![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cranial Nerves
How many? Where? |
12 Pairs
Arise from underside of brain |
|
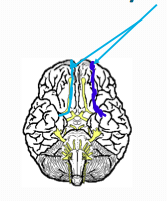
What?
What number? What is function? |
Olfactory
I Smell Sensory Anosmia -loss of smell |
|
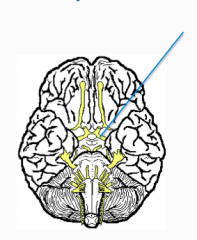
What?
What number? What is function? |
Optic
II Vision Sensory Anopsias - blindness in eye |
|
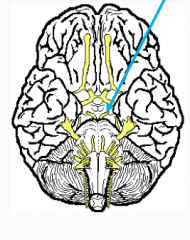
What?
What number? What is function? |
Oculomotor
III Motor (Voluntary) - moves eyeball and eyelid Double vision, ptosis (upper eyeliddroop) if III damaged |
|
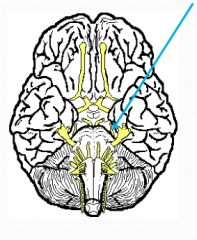
What?
What number? What is function? |
Trochlear
IV Motor - Moves eye downward and laterally SMALLES CRANIAL NERVE Doublevision; decreased ability to rotate if IV damaged |
|
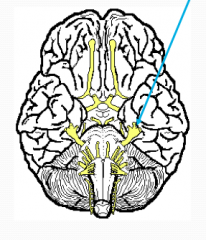
What?
What number? What is function? (3 devisions) |
Trigeminal
V Opthamalic Division -sensory, anterior scalp, nose eyelid sensation; crying Maxillary Division - sensory, pain & tough of palate, upper teeth, skin of cheek, upper lip, lower eyelid Mandibular Division - sensory & motor; chewing, sensations from lower teeth, gum and lip LARGES CRANIAL NERVE Eye cannot be moved laterally if VIdamaged |
|
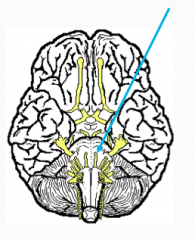
What?
What number? What is function? |
Abducens
VI Motor - Extrinsic eye muscles, abducts eyeball Bell’s palsy if damaged |
|
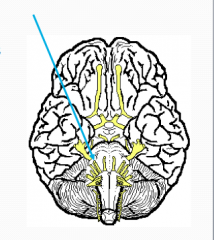
What?
What number? What is function? |
Facial
VII Motor - expression Sensory - taste large nerve |
|
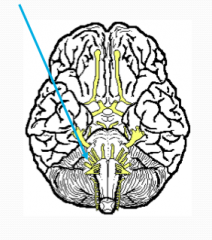
What?
What number? What is function? |
Vestibulocochlear
VIII Vestibular branch - balance Cochlear branch - hearing |
|
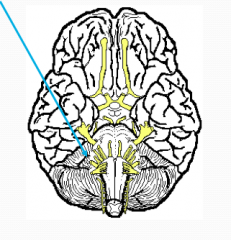
What?
What number? What is function? |
Glossopharynegeal
IX Motor - swallowing Swallowing and taste impaired if IXdamaged |
|
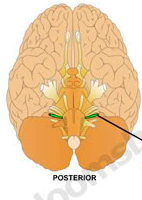
What? What number? What is function?
|
Vagus
X -only cranial nerve to extend beyond head and neck - sensory & motor automatic |
|
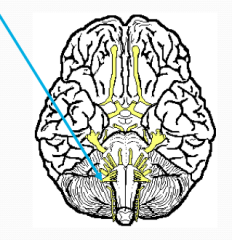
What?
What number? What is function? |
Accessory
XI Motor - muscles of soft palate, pharynx and larynx, swallowing shrugging shoulders and turning head difficult if damaged |
|
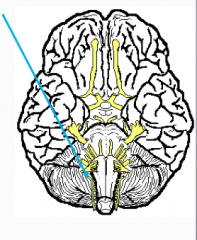
What?
