![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epiglottis
|
Prevents the food from going into the trachea, it covers the opening to trachea when food is swallowed
|
|
|
Larynx
|
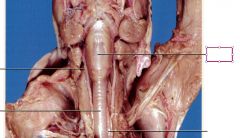
enlarged, oval-shaped region cranial to the trachea that contains the vocal cords
|
|
|
Trachea
|
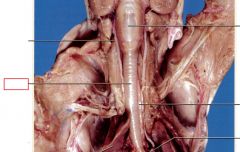
tube extending from the larynx to the lungs through which air is transported during respiration
|
|
|
Esophagus
|
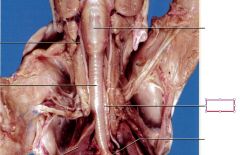
Muscular passage way that connects the mouth and oral cavity to stomach (lies beneath trachea)
|
|
|
Thyroid gland
|
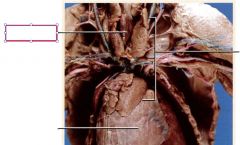
produces hormones that regulate metabolism and growth located on the ventral surface of the trachea just caudal to the larynx; produces thyroxine and calcitonin.
|
|
|
Lungs
|
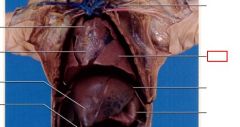
receives oxygen (good air) and expels carbon dioxide (depleted air).
|
|
|
Heart
|
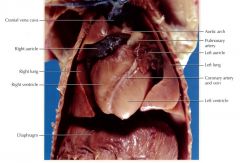
pumps blood to the whole body
|
|
|
Diaphragm
|
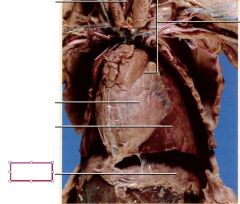
under the lungs, muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities; allows the thoracic cavity to expand and compress drawing in fresh air when expanding and expelling stale air with each compression.
|
|
|
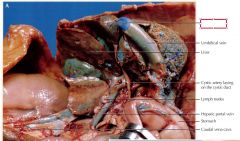
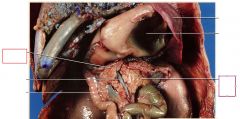
Liver
|
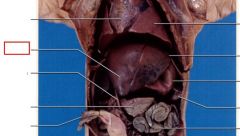
the largest organ in abdominal region, produces bile which is stored in gall bladder, converts glucose to glycogen for storage, detoxifies, absorbed digested compounds
|
|
|
gall bladder
|
located on the underside of the liver, stores bile and releases it into the duodenum.
|
|
|
stomach
|
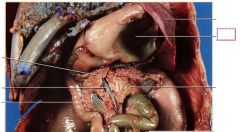
Produces hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen, which aid in the chemical breakdown of food
|
|
|
pancreas
|
Produces digestive enzymes and delivers them through the pancreatic duct to the duodenum, secretes insulin
|
|
|
Common bile duct
|
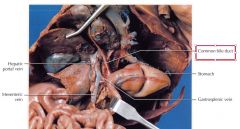
Transports bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum
|
|
|
Duodenum
|
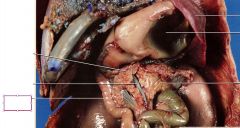
Receives chyme from the stomach along with bile and digestive enzymes from the gallbladder and pancreas, first section of the small intestine
|
|
|
Jejunum
|
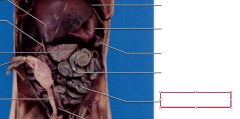
middle portion of the small intestine extending from the duodenum to the ileum; primarily responsible for nutrient absorption.
|
|
|
Ileum
|

the third portion of the small intestine extending from the jejunum to the cecum; primarily responsible for absorption of nutrients.
