![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
180 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the disorder with the sex chromosomes XXY?
|
Klinefelter's
|
|
|
Name the common findings of Klinefelter's
|
Testicular atrophy, fibrosis of seminiferous tubules leading to absence of spermatogenesis and loss of Sertoli cells, eunuchoid body shape, tall, long extremities, gynecomastia, female hair distribution
|
|
|
Kleinfelter's is associated with significant mental retardation: TRUE OR FALSE
|
FALSE
|
|
|
What are the FSH, LH and T level's in Klinefelter's
|
Increased FSH, Increased LH, Decreased T
|
|
|
What is the karyotype for Klinefelter's
|
XXY
|
|
|
Why is there increased FSH in Klinefelter's?
|
Absence of sertoli cells --> Decreased inhibin --> Inc FSH
|
|
|
Why is there increased LH in Klinefelter's?
|
inc FSH --> inc Aromatase in Leydig --> convert T to estradiol --> low testosterone --> inc LH
|
|
|
What leads to increased estrogen in Klinefelter's?
|
Abnormal leydig fx --> dec testosterone --> Inc. LH --> Inc estrogen
|
|
|
What are some common findings of Turner's?
|
Short stature, ovarian dysgenesis (streak ovary), devoid of oocytes by 2 yrs, webbing of neck, preductal coarctation of aorta, lymphedema in hands and feet of infants
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of primary amenorrhea?
|
Turner's
|
|
|
Karyotype for Turner's
|
XO
|
|
|
What are estrogen, FSH, LH levels in Turners?
|
Dec estrogen, Inc LH and Inc FSH
|
|
|
What is the pathophysiology of webbed neck in Turner's
|
Dilated lymphatic channels
|
|
|
What is Turner's associated with?
|
Horseshoe kidney, hypothyroidism, coarctation of the aorta, and bicuspid aortic valve
|
|
|
What is the cause of XYY karyotype?
|
Paternal nondysjunction
|
|
|
What are clinical findings in XYY double Y males?
|
Phenotypically normal, very tall, severe acne, antisocial behavior. Normal fertility
|
|
|
Fertility is abnormal or normal in XYY males?
|
Normal
|
|
|
What are some causes of female psuedohermaphrodite?
|
Excessive and inappropriate exposure to androgenic steroids during early gestation (congenital adrenal hyperplasia or exogenous administration of androgens during pregnancy)
|
|
|
What condition occurs when ovaries are present but external genitalia are virilized or ambiguous?
|
Female pseudohermaphrodite (XX)
|
|
|
What condition occurs when testes are present but external genitalia are female or ambiguous?
|
Male pseudohermaphrodite (XY)
|
|
|
What is the most common form of male pseudohermaphrodite?
|
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
|
|
|
What could be the cause of sudden respiratory peripartal difficulty?
|
Amniotic fluid embolism
|
|
|
What causes amniotic fluid embolism and what is a hematologic complication?
|
Tear in placental membrane and rupture of maternal veins, infusing of amniotic fluid and procoagulants. . DIC in pulmonary microcirculation --> DIC
|
|
|
What is amniotic fluid aspiration syndrome?
|
When a neonate is unable to expel amniotic fluid at birth
|
|
|
What is a true hermaphrodite (46, XX or 47 XXY)
|
Both ovary and testicular tissue present; ambiguous genitalia
|
|
|
Pathophys of androgen insensitivity syndrome; findings
|
Defect in androgen receptor resulting in normal-appearing female; female external genitalia with rudimentary vagina; uterus and uterine tubes generally absent; develops testes (inguinal herniae), primary amenorrhea in adulthood.
|
|
|
How are the levels of T, estrogen, and LH in Androgen insensitivity syndrome?
|
All high or varying depending on degree of insensitivity
|
|
|
What condition is there ambiguous genitalia until puberty?
|
5a-reductase deficiency
|
|
|
What is the problem in 5a-reducatse deciiency and what happens as a result?
|
Unable to convert testosterone to DHT --> Inc. testosterone @ puberty causes masculinization/ increased growth of external genitalia.
