![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Hypoxia |
Not enough oxygen in the tissue |
|
|
|
Hypoxemia |
Decrease of oxygen in the bloodstream |
|
|
|
Thrombosis |
Formation of blood clot |
|
|
|
Cyanosis |
Bluish descoliration of the skin |
|
|
|
Dyspnea |
Difficult/Painful breathing |
|
|
|
Apnea |
Abcess of breathing |
|
|
|
Bradypnea |
Slow and shallow breathing |
|
|
|
Tachypnea |
Fast breathing |
|
|
|
Hypertermia |
High temperture |
Febrile, pyraxia |
|
|
Hypothermia |
Low temperture |
|
|
|
Systolic Pressure |
The pressure of the blood when heart is contracting |
|
|
|
Diastolic Pressure |
When the heart is at rest between contractions |
|
|
|
Normal B/P |
BELOW 120/80 |
|
|
|
Pulse pressure |
The diffrence between the systolic and diastolic pressure |
|
|
|
Hypertension |
140/90 |
|
|
|
Cuff is too small |
Blood pressure will ⬆ |
|
|
|
Cuff is too big |
Blood pressure will ⬇ |
|
|
|
Vitals for pain |
B/P, Pulse and Respirations |
|
|
|
Nursing roles |
Caregiver, Advocate, Teaching, Coordinator |
|
|
|
Nursing practice Act |
Each state has 1 and it tells us nurses what to do |
|
|
|
Neglegance |
Failure to do something that causes hard to patient |
|
|
|
Malpractice |
Negligence of professional personel |
|
|
|
Living will |
Patient writes down what he wants in case something were to happen |
|
|
|
Direct Power of Attorney |
Designated person whom decides for the patient if something goes wrong |
|
|
|
Defamation |
To ruin someones reputation |
|
|
|
Libel |
Written defamation |
|
|
|
Slander |
Verbal defamation |
|
|
|
Assult |
Threat verbally |
|
|
|
Battery |
Physical touch, against their will |
|
|
|
Restraints |
Must have drs order Harm to self or others |
|
|
|
Standards of care |
Expectations we set as LVNS |
|
|
|
Good Samaritan Act |
Protects professionals who give emergency care outside the health care system(under scope of practice) |
|
|
|
Client Advocate |
Protects patients rights |
|
|
|
Communication |
Sender➡Message➡Receiver➡Feedback |
|
|
|
Verbal communication |
Verbal, written |
|
|
|
NON-verbal |
Head gesture, body language |
|
|
|
Empathy |
Ability to understand someones situation "walk in their shoes" |
|
|
|
Ethonsintrism |
The idea that ones race is better than anyone else's race |
|
|
|
Stereotyping |
Generalization |
|
|
|
Maslows |
Psychosocial Safety and security Love and belonging Self esteem Self actualization |
|
|
|
Nursing process |
Assest: collect date Diagnose: whats going on Plan: Goal, interventions Implement: put in action document Evaluate: re-assest |
|
|
|
Subjective |
Patient can tell you |
|
|
|
Objective |
Evidence, lab results, change of mood. Vital signs |
|
|
|
Visual assesment |
Palpitation Percussion Osculation |
|
|
|
Chain of infection |
Causitive agent Reservoir Portal of exit Mode of transfer Portal of entry Susceptible host |
|
|
|
Pathogen |
Disease causing microorganism |
|
|
|
Asepsis |
Destruction of infectious agents after they leave the body |
|
|
|
Medical asepsis |
Redusing the risk for transmission of orgasims |