|
|
|
Kidneys
|
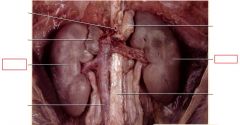
bean shaped organs on either side of spine, filters the blood creating a highly-concentrated metabolic by-product (urine), also responsible for maintaining a homeostatic balance of salts, fluids, and ions within the body (osmoregulation)
|
|
|
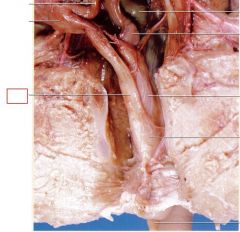
Ureters
|
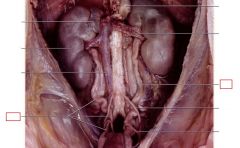
connects kidney to bladder
|
|
|
Urinary Bladder
|
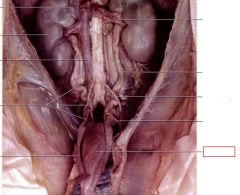
stores urine until it is eliminated from the body through the urogenital opening
|
|
|
Urethra
|
(Male)Receives seminal secretions from testes and accessory glands; also drains excretory products from urinary bladder. (Female) Drains excretory products from urinary bladder (no reproductive function in females)
|
|
|
Renal Arteries
|
carry blood into kidneys
|
|
|
Renal Veins
|
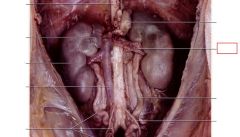
carry blood out of kidneys
|
|
|
Ovaries
|
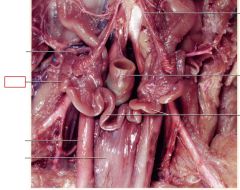
paired female gonads located caudal to the kidneys, produces eggs and sex hormones in females
|
|
|
oviducts
|
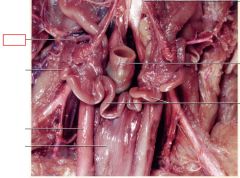
passage from the ovaries to the uterus, receives egg at ovulation; site of fertilization
|
|
|
Uterus
|
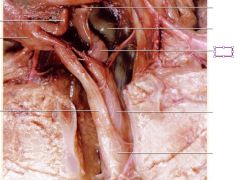
uterine body and uterine horns –where implantation of the embryos occur and extends into the cervix (junction between uterus and vagina
|
|
|
Vagina
|
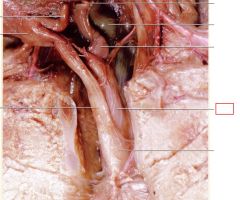
from the cervix – serves as part of the birth canal
|
|
|
Urogenital opening
|
opening of the urethra (in males) or the urogenital sinus (in females) through which urine passes as it is eliminated from the body
|
|
|
Scrotum
|
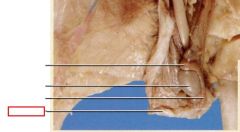
pouch extending from the caudal region of the male that contains the testes. Allows the temperature of the testes to be maintained at a lower temperature than the abdominal cavity
|
|
|
Testes
|
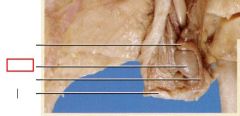
found between the base of the kidneys and the scrotal sacs, where sperm and sex hormones in males is produced
|
|
|
Penis
|
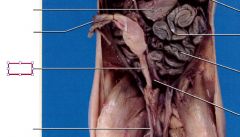
eliminates urine from the body and transfers semen into female reproductive tract
|
|
|
Bulbourethral glands
|
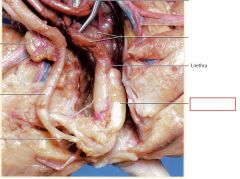
lie on each side of urethra these glands produce alkaline secretions that assist in lubrication during intercourse and also aid in neutralizing vaginal acidity
|
|
|
Ventricle, left & right
|
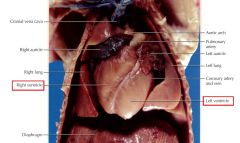
chamber of the heart that pumps blood out of the heart into an artery
|
|
|
Atrium, left & right
|
chamber of the heart that receives blood
|
|
|
Coronary Arteries
|
one of several small arteries located on the surface of the heart that supply freshly-oxygenated blood to the tissue of the heart.
|
|
|
cranial vena cava
|
vein returning deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body to the right atrium of the heart
|
|
|
caudal vena cava
|
vein returning deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body to the right atrium of the heart
|
|
|
Auricle
|
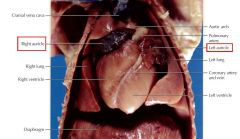
flap-like, outer region covering the cranial portion of each atrium.
|
|
|
pulmonary artery
|
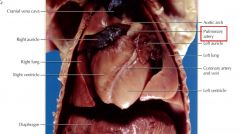
carries deoygenated blood from right ventricle of the heart to the lungs
|
|
|
Pulmonary veins
|
carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
|
|
|
aorta
|
carries blood from the left ventricle to the body
|
|
|
Ductus arteriosus
|
short connection joining the pulmonary trunk with the aorta and allowing a portion of the blood from the pulmonary trunk to enter the aorta instead of flowing to the lungs; present only during fetal development.
|
|
|
Brachiocephalic vein & trunk (artery)
|
major branch of the aorta that supplies blood to the head and upper trunk region of the body.