|
|
|
How are the levels of T/estrogen/LH in 5a-reductase deficiency?
|
Normal
|
|
|
What is the pathophysiology of a hydatidiform mole?
|
Cystic swelling of chorionic villi and proliferation of chorionic epithelium (trophoblast)
|
|
|
Hydatidiform moles are the most common precursor of
|
Choriocarcinoma
|
|
|
What are some descriptions of appearance for hydatidiform moles?
|
"Honey-combed uterus" "cluster of grapes"
|
|
|
The uterus is enlarged abnormally in partial hydatidiform moles: true or false
|
False, only in complete hydatidiform moles
|
|
|
Moles can lead to what complication of the uterine
|
Uterine rupture
|
|
|
Karyotype for two different classes of moles
|
Complete: 46,XX(90%) and 46,XY. Partial: 69, XXY
|
|
|
What are some differences between complete and partial hydatidiform moles
|
Complete: entire placenta neoplastic, markedly increased hCG, 2% convert to choriocarcinoma, No fetal parts seen Partial: not all villi are neoplastic or dilated, somewhat increased hCG, rare conversion to choriocarcinoma, fetal parts present
|
|
|
What are the components of a complete and partial hydatidiform mole
|
Complete: 2 sperm and empty egg. Partial: 2 sperm and 1 egg
|
|
|
With which hydatidiform mole do you see a snowstorm pattern on ultrasound?
|
Complete mole
|
|
|
What is a common cause of recurrent miscarriages in the 1st weeks?
|
low progesterone levels (no response to B-hCG
|
|
|
Leiomyomas have an increased incidence in what race
|
Blacks
|
|
|
Peak occurance of leiomyoma at what age
|
20-40
|
|
|
Leiomyomas are sensitive to what and increase and decreases in what stages for female
|
Estrogen sensitive, Tumor size increases with pregnancy and decreases with menopause
|
|
|
Benign smooth muscle tumor of the myometrium, malignant transformation rare
|
Leiomyoma (fibroid)
|
|
|
What is the histological finding of leiomyomas?
|
Whorled pattern of smooth muscle bundles
|
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of leiomyomas?
|
May be asymptomatic or may cause abnormal uterine bleeding. Severe bleeding may lead to iron deficiency anemia
|
|
|
Describe a leiomyosarcoma
|
Bulky, irregularly shaped tumor with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage, typically arising de novo. Hihgly aggressive tumor with tendency to bleed. May protude from cervix and bleed.
|
|
|
Bulky, irregularly shaped tumor of myometrium with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage, typically arising de novo. Hihgly aggressive tumor with tendency to bleed. May protude from cervix and bleed.
|
Leiomyosarcoma
|
|
|
What is the order of gynecological tumor incidence?
|
Endometrial > ovarian > cervical
|
|
|
What is the order of gynecological tumors for worse prognosis?
|
Ovarian > cervical > endometrial
|
|
|
What are the levels of estrogen, LH, and FSH in premature ovarian failure?
|
Decreased estrogen, Increased LH and FSH
|
|
|
First hormone irregularity to think of when thinking of PCOS
|
Increased LH
|
|
|
Enlarged, bilateral cystic ovaries manifest clinically with amenorrhea, infertility, obesity, and hirsuitism
|
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
|
|
|
How does increased LH lead to the abnormalities in PCOS
|
Inc LH --> Inc. androgen and increased estrogen --> Increase LH and decrease FSH --> follicle degeneration and fluid accumulation. Extra estrogen and androgen cause hirsutism and increase risk of endometrial cancer
|
|
|
What are the treatments for PCOS?
|
weight loss, OCPs, gonadotropin analogs, clomiphene (SERM), or surgery
|
|
|
What is a follicular cyst?
|
Distention of unruptured graafian follicle
|
|
|
Distention of unruptured graafian follicle
|
Follicular cyst
|
|
|
What is follicular cyst associated with?
