![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The neural tube will close |
6 menstral weeks |
|
|
Which is the best plane to detect Spina Bifada |
Transverse; location and configuration of ossification, musculature of back, integrity of skin line |
|
|
The sagittal plane of spine detects |
Cervical and lumbosacral curvatures, sacral caudal tapering, vertebral ossification centers. |
|
|
What structures are documented at axial sections of brain |
Cavum Septum Pellucidum, thalami, lateral ventricles, choroid plexus |
|
|
What measurements are taken at axial sections |
BPD, HC, atrium of lateral ventricle < 10mm normal |
|
|
In Oblique Axial section of brain what structures are seen? |
Cerebellum, Brain stem, Cisterna Magna (normal >3mm and < 10mm) |
|
|
Oblique Axial sections are obtained through what part of brain? |
Posterior Fossa |
|
|
Neural tube defects occur when neural tube fails to close by. |
6 weeks |
|
|
Neural Tube Defects allow |
Cerebrospinal Fluid to escape into amniotic fluid and maternal serum levels of AFP. |
|
|
Elevated levels of maternal AFP |
Require a targeted sonogram |
|
|
If sonogram fails to identify reason elevated MSAFP |
Recommend Amniocentesis |
|
|
Amniocentesis detects what in amniotic fluid |
Elevated Acetylcholinesterase in the presence of NTDs. |
|
|
Anencephaly |
Congenital absence of cerebral hemispheres and cranial vault |
|
|
What is the incidence of Anencephaly |
1 out of every 1000 births |
|
|
Anencephaly is more common |
In females and multiple gestations |
|
|
Anencephaly occurs with failure of neural tube to close by |
24 days gestation ( 38 menstral days) |
|
|
Anencephaly is characterized by |
Open defect covered by angiomatous stroma instead of skin an bone |
|
|
What structures of brain are present in Anencephaly? |
Brain stem and bony base of skull |
|
|
Anencephaly is associated with |
Polyhydraminos due to ineffective fetal swallowing. May also be associated with spina bifida |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Anencephaly |
Identify fetal cranium by 12 weeks ( 15 weeks latest), Absence of cranial vault and cerebral hemispheres), face and orbits present, polyhydraminos (40-50% cases) |
|
|
Acrania |
Developmental abnormality where the cranium is partially or completely absent with development of abnormal brain tissue. |
|
|
Sonographic appearance Acrania |
Lack of echogenic cranium with large amount of brain tissue, transvaginally seen at 12 weeks (16 weeks transab) |
|
|
Encephalocele |
Herniation of brain and meninges OR meninges and CSF through a cranial defect. |
|
|
Prognosis of Encepholocele |
Depends on the amount of brain involved and associated findings. |
|
|
What fetal syndrome is an encepholocelee asssociated |
Meckel- Gruber syndrome |
|
|
Encepholocele location is |
Usually midline, MC occipital, may be frontal or lateral. |
|
|
If Encepholocele is asymmetric or atypical location consider |
Amniotic band syndrome |
|
|
Sonographic findings of Encepholocele |
Purely cystic extracranial mass ( meningocele), Solid mass contiguous with cranium (cepholocele) |
|
|
Encephocele is often associated |
Hydrocephalus and polyhydraminos |
|
|
Spina Bifada |
Lack of closure of vertebral column |
|
|
Prognosis is poorest in infants who present with |
Total paralysis below the region, kyphosis, hydrocephalus |
|
|
Sonographic frontal bone appearance of Arnold Chiari 2 |
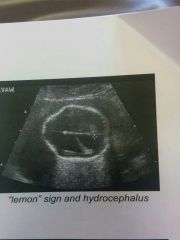
Lemon Sign- flattening of temporal/ frontal bones due to decreased inttracranial pressure. |
|
|
So no graphic appearance of posterior region in Arnold Chiari 2 |
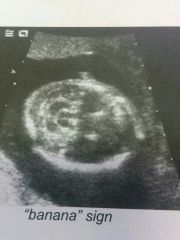
Banana Sign- obliteration of Cisterns Magna by abnormal configuration of cerebellum. |
|
|
Iniencephaly |
