![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Profundal |
Part of the lake containing bacteria and worm like organisms that can sum dead debris |
|
|
Grasslands |
Found Halfway between equator and poles Covers inferiors of major continent's Converted to agricultural use |
|
|
Biome |
Type of major land ecosystem determined mostly by features of the climate in the area |
|
|
Physical habitat characteristics |
Rocks Water Wind |
|
|
Ecology |
Study of interactions of organisms with each other and with their habitat |
|
|
Competition |
Narrow niche breadth |
|
|
Secondary succession |
Occurs on abandoned agricultural fields |
|
|
Non associative learning |
Simplest of all types of learning |
|
|
Habituation |
A type of learning in which there is a decrease in the response to a repeated stimulus |
|
|
Optimal Forging Theory |
Animals will select food items that maximize their net energy intake per unit of forging time |
|
|
Kin selection |
Favors altruism directed towards relatives |
|
|
Sign stimulus |
Egg outside a goose's nest |
|
|
Cognitive Behavior |
Having information and responding in a manner that suggests thinking is an area of animal behavior |
|
|
Oxytocin |
Stimulates uterine contraction during labor |
|
|
Defective Thyroid |
Loss of weight Increased heart rate Elevate body temperature |
|
|
Parathyroid hormone |
Calcium levels in blood don't drop too low |
|
|
Type I Diabetes |
Deficiency in beta cells |
|
|
Growth Hormone |
Stimulates growth of muscle and bone |
|
|
Vasopressin ADH |
Regulates kidney retention of water Suppressed by alcohol |
|
|
Follicle Stimulating Hormone |
Causes ovaries to become ready for ovulation |
|
|
Luteinizing Hormone |
Stimulates gonadotropin to produce testosterone and triggers ovulation |
|
|
Steroid |
Leads to Liver damage Acne and balding Larger muscles Masculinity in women |
|
|
Hermaphroditism |
Has both testes and ovaries |
|
|
Seminiferous Tubles |
Location of sperm production |
|
|
Ovulation |
Triggered by Luteinizing Hormone |
|
|
Fetus |
After 3rd month |
|
|
Gonorrhea/Chlamydia |
Leads to PID Fallopian tubes can be scarred or blocked |
|
|
HCG Human Chronic Gonadotropin |
Pregnancy tests |
|
|
Genital Herpes |
STD Virus |
|
|
Syphilis |
Leads to Blindness Heart disease Mental deficiency |
|
|
Mesoderm |
Gives rise to Skeleton Muscles Blood vessels Heart |
|
|
Ovary |
Mature ripened fruit containing fertilized seeds |
|
|
Autotrophs |
Plants that produce their own food |
|
|
Stoma |
Opening in the outermost layer of the leaf |
|
|
Vascular Systems |
Helps plants disperse water throughout |
|
|
Male gametophytes |
In a seed plant Pollen grains |
|
|
Gymnosperms |
First seed plants |
|
|
Whorl flower |
Petals that attract pollination |
|
|
Water for fertilization |
Required by ferns |
|
|
Moths |
Attracted to white, heavily scented flowers |
|
|
Plants |
Aquire minerals from the soil |
|
|
Stems |
Framework for positioning of leaves |
|
|
Stomata |
Epidermis of leaves Gases carbon dioxide and oxygen pass |
|
|
Ions |
Regulates tugor pressure within cells of leaves |
|
|
Functions of trichomes |
Regulates temp/ water balance Secrete sticky and toxic substances to deter herbivores |
|
|
Casparin strip |
Keeps water from penetrating the vascular cylinder Forces water to pass through the endodermal cells |
|
|
Transpiration |
Process by which water leaves a plant |
|
|
Cohesion adhesion tension theory |
The way water travels up the length of the stem |
|
|
Asexual reproduction |
Leads to offspring known as clones |
|
|
Runners and Rhizomes |
Reproduce asexually through horizontal stems |
|
|
Dioecious Plants |
Male and female flowers |
|
|
Angiosperms atract pollinaters by |
Nectar Colorful petals Scent |
|
|
Germination of embryo within seed takes place |
Once water and oxygen reach embryo |
|
|
Fruit |
Dissemination of seeds |
|
|
Ethylene |
Hormone put on underipe fruit to hasten ripening |
|
|
Thigmotropism |
Response of plant to touch |
|
|
Gravitropism |
Plants stem grows upward and roots grow downward |
|
|
Auxin |
Primary growth promoting hormone of plants |
|
|
Gibberellin |
Hormone used to space out flowers of grape vines |
|
|
Population |
All members of an interbreeding group or organisms in an area |
|
|
Ecosystem |
Community and non living factors within it interacts |
|
|
Commensalism |
Symbiosis in which one species benefits from the relationship but the other is not affected |
|
|
Community |
All organisms in an area |
|
|
Primary succession |
Grows where no life existed before |
|
|
As a population approaches capacity |
Increased competition for Light Mating sites Shelter Food |
|
|
Niche |
Role an organism plays within an ecosystem |
|
|
Logistic growth model |
N approaches K The growth rate slows |
|
|
Classical Conditioning |
Pavlovs dog salivating after hearing a bell |
|
|
Oeprant Conditioning |
Trial and error learning Behavior response with reward or punishment |
|
|
Imprinting |
Konrad Lorenz raised geese from birth and they treated him like he was their parent |
|
|
Map sense |
Learned ability to move in a particular direction |
|
|
Compass sense |
Innate ability to move in a particular direction |
|
|
Acid precipitation |
Is deadly Changes pH of ecosystem |
|
|
Air/water pollution results from |
Improper waste disposal Agricultural chemicals Increased industrialization |
|
|
Nuclear power plants must have |
Security Safe operations Proper waste disposal |
|
|
Biodiversity |
Makes ecosystems more stable |
|
|
Environmental issues can be solved |
Proper assessment Public education Follow through |
|
|
Global warming affects |
Rainfall Patterns Agricultural Sea level |
|
|
Leads to worldwide decline in amphibians |
Habitat deterioration Fatal infections Introduction of exotic species Toxic Chemical pollutants |
|
|
Characteristics of a developing country |
Short life expectancy High infant morality Low per capita income Rapid doubling rate |
|
|
Greenhouse effect |
High levels of carbon dioxide |
|
|
Monogamy |
Marriage between 2 people |
|
|
Polyandry |
Women has 2 or more mates |
|
|
Polygyny |
Man has more than 2 mates |
|
|
Predation |
The act of one animal preying on another |
|
|
Consumers |
Primary are herbivores Secondary are carnivores Tertiary eat secondary consumers Ex birds and turtles |
|
|
Parenchyma sclerenchyma collenchyma |
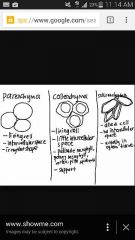
|

