![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
164 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bartholin Glands
|
help secret mucus during intercouese. found on either side of the vaginal orifice
|
|
|
utero-ovarian ligament
|
holds ovary in place on either side of the uterus
|
|
|
ovarian follicles
|
contains ovum and corpus luteum (when follicle errupts)
|
|
|
layers of the uterus
|
1. endometrium = inner
2. myometrium = middle 3. uterine serosa. = outer |
|
|
menarch
|
pre-stage or menstrual cycle
|
|
|
amenorrhea
|
absence of menstrual cycle
|
|
|
menorrhagia
|
irregular/excessive bleeding g during menstruation
|
|
|
metrorrhagia
|
irregular bleeding from uterus btwn menstrual periods
|
|
|
human chronic gonadotropin (hCG)
|
placenta produces this hormone
|
|
|
colp/o
|
vagina
|
|
|
eipisi/o
|
vulva
|
|
|
gravido/o
|
pregnancy
|
|
|
hyster/o
|
uterus
|
|
|
nat/i
|
birth
|
|
|
phor/o
|
to bear
|
|
|
-arche
|
beginning
|
|
|
-gravida
|
pregnant
|
|
|
-parous
|
bearing, bringing forth
|
|
|
-partum
|
birth, labor
|
|
|
episitomy
|
process of cutting vulva
|
|
|
primigravida
|
fist time being pregnant
|
|
|
dysplasia
|
abnormal growth of cells
|
|
|
stage 2 cervical cancer
|
cancer spread throughout cervix
|
|
|
colpscope
|
lighted endoscope put in vagina and cervix
|
|
|
uterus endometriosis
|
endometrial tissue outside uterus is inflamed
|
|
|
uterus fibroids/leiomyomas
|
cancer or growth that can grow anywhere in endometrium
|
|
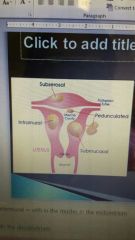
|
1. subserosal grows underneath the dnodmytrium.
2.intramural in the muscles of the endometrium 3. peduncluated stalk, outgrowth of uterus 4. submucosal below |
|
|
polycystic ovary syndrome
|
disorder of hormone secretion. symptom is irregular menstrual cycle
|
|
|
breast cancer
|
usually originates in glandular tissue or milk ducts
|
|
|
placenta previa
|
placenta is implanted in lower segment
|
|
|
ectopic pregnancy
|
pregnancy when egg implants itself outside the uterus
|
|
|
pregnancy test
|
detects for human chronic gonadotropin (released by fertilized egg (
|
|
|
transvaginal ultrasonography
|
used transducer inserted into vagina to view female internal female reproductive organs. able to detect small growths in abdomen
|
|
|
laparoscopy
|
inspect and removal of ovaries, fallopian tubes and diagnostic and treatment of endometriosis
|
|
|
cryosurgery
|
use liquid nitrogen to freeze section of cervix and destroy any precancerous cells
|
|
|
dilation and curettage
|
dilate cervix to scrape endometrial lining with curette. used after miscarriage
|
|
|
total abdominal hysterectomy
|
removal of uterus and cervix ONLY
|
|
|
vaginal hysterectomy
|
removal of uterus and cervix through incision deep inside the vagina. remove by vaginal canal. cuts ligaments attached to uterus
|
|
|
episiotomy
|
surgical incision through perineum to enlarge the vagina and assist in childbirth
|
|
|
bulbourethro glabds/cowper
|
secrete thin fluid during intercourse
|
|
|
tubal ligation
|
sterilization procedure when fallopian tubes are tied in 2 places and tubes between ligation are removed
|
|
|
Apgar score
|
numeric result to evaluate new born physical condition
|
|
|
perineum
|
located between the an us and scrotum (perineal in females)
|
|
|
epididymis
|
Where sperm mature and are stored
|
|
|
seminiforous tubules
|
create testosterone
|
|
|
prepuce
|
foreskin covering the glans penis
|
|
|
formation of sperm
|
1. seminiforous tubules
2. epididymis 3. vas deferens 4. ejaculatory duct 5. urethra 6. penis |
|
|
balan/o
|
glans penis
|
|
|
orch/o
|
testes
|
|
|
semin/i
|
semen
|
|
|
-cele
|
herniation, protrusion
|
|
|
-one
|
hormone
|
|
|
-pexy
|
foxation, put in place
|
|
|
cryptochrism
|
undescended testes
repaired by orchiopexy |
|
|
seminoma cancer
|
arises from embryonic cells in the testes. secrete human chronic gonadotropic
|
|
|
hydrocele
|
lots of fluid in scrotum