|
Hyperestrinism and endometrial hyperplasia
|
|
|
What is a corpus luteum cyst? Associated with
|
Hemorrhage into persistent corpus luteum. Associated with menstrual irregularity
|
|
|
Hemorrhage into persistent corpus luteum. Associated with menstrual irregularity
|
Corpus luteum cyst
|
|
|
What is the cause of a theca-lutein cyst and what is it associated with?
|
Due to gonadotropin stimulation. Associated with choriocarcinoma and moles
|
|
|
What ovarian tumor is equivalent to a male seminoma and is malignant?
|
Dysgerminoma
|
|
|
Which ovarian tumor is the most common malignant germ cell tumor?
|
Dysgerminoma
|
|
|
What ovarian tumor has a characteristic increase in serum LDH and has sheets of uniform cells?
|
Dysgerminoma
|
|
|
What is the tumor marker for a dysgerminoma?
|
hCG
|
|
|
What ovarian tumor is an aggressive malignancy in ovaries that is also seen in testes in boys and the sacrococcygeal area of young children? It also has a tumor marker of alpha-fetoprotein
|
Yolk sac (endodermal sinus tumor)
|
|
|
What is another name for a yolk sac tumor of the ovary?
|
Endodermal sinus tumor
|
|
|
What area can yolk sac tumors be found in young children?
|
Sacrococcygeal area
|
|
|
Teratoma is a non germ cell or germ cell tumor?
|
Germ cell tumor
|
|
|
What is another name for a mature teratoma?
|
Dermoid cyst
|
|
|
What is the most frequent benign ovarian tumor?
|
Mature tgeratoma
|
|
|
Teratomas are how many eprcent of all ovarian germ cell tumors?
|
90.%
|
|
|
Which of the teratomas is aggressively malignant? Mature or immature
|
Immature
|
|
|
What is struma ovarii?
|
A teratoma that contains functional thyroid tissue and can present as hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
What ovarian tumor has Schiller-Duval bodies?
|
Yolk sac tumor
|
|
|
Name the different germ cell tumors of the ovary
|
Teratoma, dysgerminoma, Yolk sac tumor
|
|
|
Name the different non-germ cell tumors of the ovary
|
Serous cystadenoma, serous cystadenocarcinoma, mucinous cystadenoma, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, Brener tumor, Fibromas, Granulosa cell tumor, Krukenberg tumor
|
|
|
Serous cystadenomas are what percentage of ovarian tumors?
|
20.%
|
|
|
What are risk factor genes for ovarian cancer?
|
BRCA-1, HNPCC
|
|
|
Serous cystadenocarcinomas are what percentage of ovarian tumors?
|
50.%
|
|
|
Frequently bilateral ovarian tumor, lined with fallopian tube-like epithelium. Benign
|
Serous cystadenoma
|
|
|
Frequently bilateral ovarian tumor, lined with epithelium resembling fallopian tube, malignant
|
Serous cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Which ovarian tumor has psammoma bodies?
|
serous cystadencarcinoma
|
|
|
Multilocular ovarian cyst lined by mucus-secreting epithelium. Benign
|
Mucinous cystadenoma
|
|
|
What is the name of the condition when mucinous cystadenocarcinomas form multiple intraperitoneal accumulations because of rupture or metastases?
|
Pseudomyxoma peritonei
|
|
|
Small islands of transitional epithelium within fibrous stroma of an ovarian tumor
|
Brenner tumor
|
|
|
Brenner tumors are benign/malignant and look like what organ's cells?
|
Benign. Bladder
|
|
|
What are fibromas and what syndrome are they associated with?
|
Budnles of spindle-shaped fibroblasts. Meigs syndrome - triad of ovarian fibroma, ascites, and hydrothroax
|
|
|
With what ovarian tumor do you get a pulling sensation in the groin?
|
Fibroma
|
|
|
What ovarian tumor secretes estrogen and causes precocious puberty in kids?
|
Granulosa cell tumor
|
|
|
What problems can granulosa cell tumors cause clinically?
|
Estrogen secreting --> precocious puberty (kids). Cause endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma in adults because of unoppossed estrogen secreting tumor which can then cause vaginal bleeding as well
|
|
|
What is the common pathological finding in Granulosa cell tumors and what are they?