|
|
|
Surgical asepsis |
Getting rid of microorganism and spores in materials that prevents patients from having them |
|
|
|
Steralization |
Removement of microorganisms and spores reducing the # of organisms |
|
|
|
Nosconomial |
Facility acquired agent |
|
|
|
Body mechanics |
Prevents injury |
|
|
|
Supine |
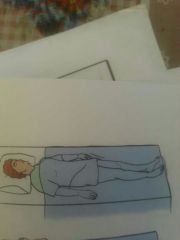
|
|
|
|
Prone |
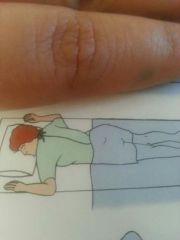
|
|
|
|
Dorsal recumbent |

Birth position |
|
|
|
Lithotomy |
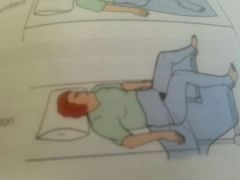
Papsmear |
|
|
|
Sims |
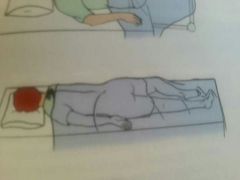
|
|
|
|
Knee chest |
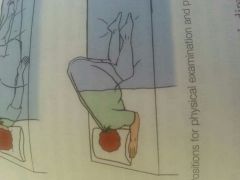
|
|
|
|
Adbuction |
Moving body part away from midline |
|
|
|
Adduction |
Moving body part towards midline of body |
|
|
|
Foot board |
To prevent foot drop |
|
|
|
Atrophy |
Wasting away of muscle not in use |
|
|
|
Contracture |
Permanate shortage of muscle |
|
|
|
Hypostatic pneumonia |
Inability to cough out secretions |
|
|
|
Atteletics |
Lung collapse |
|
|
|
Pressure ulcer |
Skin integrity, break in skin due to unrelieved pressure |
|
|
|
Stage 1 pressure ulcer |
Non-blanchable redness |
|
|
|
Stage 2 |
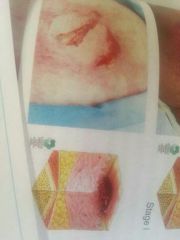
Irritma with vesicle |
|
|
|
Stage 3 |
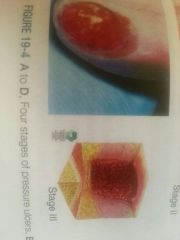
Sub Q |
|
|
|
Stage 4 |
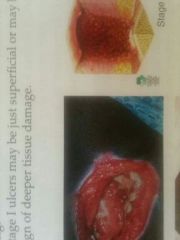
Visiable to the bone |
|
|
|
Edema |
Swelling |
|
|
|
Acitis |
Accumulation of fluid in abdomen |
|
|
|
Emesis |
Vommiting |
|
|
|
Flatulant |
Excessive gas |
|
|
|
Jondis |
Yellowing of skin |
|
|
|
Necrosis |
Dying of tissue |
|
|
|
Incontenence |
Inability to hold urine |
|
|
|
Retention |
Inability to release urine |
|
|
|
Anuria |
Abscess of urine |
|
|
|
Polyuria |
Excessive urination |
|
|
|
Hematuria |
Blood in urine |
|
|
|
Nocturia |
Frequent urinitation at night |
|
|
|
Oz➡mL |
1oz➡ 30ml |
|
|
|
3 sources of energy |
Carbs, fats, protein |
|
|
|
Elimination |
Process of excreating of waste products |
|
|
|
Clear liquid diet |
Anything light can pass through Low in protein, minerals, vitamis, fats and calcium |
|
|
|
Full liquid diet |
Anything that has milk in it Low in iron, protein, calories |
|
|
|
High in calories |
Tasty and salty |
|
|
|
Fecal impaction |
Precense of hard stool |
|
|
|
Normal stool |
Bile, water, fiber, bacteria |
|
|
|
Types of digestion |
Mechanical and chemical |
|
|
|
Insensible fluid lost |
Output that can not be measurable Sweat, and breathing |
|
|
|
Digestion take place 1st |
Mouth |
|
|
|
Derma |
Skin |
|
|
|
Myo- |
Muscle |
|
|
|
Arthro |
Joint |
|
|
|
Osteo |
Bone |
|
|
|
Phlebo |
Vein |
|
|
|
Cyte |
Cell |
|
|
|
-emia |
Blood condition |
|
|
|
-oma |
Tumor |
|
|
|
-stomy |
Artificial opening |
|
|
|
-ectomy |
Excission, cutting out |
|
|
|
-tomy |
Process of cutting |
|
|
|
S or O |
Pain |
|
|
|
S or O |
Nausea |
|
|
|
S or O |
Insomnia |
|
|
|
S or O |
Skin color |
|
|
|
Prulent |
Containing pus |
|
|
|
Active ROM |
Patient can do for himself |
|
|
|
Passive ROM |
Performed by caregiver or RNA |
|

