![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
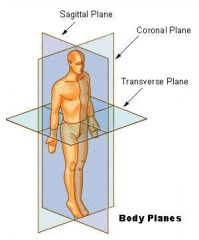
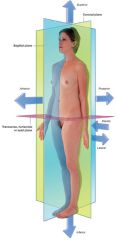
What is the coronal plane of the body?
|
|
|
|
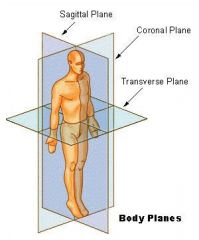
What is the sagittal plane of the body?
|
|
|
|
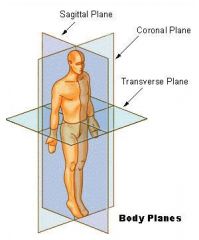
What is the transverse plane of the body?
|
|
|
|
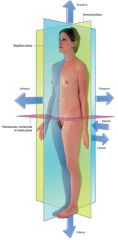
What is the medial view?
|
|
|
|
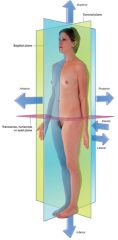
What is the lateral view?
|
|
|
|
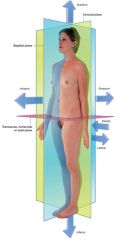
What is the superior view?
|
|
|
|
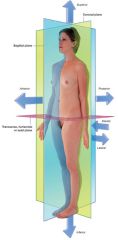
What is the inferior view?
|
|
|
|
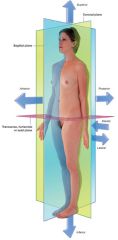
What's the anterior/ventral view?
|
|
|
|
What's the posterior/dorsal view?
|
|
|
|
What is a ligament?
|
A short band of tough, flexible, fibrous connective tissue that connects two bones or cartilages or holds together a joint
|
|
|
What is a tendon?
|
A flexible but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a bone
|
|
|
What is fascia?
|
CT containing fat that separates, supports and interconnects organs and structures, emabling the movement of one structure relative to another, and allows the transit of vessels and nerves from one area to another
|
|
|
What is superficial/subcutaneous fascia? What are its functions? (6)
|
Lies just deep, connected to dermis
Made of loose CT Contains a large amount of fat Allows movement of the skin over deeper areas of the body Acts as a conduit for vessels and nerves coursing to and from the skin Serves as an energy/fat reservoir |
|
|
What is deep fascia?
|
Consists of dense, organised CT
Outer layer attached to deep surface of superficial fascia Forms covering over most of the deeper body regions Compartmentalises groups of muscles with similar functions and innervations |
|
|
What does thick, deep fascia form?
|
Fascial retinacula
|
|
|
What is the function of fascial retinacula?
|
Hold tendons in place and prevent them from bowing during movements at the joints
|
|
|
What are the names for the different sections of a long bone from top to bottom?
|
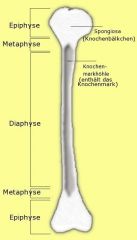
Epiphysis, metaphysis, diaphysis, metaphysis, epiphysis
|
|
|
What is an afferent nerve?
|
One going towards the CNS, normally sensory
|
|
|
What is an efferent nerve?
|
One leaving the CNS, normally motor
|
|
|
What part of the spinal chord do motor nerves leave from?
|
The 'ventral'
|
|
|
What part of the spinal chord do sensory nerves move into?
|
The 'dorsal'
|
|
|
What are the atlas and axis?
|
Top vertebrae (C1) and second vertebrae (C2) respectively
|
|
|
What does the atlas enable?
|
Head nodding
|
|
|
What does the axis enable?
|
Left/right movement
|