|
Call Exner bodies - small follicles filled with eosinophilic secretions
|
|
|
What is a Krukenberg tumor?
|
GI malignancy that metastasizes to ovaries, causing a mucin-secreting signet cella denocarcinoma
|
|
|
GI malignancy that metastasizes to ovaries, causing a mucin-secreting signet cella denocarcinoma
|
Krukenberg tumor
|
|
|
Vaginal squamous cell carcinoma is usuallly secondary to
|
Cervical squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What type of vaginal carcinoma affects women who have had exposure to DES in utero?
|
Clear cell adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
What vaginal carcinoma affects girls <4 years old and consist of spindle shaped tumor cells that are desmin positive?
|
Sarcoma botryoides
|
|
|
Multiple polypoid masses "a bunch of grapes" projecting into vagina, protuding from vulva
|
Sarcoma botryoides
|
|
|
Characteristics of a fibroadenoma in breast
|
Small, mobile, firm mass with sharp edges
|
|
|
What breast tumor is the most common tumor in those <25 years old
|
Fibroadenoma
|
|
|
What happens to fibroadenomas with increased estrogen and are they malignant?
|
Increase size and tenderness with increased estrogen; not a precursor to breast cancer
|
|
|
Characteristics of intraductal papilloma in breast
|
Small tumor that grows in lactiferous ducts. Typically beneath areola. Serous or bloody nipple discharge
|
|
|
Small tumor that grows in lactiferous ducts. Typically beneath areola. Serous or bloody nipple discharge
|
Intraductal papilloma
|
|
|
Are intraductal papillomas malignant or benign
|
Slight increase in risk for carcinoma
|
|
|
Characteristics of Phyllodes tumor
|
Large bulky mass of connective tissue and cyssts. "Leaf-like" projections from cyst wall ulceration of overlying skin.
|
|
|
Phyllodes tumor: when most common for pts and malignant or benign
|
Most common in 6th decade. Some may become malignant
|
|
|
What is vaginal adenosis?
|
Precursor lesion to clear cell adenocarcinoma. Mucosal columnar epithelium lined crypts in areas normally stratified squamous
|
|
|
Precursor lesion to clear cell adenocarcinoma. Mucosal columnar epithelium lined crypts in areas normally stratified squamous
|
Vaginal adenosis
|
|
|
What is a papillary hidradenoma of the vulvar?
|
Most common benign neoplasm of vulvar. Origniate from apocrine sweat glands. Labial nodule that ulcerates and bleeds. Rx - excision
|
|
|
Most common benign neoplasm of vulvar. Origniate from apocrine sweat glands. Labial nodule that ulcerates and bleeds. Rx - excision
|
Papillary hidradenoma of vulvar
|
|
|
Vulvar squamous carcinoma is associatedw ith which viruses?
|
HPV 16, 18
|
|
|
What is the single most important prognostic factor for malignant breast tumors?
|
Axillary lymph node inolvement
|
|
|
What tumor fills breast ductal lumen?
|
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
|
|
|
Early malignancy without basement membrane penetration that fills ductal lumen of breast
|
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
|
|
|
Early malignancy that fills intralobular ductules and acini without basement membrane penetration
|
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
|
|
|
What malignant breast tumor is the worst and most invasive?
|
Invasive ductal
|
|
|
What malignant breast tumor is the most common?
|
Invasive ductal
|
|
|
What are the characteristic of an invasive ductal tumor?
|
Firm, fibrous mass. Small, glandular, duct-like cells
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of invasive lobular breast tumors?
|
Orderly row of cells "Indian file"
|
|
|
Which malignat breast tumor has often multiple present bilaterally and has orderly row of cells.
|
Invasive lobular
|
|
|
What malignant breast tumor is ductal and has central areas of caseous necrosis?
