome |
ALL ("we all fall down")
AML |
|
|
neoplasms associated with
xeroderma pigmentosum & albinism |
melanoma
basal cell carcinoma squamous cell carcinomas esp |
|
|
gastric adenocarcinoma is associated with (3)
|
chronic atrophic gastritis
pernicious anemia postsurgical gastric remnants |
|
|
tuberous sclerosis = (3)
|
facial angiofibroma
seizures mental retardation |
|
|
neoplasms associated with
tuberous sclerosis |
astrocytoma
angiomyolipoma cardiac rhabdomyoma |
|
|
neoplasms associated with
actinic keratosis |
squamous cell carcinoma of skin
|
|
|
barrett's esophagus is associated with _ cancer
|
esophageal adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
neoplasms associated with
plummer vinson syndrome |
squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus
|
|
|
plummer vinson triad
cause? |
iron deficiency -->
atrophic glossitis esophageal webs anemia |
|
|
(3) --> hepatocellular carcinoma
|
cirrhosis 2^ alchol, hep b, hep c
|
|
|
neoplasms associated with
ulcerative colitis |
colonic adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
neoplasms associated with
paget's disease of the bone |
2^ osteosarcoma
fibrosarcoma |
|
|
neoplasms associated with
immunodeficiency |
lymphomas
|
|
|
autoimmune diseases e.g. (2)
--> lymphoma |
hashimoto's thyroiditis
myasthenia gravis |
|
|
neoplasms associated with
acanthosis nigricans |
BLUStering malignancy
breast lung uterus stomach |
|
|
acanthosis nigricans = (2)
|
hyperpigmentation
epidermal thickening |
|
|
malignant melanoma is associated with _ of the skin
|
dysplastic nevus
|
|
|
neoplasms associated with
radiation exposure (2) |
sarcoma
papillary thyroid cancer |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
abl |
CML
tyrosine kinase |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
c-myc |
Burkitt's lymphoma
transcription factor |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
bcl-2 |
follicular and undifferentiated lymphomas
inhibits apoptosis |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
erb-B2 |
breast
ovarian gastric carcinomas tyrosine kinase |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
ras |
colon carcinoma
GTPase |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
L-myc N-myc |
Lung tumor
Neuroblastoma transcription factor transcription factor |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
ret |
MEN II and III
tyrosine kinase |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
c-kit |
gastrointestinal stromal tumor aka GIST
cytokine receptor |
|
|
oncogenes whose product is a tyrosine kinase
|
abl
erb-B2 ret |
|
|
oncogenes whose product is a transcription factor
|
c-myc
L-myc N-myc |
|
|
an oncogene whose product is an anti-apoptotic molecule
|
bcl-2
|
|
|
an oncogene that's a GTPase
|
ras
|
|
|
ras's gene product is a _
|
GTPase
|
|
|
9 oncogenes
|
c-myc
L-myc N-myc abl bcl-2 erb-B2 ret ras c-kit |
|
|
11 tumor suppressor genes
|
Rb
p53 p16 BRCA1 BRCA2 APC DPC DCC WT1 NF1 NF2 |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
Rb |
retinoblastoma
osteosarcoma blocks G1 --> S phase |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
p53 |
most human cancers
Li-Fraumeni syndrome blocks G1 --> S phase |
|
|
tumor suppressor genes whose products block
G1 --> S phase |
Rb
p53 |
|
|
tumor and gene product associated with
BRCA1 BRCA2 |
breast and ovarian
breast -------------------------- DNA repair protein |
|
|
tumor associated with p16
|
melanoma
|
|
|
tumorr associated with APC
|
colorectal cancer (FAP)
|
|
|
pancreatic cancer is associated with _ gene
|
DPC
|
|
|
colon cancer is associated with (2) tumor suppressor genes
|
APC
DCC |
|
|
Rb chromosome
|
13q
|
|
|
p53 chromosome
|
17p
|
|
|
BRCA1
BRCA2 chromosomes |
17q
13q |
|
|
p16 chromosome
|
9p
|
|
|
APC chromosome
|
5q
|
|
|
WT1 chromosome
|
11p
|
|
|
NF1
NF2 chromosomes |
17q
22q |
|
|
DPC
DCC chromosomes |
18q
|
|
|
tumor markers:
PSA prostatic acid phosphatase |
prostate carcinoma
BPH prostatitis ------------------------ prostate carcinoma |
|
|
tumor markers:
CEA |
carcinoembryonic antigen
nonspecific 70% of colorectal and pancreatic cancers also in cancers of: --gastric --breast --thyroid medullary |