Rare malformation where the occiput is fused to the cervucal region. Cervical spina bifada and occipital encephalocele are present. |
|
|
Sonographic findings of Iniencephaly |
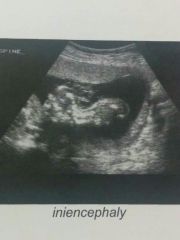
Marked head and neck hyperextension, occipital encephalocele/cervical spina bifida. |
|
|
Ventricle omega my/Hydrocephalus |
Dilation of ventricular system 2ndary to an increase in an increase in volume of CSF. |
|
|
Effects of hydrocephalus |
Flattening of parenchyma and spread of CSF which causes brain damage |
|
|
What ate the classifications of Hydrocephalus |
Obstructive/None communicating, Communicating, Idiopathic. |
|
|
How is Obstructive/ Non communicating hydrocephalus caused |
Obstruction of CSF flow d/t aqueductal stenosis |
|
|
Describe the flow if the CSF through the ventricles. |

Lateral ventricle----- interventricular foramen/ foramen of Moro---Third ventricle- ----Cerebral Aqueduct/ Aqueduct of Sylvius-------4th ventricle |
|
|
Ventriculomegaly/ hydrocephalus |
Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). |
|
|
Effects of hydrocephalus incluxe |
Flattening of parenchyma and spread of CSF, which causes brain damage. |
|
|
What are the classifications of hydrocephalus |
Obstructive or Non communicating, Communicating, Idiopathic. |
|
|
Obstructive/Non-communicating causes |
Caused by obstruction of CSF flow due to aqueductal stenosis ( narrow Aqueduct of Sylvius due to inflammation or developmental process), CNS anomaly ( spina Bifada, Dandy Walker malformation), tumor. |
|
|
Communicating Hydrocephalus |
Dilation of ventricles caused by obstruction of CSF flow outside of ventricular system. Caused by faulty absorption or increased CSF production. |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of hydrocephalus |
Presence of excess fluid in lateral ventricles, >1cm, dangling choroid plexus, |
|
|
Associated sonographic findings of hydrocephalus |
Polyhydraminos, abnormal fetal lie, hepatomegaly and fetal ascites with associated infection, meningomyocele me Dandy Walker formation, intracranial tumor. |
|
|
Transverse Sonographic findings of Spina Bifada |
Splaying of posterior elements into U or V configuration. Cystic structure extending from the back when sac is intact. Appears small, simple cystic or a cyst with septations and or solid matter. |
|
|
Sagittal appearance of Spina Bifada |
Splaying of parallel ossification centers. Soft tissue defect or discontinuity of skin and muscle of posterior back. |
|
|
Associated Intracranial findings of Spina Bifada |
Secondary to Arnold Chiari 2 |
|
|
Holoprosencephaly |
Spectrum of disorders resulting from absent or incomplete division of the forebrain into cerebral hemispheres and lateral ventricles. |
|
|
What is holoprosencephaly associated with |
Facial anomalies ( the face predicts the brain). Range from cyclopia (single orbit) with a proboscis, to hypotelorism (close- set eyes) to facial clefts. |
|
|
Name the types of holoprosencephaly |
Alobar, Semi- lobar, Lobar |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Alobar holoprosencephaly |
Most severe form, monoventricle, fused thalami, absence of falx cerebri. |
|
|
Appearance of Semi-lobar holoprosencephaly |
Partial separation of ventricles & hemispheres with occipital lobe present, incomplete fused thalami. |
|
|
Lobar holoprosencephaly |
Least severe form, Normal separation of thalami, hemispheres and ventricles, absent cavum septum pellucidum and olfactory tracts. |
|
|
Hydranencephaly |
Destructive disorder due to bilateral internal carotid artery occlusion or malformation. |
|
|
Hydraencephaly is characterized by |
Near total lack of cerebral hemispheres with intact and normally developed meninges and skull. |
|
|
Sonographic findings of Hydranencephaly. |