|
Comedocarcinoma
|
|
|
Characteristics of an inflammatory breast tumor
|
Dermal lymphatic invasion by breast carcinoma. Peau d'orange . 50% survival in 5 yrs
|
|
|
Dermal lymphatic invasion by breast carcinoma. Peau d'orange . 50% survival in 5 yrs
|
Inflammatory breast tumor
|
|
|
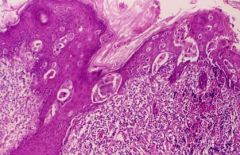
Describe Paget's disease and Paget cells
|
Disease = eczematous patches on nipple. Cells = largecells in epidermis with clear halo
|
|
|
Paget's disease suggests what and is seen in what two parts of the female
|
Suggest underlying carcinoma. Breast and vulva
|
|
|
Describne a mucinoid (colloid) carcinoma
|
Pools of extracellular mucus surrounding clusters of tumor cells. Having a gelatinous consistency
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of "breast lumps" from age 25 to menopause?
|
Fibrocystic disease
|
|
|
When do you get pain with fibrocystic disease? Bilateral or unilateral?
|
Premenstrual; bilateral
|
|
|
What are the four different types of fibrocystic disease?
|
1. Fibrosis 2. Cystic 3. Sclerosing adenosis 4. Epithelial hyperplasia
|
|
|
Describe the features of fibrosis type fibrocystic disease
|
Hyperplasia of breast stroma
|
|
|
Describe the features of cystic type fibrocystic disease
|
Fluid filled, blue dome
|
|
|
Describe the features of sclerosing adenosis fibrocystic disease. What is it often confused with?
|
Increasing acini and intalobular fibrosis; microcalcifications; proliferation of small ductules/acini in lobule - pattern often confused with infiltrating ductal cancer
|
|
|
Describre the features of epithelial hyperplasia fibrocystic disease. Who does it occur in ?
|
Increase in number of epithelial cell layers in terminal duct lobule. Ducts are estrogen sensitive. Increase risk of carcinomna with atypical cells. Occurs in women > 30 years of age
|
|
|
Describe features of fat necrosis in the breast and how it occurs typically?
|
A benign painless lump; lipid laden macrophages, mammographic calcifications may be present; forms as a result of injury to breast tissue.
|
|
|
What is acute mastitis, when and how does it happen, and what is the most common pathogen?
|
Breast abscess; during breast-feeding, increased risk of bacterial infection through cracks in the nipple; S. aureus is the most common pathogen
|
|
|
Breast abscess; during breast-feeding, increased risk of bacterial infection through cracks in the nipple; S. aureus is the most common pathogen
|
Acute mastitis
|
|
|
What drugs cause gynecomastia?
|
psychoactive drugs, Spironolactonee, Digitalis, Cimetidine, Alcohol, Ketoconazole (Some Drugs Creat Awesome Knockers)
|
|
|
What are two pathologic conditions that lead to gynecomastia
|
Hyperestrogenism (cirrrhosis, testicular tumor, puberty, old age), Klinefelter's syndrome
|
|
|
Dysuria, frequency, urgency, low back pain are symptoms of what in a male
|
Prostatitis
|
|
|
The prostate gland undergoes _________ in BPH
|
Hyperplasia (not hypertrophy)
|
|
|
Why does the prostate gland undergo hyperplasia in BPH?
|
Age-related increase in estradiol with possible sensitization of the prostate to the growth-promoting effects of DHT
|
|
|
BPH is characterized by a nodular enalargement of what lobes?
|
Periurethral (lateral and middle) lobes
|
|
|
BPH leads to what complications of the urinary tract
|
Distention and hypertrophy of the bladder, hydronephrosis and UTIs
|
|
|
Is BPH a premalignant lesion
|
No
|
|
|
What is the lab finding associated with BPH
|
Increased prostate specific antigen (PSA)
|
|
|
Where do prostatic adenocarcinomas arise from typically?
|
Posterior lobe (peripheral zone)
|
|
|
How are prostatic adenocarcinomas most frequently diagnosed
|
By digital rectal examination (hard nodule) and prostate biopsy
|
|
|
What are useful tumor markers of prostatic adenocarcinoma
|
Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) and PSA (increased total PSA, with DECREASED fraction of free PSA)
|
|
|
What does lower back pain and an increase in serum alkaline phosphatase and PSA indicate?