|
|
tumor marker:
alpha-fetoprotein (3) |
mormally made by fetus
hepatocellular carcinomas nonseminomatous germ cell tumors of the testis (e.g. yolk sac tumor) |
|
|
tumor marker
CA-125 |
ovarian
malignant epithelial tumors |
|
|
tumor marker
S-100 |
melanoma
neural tumors astrocytomas |
|
|
tumor marker
alkaline phosphatase |
metastases to bone
obstructive biliary disease Paget's disease of bone |
|
|
tumor marker
bombesin |
neuroblastoma
lung gastric |
|
|
tumor marker
TRAP (tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase) |
hairy cell leukemia
|
|
|
hairy cell leukemia is a neoplasm of _ cells
|
B cells
|
|
|
tumor markers:
CA-19-9 |
pancreatic adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
HHV-8 --> ____ cancers
|
--Kaposi's sarcoma
--body cavity fluid B-cell lymphoma |
|
|
H pylori causes _ gastric cancer
|
gastric adenocarcinoma
gastric lymphoma |
|
|
aflatoxins are notably produced by _
cause what? |
aspergillus
hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
vinyl chloride C2 H3 Cl -->
|
angiosarcoma
|
|
|
_ carcinogens causes angiosarcoma
|
vinyl chloride
asbestos |
|
|
nitrosamines cause cancer @
|
esophagus
stomach |
|
|
cigarette smoke causes _ cancers
|
larynx
--squamous cell carcinoma lung --squamous cell carcinoma --small cell carcinoma kidney --renal cell carcinoma bladder --transitional cell carcinoma |
|
|
CCl4 -->
|
liver
--centrilobular necrosis --fatty change |
|
|
asbestos -->
|
mesothelioma
bronchogenic carcinoma |
|
|
arsenic -->
|
skin
--squamous cell carcinoma liver --angiosarcoma |
|
|
naphthaleene (aniline) dyes -->
|
bladder
--transitional cell carcinoma |
|
|
alkylating agents -->
|
leukemia
|
|
|
paraneoplastic effects
___ --> ACTH or ACTH-like peptide |
small cell lung carcinoma
|
|
|
paraneoplastic effects
____ --> ADH |
small cell lung carcinoma
intracranial neoplasms |
|
|
small cell lung carcinoma --> ___ paraneoplastic products
|
ACTH
ADH |
|
|
hypercalcemia as a paraneoplastic effect
|
squamous cell lung
renal cell carcinoma breast carcinoma --> PTH-related peptide TGF-beta TNF IL-1 --> hypercalcemia |
|
|
cushing syndrome as a paraneoplastic effect
|
small cell lung carcinoma
--> ACTH or ACTH-like peptide |
|
|
SIADH as a paraneoplastic effect
|
small cell lung carcinoma
intracranial neoplasms --> ADH --> SIADH |
|
|
polycythemia as a paraneoplastic effect
|
renal cell carcinoma
hemangioblastoma --> erythropoietin |
|
|
hemangioblastoma is ____
|
spinal
brain stem cerebellar very vascular |
|
|
gout
urate nephropathy as paraneoplastic effects |
leukemias
lymphomas --> hyperuricemia due to excess nucleic acid turnover (i.e., cytotoxic therapy) |
|
|
psammoma bodies
(image) |
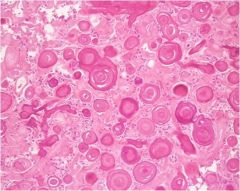
|
|
|
psammoma bodies are _
|
laminated
concentric calcific spherules |
|
|
psammoma bodies are seen in (4)
|
PSaMMoma:
1. Papillary adenocarcinoma of thyroid 2. Serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma of ovary 3. Meningioma 4. Malignant mesothelioma |
|
|
cancer epidemiology:
|
male, female
incidence: prostate 32%, breast 32% lung 16%, 13% colon and rectum 12%, 13% --------------------------------- mortality: lung 33%, 23% prostate 13%, breast 18% |
|
|
tumors that metastasize to brain
|
Lots of Bad Stuff Kills Glia
lung breast skin (melanoma) kidney (renal cell carcinoma) GI |
|
|
two general comments about cancer that metastasizes to the brain
|
approximately 50% of brain tumors are from metastases
multiple well-circumscribed tumors @ gray/white matter junction |
|
|
the most common sites of metastasis
|
1. regional lymph nodes
2. lung & liver |
|
|
the most common tumors that metastasize to the liver
|
Cancer Sometimes Penetrates Benign Liver
Colon > Stomach > Pancreas > Breast > Lung |
|
|
these 1^ tumors metastasize to bone
|
P.T.T. Barnum Loves Kids
**Prostate Thyroid Testes **Breast Lung Kidney ** most common |
|
|
bone tumors: 1^ or metastatic are more common?
liver? brain? |
metastatic are far more common
metastatic >> 1^ 50% / 50% |
|
|
two types of bone metastases
which organs do they come from? |
lung --> lytic
prostate --> blastic breast --> lytic and blastic |