Large fluid filled cranium (macrocephaly), absent cerebral tissue/ cortical mantle, falx cerebri, normal midbrain and basal ganglia(thalami), polyhydraminos. |
|
|
Dandy- Walker Malformation |
Complete or partial absence of cerebellar vermis and posterior fossa cystic dilatation communicating with 4th ventricle. |
|
|
What % of fetuses with Dandy Walker have hydrocephalus? |
80% |
|
|
DWM is associated with |
Some autosomal recessive syndromes, maternal infection, diabetes melllitus, and exposure to alcohol and Coumadin. |
|
|
Sonographic findings of DWM |
Complete or partial agenesis of the cerebellar vermis with flattened cerebellar hemispheres, large midline cystic structure in posterior fossa. |
|
|
What is Dandy Walker Malformation associated with |
Ventriculomegaly and polyhydraminos. |
|
|
How is Dandy Walker Malformation differentiated from subarachnoid Cyst? |
By contiguity with 4th ventricle. |
|
|
At what fetal age is the corpus callosum complete |
20 weeks |
|
|
Rate that Agenesis occurs |
1-3 per 1000 births |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of A genesis of Corpus Callosum |
Absence of Cavum Septum Pellucidum, elevated dilated 3rd ventricle, widely separated frontal horns of lateral ventricles with enlarged occipital horn, teardrop shaped ventricles displaced upward and outward. |
|
|
Vein of Galen aneurysm |
Rare arteriovenous malformation (AVM) causing increased floe through vein of Galen. |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Vein of Galen aneurysm |
Well defined midline vascular structure superior and posterior to thalamus with turbulent and/or arterial flow. |
|
|
Choroid Plexus Cysts |
Small cysts within choroid plexus. |
|
|
Choroid plexus cysts have an infrequent association with |
Aneuploidy specifically Trisomy 18 |
|
|
Most common Intracranial tumors |
Teratomas |
|
|
Lissencephaly |
Caused by abnormal migration of neurons where the brain lacks sulci and gyri and appears smooth. |
|
|
When is diagnosis made for Lissencephaly |
3rd trimester |
|
|
What is Lissencephaly associated with? |
Mild ventriclulomegaly and possible abnormal corpus callosum. |
|
|
Schizencephaly |
Clefts in the cerebral hemispheres in the region of primary fissures. |
|
|
How does brain appear in Schizencephaly |
Split into anterior and posterior parts. |
|
|
Porencephaly |
Presence of cystic areas within the cerebral parenchyma. Cysts vary in size and may communicate with the ventricular system. |
|
|
How is Porencephaly caused |
Intracranial hemmorhage encephalo malacia. |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Porencephaly |
Simple cystic structures within cerebral parenchyma. |
|
|
Microcephaly |
Decreased head size. More than 3 Standard deviations below the mean. |
|
|
Causes of microcephaly |
Chromosomal abnormalities and exposure to terratogens. |
|
|
Sacrococcygeal Teratoma |
Rare tumor arising from the embryonic cells of sacum/coccyx. |
|
|
Grades of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma |
Three : benign (mature), immature, malignant. |
|
|
Sacroccoccygeal teratomas location |
External, intrapelvic, intra- abdominal. Frequently hypervascular and consist of cystic and solid components. |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Sacrococcygeal tetatoma |
Complex large mass, polyhydraminos,assoc with increased AFP, may have hydrops fetalis. |
|
|
Caudal Regression Syndrome |
Spectrum of skeletal anomalies of lower spine and limbs (sacral agenesis, lumbar spine and lower thoracic agenesis) 16% associated with diabetes mellitus |
|
|
Scoliosis and Kyphosis |
Abnormal curvature of spine may involve any segment. MC thoracolumbar region. |
|
|
Scoliosis and Kyphosis associated with which defects |
Structural (CNS and VATER). Severe curvatures assoc with lethal anomalies( anencephaly, limd body wall complex, amniotic band syndrome) |