|
|
|
Subclavian vein & arteries
|
dumps blood directly into the brachiocephalic vein. (which carries blood to the forelimb and upper portion of the body)
|
|
|
Subscapular vein
|
subscapular vein and the axillary vein, both leading from the arm pit, come together to form the subclavian vein
|
|
|
external & internal jugular vein
|
lead from the neck region down into the vena cava, along with the internal jugular veins running medially alongside the trachea from the head toward the heart
|
|
|
common carotid artery
|
carry blood to the head and brain
|
|
|
External iliac veins & arteries
|
vessels become the femoral veins and arteries supply and receive blood from the legs.
|
|
|
hepatic portal vein
|
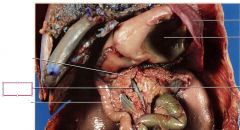
carries blood from the small intestines and pancreas to the liver, where it is filtered before returning to the rest of the body
|
|
|
umbilical arteries
|
carry blood from the fetus to the placenta
|
|
|
umbilical vein
|

carries oxygen and nutrient rich blood to the fetus from the fetal side of the placenta
|
|
|
spleen
|
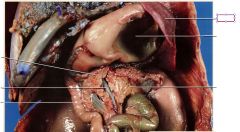
stores new red blood cells ,blood, recycles worn-out red blood cells, and produces lymphocytes.
|
|
|
anus
|
opening of the rectum through which undigested food particles (feces) are eliminated from the body.
|
|
|
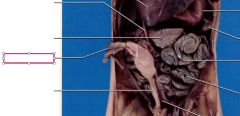
Genital papilla
|
small, fleshy projection next to the urogenital opening of the female fetus
|
|
|
Mammary papilla
|
In females, these will develop into the mammary glands and will be used to secrete milk during lactation for the newborn young
|
|
|
Umbilical cord
|
attachment between the maternal placenta and the fetus through which gases, nutrients, and nitrogenous wastes are transported during embryonic development.
|
|
|
Mandibular gland
|
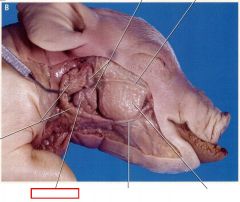
salivary gland in mammals that releases fluids into the mouth to facilitate swallowing and digestion
|
|
|
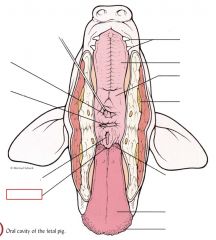
Hard palate
|
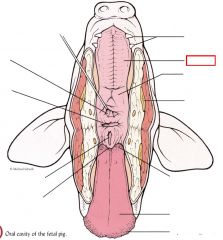
bony plate separating the rostral portion of the oral cavity from the nasopharynx in mammals. Roof of the mouth
|
|
|
Parotid gland
|
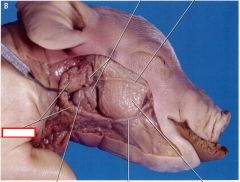
large, prominent salivary gland located beneath the skin near each ear of the pig. produce secretions that combine in the mouth to produce saliva
|
|
|
Soft palate
|
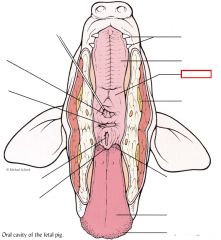
cartilaginous region of the roof of the mouth that separates the oral cavity from the nasal passageway; located toward the back of the mouth.
|
|
|
Sublingual gland
|
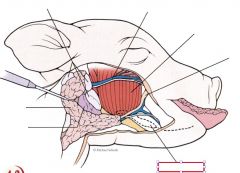
salivary gland located underneath the skin and alongside the tongue of the pig
|
|
|
Cecum
|
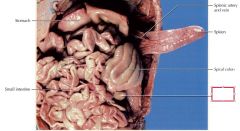
Small, blind-ended out-pocket demarcating the beginning of the large intestine that has no function in carnivores and omnivores , also known as the appendix.
|
|
|
Colon
|
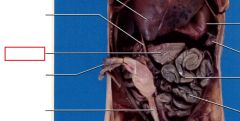
Responsible for reabsorption of water and electrolytes; transports feces to the rectum by peristalsis, broken into three sections ascending colon, the transverse colon, and the descending colon, also known as the large intestine
|
|
|
Rectum
|
Final site of water reabsorption and feces dehydration, last section of the large intestine
|
|
|
pinnae |
ears |
|
|
vibrissae |
whiskers |
|
|
digits |
hooves |
|
|
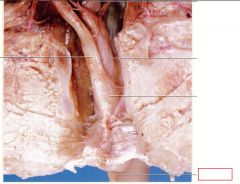
pharynx |
tube-like structure that connects oral and nasal cavities to the larynx; provides passageway for respiratory and digestive tracts |