What number? What is function? |
Hypoglossal
XII Motor - movement of tongue, chewing, swallowing if damaged, difficulty speaking and swallowing |
|
|
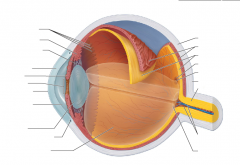
What three layers does the eyeball contain?
|
Fibrous
Vascular Sensory |
|
|
internal cavity is filled with fluids
|
humors
|
|
|
Fibrous Layer
|
outermost layer
two regions sclera and cornea |
|
|
sclera
|
opaque posterior region
protects and shapes eyeball anchors extrinsic eye muscles |
|
|
Cornea
|
Transparent anterior 1/6 fibrous layer
bends light as it enters the eye numerous pain receptors contribute to blinking and tearing reflexes |
|
|
Vascular layer
|
middle pigmented layer
three regions: choroid ciliary body iris |
|
|
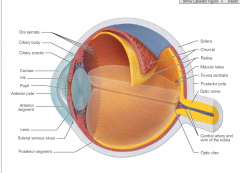
choroid region
|
posterior portion of the uvea
supplies blood to all layers of the eyeball brown pigment absorbs light to prevent visual confusion |
|
|
Ciliary Body
|
ring of tissue surrounding the lens
controls lens shape and holds lens in position |
|
|
Iris
|
colored part of the eye
|
|
|
Retina
|
sensory layer
two-layered membrane Pigmented layer (outer): absorbs light and prevents its scattering stores vitamin A Neural layer (inner) photoreceptor cells that transmit and process signals |
|
|
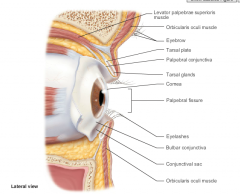
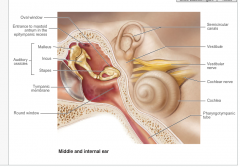
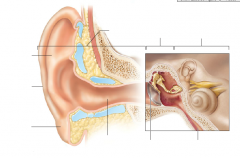
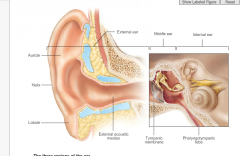
external ear is composed of?
|
Auricle: helix (rim)lobule (earlobe) External acoustic meatus: short, curved tube like with skin bearing hairs tympanic membrane eardrum |
|
|
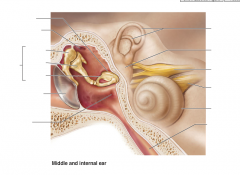
middle ear
|
a small, air-filled, muscosa-lined cavity in the temporal bone
|
|
|
what is the epitymanic recess?
|
superior portion of the middle ear
|
|
|
what is the pharngotmpanic tube?
|
connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx
|
|
|
what are the three ear bones?
|
malleus
incus stapes |
|
|
What are the three biggest overview of spinal nerves?
|
1. send info from sensory receptors to spinal cord
2. carry info from spinal cord to effectors 3. spinal nerves are mixed nerves because they contain both sensory and motor axons |
|
|
Spinal nerve division
|
31 pairs
8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral 1 coccygeal |
|
|
Spinal nerve plexuses
|
groups of nerves that work together
1. cervical plexus 2. brachial plexus 3. lumbar plexus 4. sacral plexus |
|
|
cervical plexus
|
anterior rami - branches of the spinal nerve
phrenic nerve - diaphragm, breathing |
|
|
Brachial plexus
|
serves shoulders and upper limbs
|
|
|
Lumbar Plexus
|
skin and muscles of abdominal wall
|
|
|
sacral plexus
|
gluts, most of lower limbs
|
|
|
whatis a reflex?
|
quick, automatic, subconscious, involuntary response to stimuli
|
|
|
What is the functional unit of nervous system?
|
nerve pathway
|
|
|
What are the reflex arc components?
|
receptor
sensory neurons integration center motor neuron effector |
|
|
Stretch Reflexes
|
Knee jerk reflex
|
|
|
Deep tendon Reflex
|
Biceps, triceps
|
|
|
Flexor Reflex
|
hamstring (steping on a nail)
|
|
|
Superficial Reflex
|
Pantar reflex (stroking foor)
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