|
|
|
testicular torsion
|
twisting of spermatic cord that decreases blood flow
|
|
|
varicocele
|
enlargement of veins in the spermatic cord
|
|
|
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
|
enlargement if prostate glad
usually have trouble emptying bladder |
|
|
peyroine
|
abnormal scar tissue inside penis, causes bending of an erect penis
|
|
|
phimosis
|
narrowing of the prepuce. foreskin will come over a the opening of the urethra
|
|
|
priapism
|
blood can't be drained from penis. does not need to by aroused
happens with patients who are anemic |
|
|
spermatocele
|
cyst in the epididymis
|
|
|
chlamydia
|
STD
males- burning when urinating and white discharge females- can be asymptomatic with yellow discharge |
|
|
gonorrhea
|
inflammation if mucosa of genital tract
males- dysuria yellow mucopurulent discharge females - maybe asymptomatic with vaginal discharge |
|
|
herpes genitalis
|
Infection of skin and genital due to herpes simplex 2
-shows signs of blisters and redness |
|
|
Human Papillomavirus
|
infection if skin and mucous membranes outside the genital
|
|
|
prostate specific antigen
|
levels of prostate specific antigen in blood. made by prostate gland. high levels means enlargement of prostate
|
|
|
digital rectal examination
|
use fingers to determine size and shape of prostate and rectal wall
|
|
|
vasectomy
|
cutting and tying the vas deferens
|
|
|
Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP)
|
widen urethra by making small incisions in bladder and prostate gland
|
|
|
transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
|
removal of prostatic tissue through urethra using a resectoscope
|
|
|
cortex
|
outer kidney
|
|
|
medulla
|
inner kidney
|
|
|
urine production
|
1.glomerular filtration (removes water salts sugar and urea from the bloodstream and collect it in Bowman capsule
2. tubular reabsorption 3. tubular secretion - blood stream to renal tubule |
|
|
renin
|
when blood flows too slow, this hormone will increase blood pressure
|
|
|
glomerulus
|
collection of capillaries
|
|
|
renal tubule
|
attached to bowman capsule
|
|
|
efferent arteries
|
EXIT and leave the kidney
|
|
|
renal pelvis
|
Reservoir in kinsey to collect urine
|
|
|
formation and expelling urine
|
1. bloodstream 2. glomerulus 3. bowmans capsule 4. renal tubule 5.renal pelvis 6 . ureter 7.bladder 8.urethra 9. urinary meatus
|
|
|
cyst/o
|
urinary Bladder
|
|
|
dips/o
|
thirst
|
|
|
pyel/o
|
renal pelvis
|
|
|
vesic/o
|
urinary bladder
|
|
|
-cele
|
hernia
|
|
|
-poietin
|
substance that forms
|
|
|
-tripsy
|
to crush
|
|
|
genitourinary
|
organs of reproduction and urination
|
|
|
hydronephrosis
|
buildup of urine in kidneys due to obstruction of urine flow
|
|
|
renal cell carcinoma
|
hypernephroma cancerous tumor
|
|
|
Diabetes Insipidus
|
lack of ADH response, prevents water from being absorbed
|
|
|
diabetes mellitus
|
inadequate secretion ot improper utilization of insulin
|
|
|
polyphagia
|
Always eating
|
|
|
creatine clearance test
|
test amount of creatine in urine. if a lot indicates kidney damage
|
|
|
Hemodialysis
|
removal of waste products from blood through a machine
|
|
|
peritoneal dialysis
|
removal of waste products through peritoneum of abdominal cavity
|
|
|
pyelolithotomy
|
incision into renal pelvis to remove a stone
|
|
|
diuretic
|
increases amount of urine secreted
|
|
|
enuresis
|
involuntary discharge of urine
|
|
|
diuresis
|
condition of excretion increased amounts of urine
|
|
|
hemostasis
|
blood clotting
|
|
|
basophils
|
contains heparin to decrease blood clotting and histamine for allergic reacions
|
|
|
eosinophils
|
will 'eat' substances that cause the allergic reaction
|
|
|
neutrophils
|
phagocytes
|
|
|
monocytes
|
phagocytes to fight disease
|
|
|
lymphocyte
|
creates antibodies and memory cells
|
|
|
megakaryocytes
|
tiny fragments that break off to form Platelets
|
|
|
fibrin
