![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
QC system |
minimize analytic errors |
|
|
QA |
all the systemic action necessary to produce adequate patient care |
|
|
Qualitative |
+/- |
|
|
Quantitative |
actual number |
|
|
Mean, Median, Mode Range |

|
|
|
Gaussian Curve/Bell Curve |
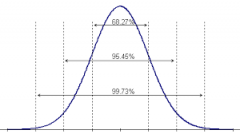
|
|
|
CV |
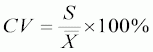
The smaller the CV the more precise; less then 5% is good |
|
|
Accuracy |
agrees with the true value |
|
|
Precision |
agreement between replicate measurements |
|
|
Random Error |
related to Precision |
|
|
Systemic error |
related to accuracy; effects all samples |
|
|
Bias |
the amount by which an analysis varies from the correct result |
|
|
Reference interval |
range that includes 95% of a healthy population |
|
|
Evaluation studies |
|
|
|
Interference studies |
|
|
|
Comparative method |
may be the reference method |
|
|
Linear regression y-axis |
test method |
|
|
Linear regression x-axis |
reference |
|
|
Linear regression slope |
constant systemic error |
|
|
Linear regression measures |
constant systematic error: The constant difference between the test method and the comparative method are proportional to analyte concentration |
|
|
Random Error |
measure by the standard error of the estimate |
|
|
Proportional error |
differences between the test method and the comparative method are proportional to analyte concentration |
|
|
1 2s |
Exceeds +/- 2SD- Warning rule |
|
|
1 3S |
Exceeds the mean by +/- 3DS Random error |
|
|
2 2S |
exceeds the same mean either by +2 or =2 Systemic error |
|
|
R 4S |
one point +2SD and -2SD form the other Random error |
|
|
4 1S |
Four exceed the mean by either =/+1SD around the mean systemic error |
|
|
10 X |
10 points fall on one side of the mean |
|
|
Westgard rules: random error |
13S, R4s |
|
|
Westgard rules: systemic error
|
2 4 10 2s 1S x |
|
|
Diagnostic specificity |
|
|
|
Diagnostic sensitivity |
|
|
|
Positive Predictive Value |
TP ------ X100 TP+FP |
|
|
Negative Predictive Value |
TN ---------- X 100 TN+FN |
|
|
Management styles |
|
|
|
Theory X |
employees are lazy, motivated by money: authoritarian |
|
|
Theory Y |
employees are creative and willing to put talent to use: participative |
|
|
Hertzberrg Theory |
|
|
|
Work teams |
|
|
|
Fixed cost |
don't change if the volume changes |
|
|
Variable cost |
do change with workload |
|
|
Total cost |
Fixed+variable |
|
|
Direct cost |
test specific cost |
|
|
Indirect cost |
expenditures after direct costs have been made |
|
|
Number of tests to break even (T)= |
Fixed cost ------------------- A-V A: average revenue of the lab V: variable cost |
|
|
Revenue |
F (total fixed cost) CM CM=(A-V)/A |

