![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a fever of unknown origin?
|
1. illness >3wks
2. Temp >101F (38.3C) on several occasions 3. No dx, despite 1 wk intensive evaluation |
|
|
What are the classifications of patient types in the fever of unknown origin? Why does it matter?
|
Classic (safe to investigate as outpatient)
Neutropenia/transplant Nosocomial HIV/AIDs ------ Changes possible etiologies (risks) |
|
|
What are common etiologies of fevers of unknown origin
|
Infectious (most common)
Malignancy Immunologic (+rheumatological) Misc (least common) |
|
|
What are the Infectious causes of FUO?
|
Localized
1. Intra-abdominal abscess 2. Endocarditis 3. Osteomyelitis 4. UTI 5. Sinusitis Systemic 1. Bacterial (TB, typhoid, brucellosis) 2. Viral (EBV/CMV/HIV) 3. Fungal 4. Parasitic (malaria/hepatic amebiasis) |
|
|
What are the malignant (neoplasm) causes of FUO?
|
Lymphoproliferative & Hematological (lymphoma)
Adenocarcinoma Lymphoproliferative disorders assoc. transplantation Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) Castleman's Disease |
|
|
What are the immunological causes of FUO?
|
Adult Still's
Temporal arteritis & polymyalgia rheumatica (elderly) Vasculitis IBD Sarcoidosis |
|
|
What are the misc. causes of FUO?
|
Hematoma (recent surgery?)
Pulmonary embolus/DVT (dyspnea exertion & tachypnea or calf pain) Drugs (dilantin, phenytoin, antibiotics) Fictitious or self induced Endocrine (Elevated - Addisons/thyroiditis) |
|
|
What are the steps in evaluating FUO?
|
1. COMPLETE HX
2. Document fever & pattern 3. Basic Labs 4. Individualized evaluation (echo, cultures, CTs, serology) 5. Invasive tests |
|
|
What is the diagnostic evaluation for fevers of unknown origin?
|
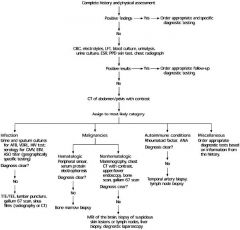
|
|
|
What interleukins, Tumor necrosis factors and Interferons are associated w/ fever?
|
IL1 - endogenous pyrogen that causes fever
IL6 - endogenous pyrogen that causes fever TNFa - Mediates septic shock & activates endothelium IFNg - Activates macrophages & Th1, represses Th2. |
|
|
What are steps in endogenous Fever?
|
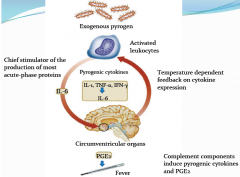
...PGE2 changes hypothalamic set point which induces peripheral fever behaviors (shiver/vasoconstrict)
|
|
|
What should one be careful with in diagnosing a UTI?
|
Could be glomerulnephritis from GAS sequelae. Make sure to get blood culture.
|
|
|
What are some findings in Endocarditis? How does it initially present?
|
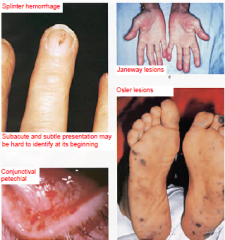
|
|
|
How would adult Still's disease present?
|
(immunologic)
Major - Fever >39 for at least 1 wk Arthralgia for >2wks Nonpruitic Rash Leukocytosis Minor - sore throat, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, abnormal liver fx, Neg ANA/RF tests |
|
|
How would Temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica present?
|
>50yo
New onset localized HA Tenderness/decrease ppulse of temporal artery ESR >50 Diagnosis made by necrotizing arteritis w/ multinucleated giant cells (dx often made clinically to prevent vision loss) |