|
elastic fiber protein that helps with clotting
|
|
|
-apheresis
|
removal
|
|
|
-cytosis
|
slight increase in the number of cells
|
|
|
pernicious anemia
|
disorder in the number of RBC bc can't absorb B12
|
|
|
polycylhemia vera
|
increased RBC makes blood thick
|
|
|
hyperplastic
|
keeps produces RBC
|
|
|
autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura
|
patients body attacks own platelets
|
|
|
mononucleosis
|
increased amount of leukocytes
|
|
|
prothrombin test
|
test ability to clot
|
|
|
apheresis/plasmaphersis
|
separation of blood into parts
|
|
|
pleurodynia
|
pain of the outer cavity
|
|
|
rales
|
crackling or popping sound bc of fluid in alveoli
|
|
|
asphyxia
|
with out a puls
|
|
|
rhonchi
|
rumbling sound due to obstruction in bronchi. blocked by sputum (materials expelled by upper respiratory)
|
|
|
stridor
|
whistling sound during inspiration due to obstruction in larynx or pharynx
|
|
|
wheeze
|
airy noise due to narrow passage way
|
|
|
croup
|
viral infection in kids due to obstruction in larynx
|
|
|
pertusis
|
whooping cough infection of larynx bronchi and trachea
|
|
|
pneumonia
|
infection of pus in aveoli
|
|
|
atelectasis
|
collapsed lung
|
|
|
hypoxemia
|
decreased oxygen in the BLOOD
|
|
|
acid fast bacilli
|
test materials dispelled by the upper respiratory (sputum)
|
|
|
pulse oximetery
|
measure oxygen in the blood
|
|
|
tracheostomy
|
creation of artificial opening in trachea
|
|
|
tracheotomy
|
Incision of artificial trachea
|
|
|
blood flow
|
deoxygenated blood will flow into the superior/inferior vena cava to the right atrium through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle through semilunar valve to the pulmonary artery to the lung. now oxygenated blood will flow to the pulmonary vein to the left atrium through the bicuspid/mitral valve to the left ventricle through a semilunar valve then to the aorta
|
|
|
myocardium
|
middle and thickest layer of the heart
|
|
|
lub
|
the closing of AV valves
|
|
|
sphygmic
|
pertaining to pulse
|
|
|
myocardial infarction
|
heart attack
|
|
|
myocardial ischemia
|
restriction of blood. can relieve through a stent
|
|
|
nonocclusive thrombus
|
clog that leads to angina
|
|
|
cardiac tamponade
|
compression of the heart due to increased fluid in the pericardium
|
|
|
Coarctation of aorta
|
narrowing of the aorta leads to hypertension
|
|
|
congestive heart failure
|
inefficient cardiac circulation
|
|
|
raynaud disease
|
cyanosis of fingers and toes due to vascular constriction
|
|
|
aneurysm
|
widening I'd the arterial wall
|
|
|
varicose veins
|
swollen and twisted veins due to damaged valves
|
|
|
creatine kinase
|
have increased amounts when muscle is damaged
|
|
|
troponin
|
increase protein release when HEART is damaged
|
|
|
c - reactive protein
|
inflammation measure
|
|
|
doppler sonography
|
sound wave and velocity flow of blood
|
|
|
echocardiography
|
recording of the structure and function of heart during exercise and rest
|
|
|
endarterectomy
|
removal of plaque from the artery
|
|
|
lymphatic right side
|
drains the head neck and thorax
|
|
|
spleen
|
destroys RBC and activates B Cells when antigen present
|
|
|
thymus
|
creates immune response in children
|
|
|
acquired immunity
|
getting a vaccination
|
|
|
passive immunity
|
body creates IgG to fight disease
|
|
|
phylaxis
|
protection
|
|
|
pathology immunodeficiency
|
lack of lymphocytes B and T. no immune system. bubble boy
|
|
|
anaphyalxis
|
severe symptoms
|
|
|
Hodgkins lyphoma
|
malignant tumor in spleen and lymph nodes due to a error in DNA
|
|
|
non hodgkin lyphoma
|
tumors develop from lymphocytes
-follicular lymphoma and large cell lymphoma |
|
|
malignancies multiple myeloma
|
tumor of bone marrow cells. increased IgG and calcium ions. will show a punched out hole in xray
|
|
|
immunoelectrophoresis
|
measure immunoglobulin s based on charge to mass ratio
|