|
Prostatic adenocarcinoma osteoblastic metastases
|
|
|
What is the histological finding in prostatic adenocarcinoma
|
Small infiltrating glands with prominent nucleoli
|
|
|
Name of condition for undescended testis (one or both)
|
Cryptorchidism
|
|
|
What increases the risk of cryptorchidism and what does cryptoorchidism increase the risk of
|
Prematureity increases risk of cryptorchidism; Increased risk of germ cell tumor
|
|
|
What is the most common testicular tumor
|
Seminoma
|
|
|
Seminomas affect males mainly in the age range
|
15-35
|
|
|
Describe the histological findings of a seminoma
|
Large cells in lobules with watery cytoplasm and a "fried egg" appearance
|
|
|
Which testicular germ cell tumor is malignant, presents with painless testicular enlargement, is radiosensitive, and has late metastasis and excellent prognosis?
|
Seminoma
|
|
|
Which testicular tumor is malignant, pianful, and has a glandular/papillary morphology, and can differentiate to other tumors?
|
Embryonal carcinoma
|
|
|
What is the morphology of an embryonal testicular carcinoma?
|
Glandular/papillary morphology
|
|
|
What testicular tumor has Schiller-Duval bodies and what do these bodies resemble?
|
Yolk sac (endodermal sinus) tumor, resembles primitive glomeruli
|
|
|
What is the tumor marker for yolk sac testicular tumor?
|
Increased alpha-fetoprotein
|
|
|
What testicular tumor has an increase in hCG levels and is malignant?
|
Choriocarcinoma
|
|
|
What is differnet about male teratomas?
|
Mature teratoma in males is most often malignant
|
|
|
What percentages of testicular tumors are germ cell tumors and what percentage are non-germ cell
|
95% germ cell. 5% non-germ cell
|
|
|
Name the testicular germ cell tumors
|
Seminoma, embryonal carcinoma, yolk sac tumor, choriocarcinoma, teratoma
|
|
|
Name the testicular non-germ cell tumors
|
Leydig cell, Sertoli cell, Testicular lymphoma
|
|
|
What are some common findings in Leydig cell tumors
|
Benign, contains Reinke crystals; usually androgen producing, gynecomastia in men, precocious puberty in boys
|
|
|
Benign, androblastoma from sex cord stroma in testicle
|
Sertoli cell tumor
|
|
|
What is the most common testicular cancer in older men?
|
Testicular lymphoma
|
|
|
How are varicoceles caused?
|
Dilated vein in pampiniform plexus (can be caused by blockage of left renal vein - renal cell carcinoma) or blockage of right spermatic vein (retroperitoneal fibrosis)
|
|
|
How are hydroceles caused?
|
Increased fluid secondary to incomplete fusion of processus vaginalis --> peritoneal fluid can travel down patent processus vaginalis
|
|
|
How are spermatoceles caused?
|
Dilated epididymal duct
|
|
|
What are features of Bowen's disease? In what percent can it progress to invasive SCC?
|
Gray, solitary, crusty plaque, usually on shaft of penis or on scrotum; 10%
|
|
|
When is the peak incidence of Bowen's disease
|
5th decade of life
|
|
|
What are features of Erythroplasia of Queyrat?
|
Red velvety plaques, usually nvovling the glans, precursor to invasive SCC
|
|
|
Red velvety plaques, usually nvovling the glans, precursor to invasive SCC of penis
|
Erythroplasia of Queyrat
|
|
|
Multiple papular lesions of penis; affects younger age group than other subtype; suually does not become invasive
|
Bowenoid papulosis
|
|
|
What virus is Bowen's disease, Erythroplasia of Queyrat, and Bowenoid papulosis associatd with
|
HPV 16
|
|
|
What is the biggest risk factor for SCC of the penis
|
Not being circumcised
|
|
|
What is peyronie's disase
|
bent penis due to acquired fibrous tissue formation
|
|
|
Paget's cells: large cells in epidermis with clear halo
|

