![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
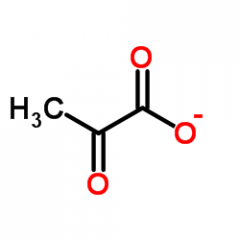
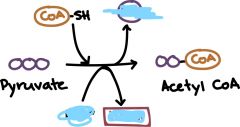
what is this? |
pyruvate |
|
|
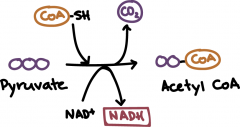
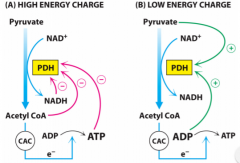
Irreversible step of CA |
pyruvate into CA |
|
|
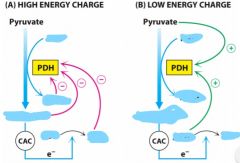
PDH regulation also called: |
critical branch point |
|
|
Critical branch point inhibited by |
high NADH, high AcCoA, high ATP (this is inhibition of PDH) |
|
|
PDH is regulated by what type of enzymes? |
allosteric |
|
|
PDH regulated by what process |
reversible phophorylation |
|
|
PDH actiavted by |
high ADP, low ATP |
|
|
|
|
|
what will positively regulate PDH? |
ADP |
|
|
What does NADH do to PDH? |
inhibit |
|
|
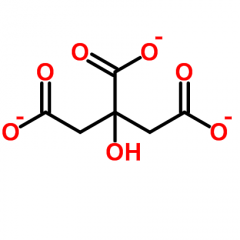
Citrate |
|
|
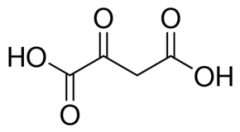
Oxaloacetate |
|
|
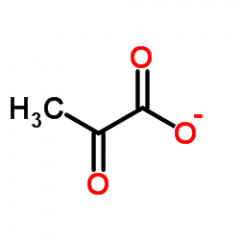
pyruvate |
|
|
what enzyme can immediately be negatively regulated by product? |
succinyl CoA |
|
|
Positive regulators of CAC |
ADP and NAD+ |
|
|
Negative regulators CAC |
ATP, NADH, immediate products |
|
|
regeneration of ATP happens via |
oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
Respiration |
ATP generating process where O2 serves as ultimate e- acceptor |
|
|
CA cycle and FA oxidation happens in the |
mitochondria |
|
|
Protons pumped from matrix into |
intermembrane space |
|
|
Outer membrane permeable or not permeable? |
permeable |
|
|
Inner permeable or impermeable |
impermeable |
|
|
Outer membrane permeability due to |
porin |
|
|
Electrons flow from where to where? |
NADH to Oxygen |
|
|
Flow of electrons to carriers endergonic or exergonic |
exergonic |
|
|
ATP synthesis endergonic or exergonic? |
endergonic |
|
|
What powers ATP synthesis? |
proton gradient established by electrons transferring to electron carrier |
|
|
pH intermembrane sace vs outer |
inter has lower pH values |
|
|
PDH monitors transition from what to what? |
pyruvate to acetyl CoA |

